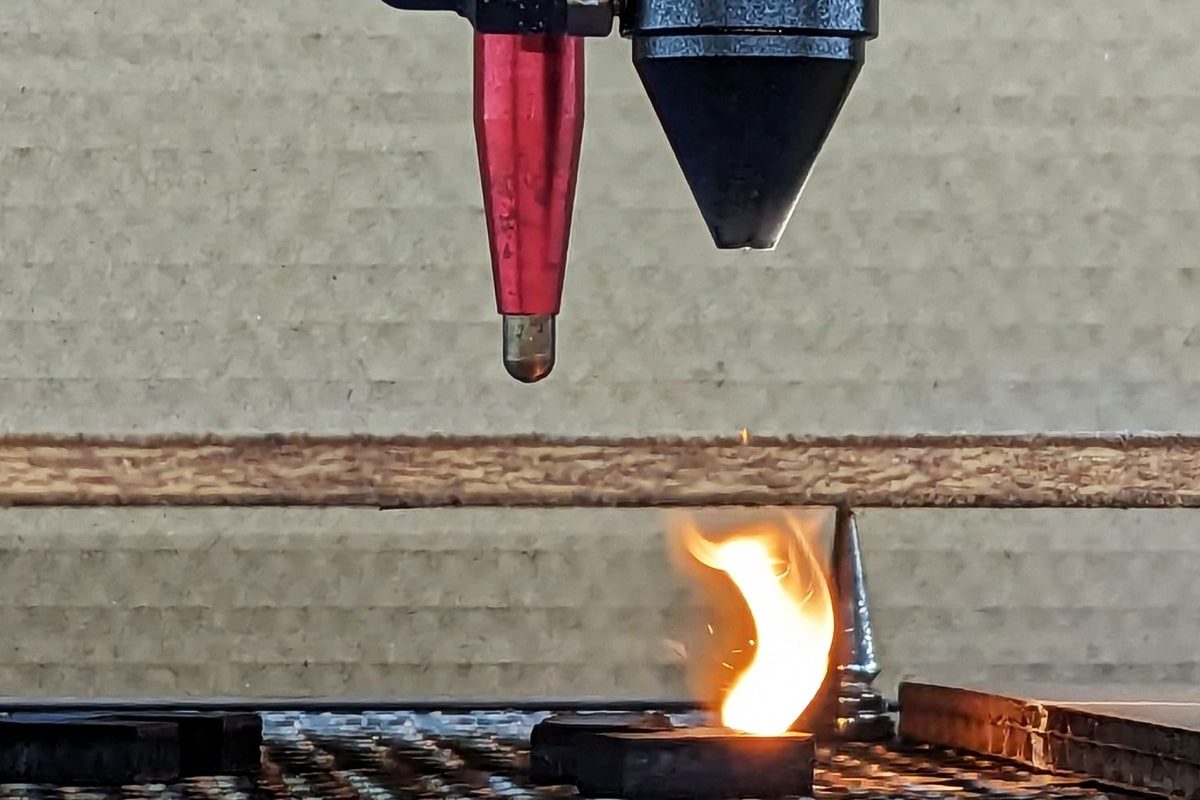
Learn About the Laser Cutting Process
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting machines use a high-energy-density laser beam to focus precisely on the surface of the material, quickly heat the target area, and locally melt, vaporize or ablate it, thereby achieving material cutting. In this process, the energy of the laser beam is concentrated on a very small point, efficiently cutting out precise shapes without affecting the surrounding materials. Laser cutting is particularly suitable for a variety of materials such as metals and plastics because these materials can react quickly at high temperatures. Another advantage of laser cutting is that it requires almost no mechanical contact with the material, thus avoiding tool wear caused by physical friction in traditional cutting methods. By controlling the power, cutting speed, and focus position of the laser beam, users can achieve fine processing of materials of different thicknesses and types. This non-contact, precise, and efficient process has been widely used in various industrial processing scenarios, from automobile manufacturing to electronic component production, demonstrating its unique technical advantages.
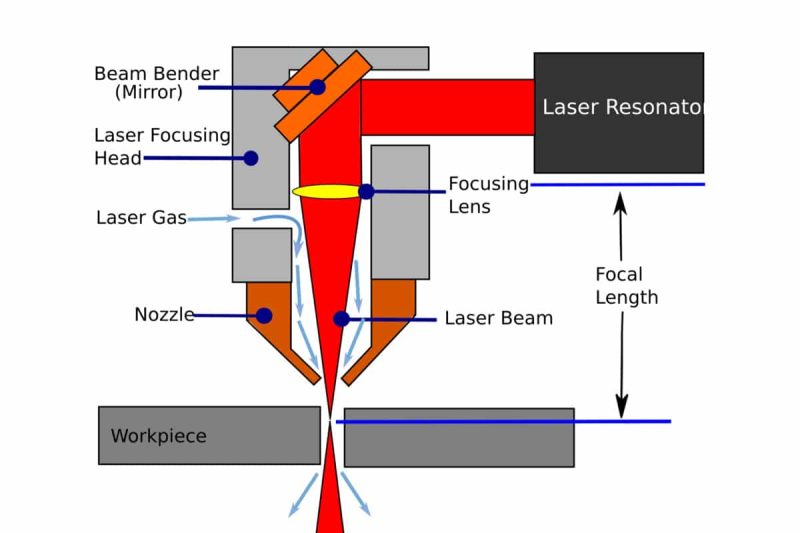
Laser Cutting Machine Main Components
Laser Generator
Cutting Head
Control System
Cooling System
Ventilation and Extraction Systems
Laser Generator Type
CO₂ Laser Generator
Fiber Laser Generator

Fire Hazard Factors in Laser Cutting
Material Properties and Flammability
Combustible Materials
- Plastics: Plastic materials are prone to fire during laser cutting due to their high ignition point and flammability, especially the high temperatures generated during the cutting process may cause them to catch fire. The gases and smoke released by plastics may also cause fires or affect the operating environment.
- Wood: Wood is a flammable material, and its surface is easily heated to ignite during laser cutting. The fiber structure of wood may cause sparks during cutting, increasing the risk of fire.
- Certain chemical materials: Certain chemical materials or synthetic materials contain flammable components, which may cause violent combustion or explosion reactions during laser cutting.
Thick Material
- Thicker materials: Thicker materials accumulate more heat during the laser cutting process, which may cause the temperature inside the material to rise to the point of self-ignition. Thicker materials are not evenly transferred during laser cutting, which also increases the risk of fire.
Oily Materials
- Surface grease: Some materials have grease, lubricants or other flammable substances on the surface. During the high-temperature laser cutting process, these greases may evaporate and cause sparks, or even ignite the surface of the material.
Improper Material Handling and Preparation
Material Is Not Clean
- Oil and dust: If the surface of the material is not cleaned, the residual oil, dust or other flammable substances can be easily ignited by the laser during the cutting process. These residues not only increase the risk of fire, but may also affect the cutting quality.
Material Stacking Too High
- Heat dissipation problem: Too thick material stacking will hinder the effective dissipation of heat, causing local temperature rise, which in turn increases the risk of fire. Improper material stacking may also cause the laser beam to not cut evenly, increasing the possibility of overheating.
Improper Cutting Method
- Improper laser settings: Incorrect laser power, cutting speed or focus settings may cause the material to be subjected to excessive heat during the cutting process, which may cause a fire. Optimization of laser parameters is critical to fire prevention.
Inadequate Ventilation and Extraction Systems
Poor Exhaust
- Smoke and heat: If the exhaust system of the laser cutting equipment is not effective enough, the smoke and heat generated during the cutting process cannot be discharged in time, which will cause heat to accumulate in the cutting area and increase the possibility of fire.
Filter Clogged
- Airflow blockage: If the filters in the air extraction system are not cleaned or replaced for a long time, it may cause airflow blockage, thus affecting the discharge of smoke and hot air. In this case, the efficiency of the exhaust system is reduced and the risk of fire increases.
Improper Ventilation Design
- Unreasonable design: Unreasonable ventilation design may lead to excessive temperature in the cutting area, thus increasing the risk of fire. A good ventilation system should ensure air circulation in the cutting area to avoid abnormal temperature rise.
Electrical Failure and Component Failure
Electrical short circuit
- Electrical system failure: Electrical short circuits or circuit failures in laser cutting equipment can cause fires. The stability and safety of the electrical system are critical to fire prevention, and regular inspection and maintenance of electrical components can effectively reduce the risk of fire.
Aging Parts
- Cable and component wear: If cables and equipment components that have been used for a long time are not replaced or maintained in time, they may age and wear out, causing short circuits or overheating, which may cause fires. Regular replacement and inspection of equipment components is essential to prevent fires.
Laser Generator Failure
- Laser generator problem: Failure of the laser generator or cutting head may cause abnormal laser power or even exceed the safe range, causing combustion. Ensuring the normal operation and timely maintenance of the laser generator can help reduce the risk of fire.
Operator Error and Lack of Training
Improper Operation
- Failure to operate in accordance with regulations: If the operator does not operate the laser cutting machine in accordance with the equipment operating procedures, such as improper settings, operating errors, etc., it is easy to cause a fire. Training operators to ensure that they are proficient in equipment operation and emergency response methods is the key to fire prevention.
Lack of Emergency Response Capabilities
- Fire safety training: Lack of effective fire safety training will result in operators being unable to take correct emergency measures when a fire occurs. Regular fire drills and safety training can help improve the ability to respond to fires.
Ignoring Safety Checks
- Equipment and environment inspection: Failure to regularly inspect equipment status and operating environment may result in potential fire hazards being missed. Establishing a systematic safety inspection process to ensure the safety of equipment and working environment is an important measure to prevent fires.

Fire Safety Measures
Appropriate Material Selection and Preparation Techniques
Use Refractory Materials
- High temperature resistant materials: Choosing high temperature resistant and fire resistant materials as cutting media, such as certain special ceramics or refractory alloys, can greatly reduce the risk of fire during the cutting process. These materials can withstand the high temperatures during laser cutting and reduce the possibility of fire.
Material Cleaning
- Surface cleaning: Before laser cutting, ensure that the surface of the material is thoroughly cleaned to remove all oil, dust and other combustible impurities. Grease and dust can easily generate sparks or cause combustion during the laser cutting process, so appropriate methods such as washing, wiping or jetting should be used to clean the surface.
Avoid Stack Cutting
- Proper stacking: Avoid stacking materials too high to ensure that the heat generated during the cutting process can be effectively dissipated. If the materials are stacked too high, it will hinder the dissipation of heat, thereby increasing the risk of overheating and fire. Maintaining the appropriate material stacking height will help maintain temperature control in the cutting area.
Install Effective Ventilation and Extraction Systems
Keep Ventilation Open
- Good ventilation: Ensure that the ventilation system in the laser cutting work area is good and timely exhaust the heat and smoke generated during the cutting process. A well-ventilated environment can effectively reduce the local temperature and reduce the risk of fire.
Clean the Filter Regularly
- Filter Maintenance: Clean and replace filters in the extraction system regularly to ensure they are functioning properly. If the filter becomes clogged, it will result in poor airflow, which will increase the temperature in the cutting area and increase the risk of fire.
Reasonable Air Circulation Design
- Optimize ventilation design: Design a reasonable air flow system to ensure that air flows freely in the cutting area. Good ventilation design can prevent the cutting area from overheating and help control the risk of fire.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection of Laser Cutting Equipment
Electrical System Inspection
- Electrical safety: Regularly check the electrical circuits and systems of the laser cutting equipment to ensure that there are no electrical short circuits or poor contact issues. Electrical failure is one of the main causes of fires, and timely detection and repair of electrical system problems can prevent potential fire risks.
Replace Aging Parts
- Component Maintenance: Regularly replace aged or worn cables and laser components. Aged components can cause system failure or overheating, which can cause a fire. Ensuring that all components remain in good working condition is key to maintaining equipment safety.
Clean the Cutting Head Regularly
- Cutting head maintenance: Clean the cutting head regularly to ensure it is free of debris or dust. A dirty cutting head may cause an uneven laser beam, generate abnormally high temperatures, and increase the risk of fire.
Operator Training on Fire Safety Regulations and Emergency Procedures
Regular Safety Training
- Fire training: Regular fire safety training should be provided to operators to enhance their safety awareness and response capabilities. The training content should include fire prevention, equipment operation specifications and emergency handling procedures to ensure that operators can effectively prevent and respond to fire risks.
Emergency Response Drills
- Fire drills: Fire emergency response drills are conducted regularly to simulate the steps to deal with a fire. Through drills, operators can become familiar with emergency measures and improve their ability to respond to actual fires.
Strict Implementation of Operating Procedures
- Compliance with procedures: Ensure that operators strictly follow operating procedures and safety regulations to reduce the risk of fire caused by human errors. Operators should understand all operating steps and safety requirements to avoid fires caused by improper operation.
Implementation of Fire Extinguishing Systems and Protective Measures
Equipped with Fire Extinguishing Equipment
- Fire extinguisher configuration: Equip appropriate fire extinguishing equipment near the laser cutting equipment, such as carbon dioxide fire extinguisher, dry powder fire extinguisher, etc. Make sure the fire extinguishing equipment is in good condition and the operator knows how to use it so that they can take quick action when a fire occurs.
Fire Alarm Systems
- Fire detection: Install an efficient fire detection and alarm system to detect fire sources and sound the alarm in time. Fire alarm systems should be tested and maintained regularly to ensure that they can work properly in emergency situations.
Thermal Insulation Protection Measures
- Thermal insulation protection: Install thermal insulation protection devices such as fireproof panels or insulation layers at key locations to prevent the spread of fire. Thermal insulation protection can effectively reduce the impact of high temperatures on equipment and the working environment, and improve overall safety.

Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Comply with Local Fire Regulations and Environmental Standards
- Compliance: Companies must understand and comply with fire regulations and environmental standards in their area. This includes understanding relevant laws, regulations, standards and specifications and applying them to the design, installation and operation of laser cutting equipment. Local fire departments and environmental protection agencies usually issue specific requirements, and companies need to keep up to date with and comply with these regulations.
- Compliance review: Regularly review and update the company’s fire safety and environmental compliance records. Ensure that laser cutting equipment and operating procedures meet the latest regulatory requirements and make necessary adjustments and improvements. Compliance reviews help prevent legal risks and fines while improving the company’s safety management level.
Periodic Equipment Inspection and Certification
- Equipment inspection: Regularly conduct comprehensive inspections on laser cutting equipment, including key components such as electrical systems, cooling systems, ventilation systems, and laser generators. The inspection content should include functional testing of the equipment, safety performance evaluation, and potential fault detection. Through regular inspections, ensure that the equipment is in good working condition during use and can effectively prevent fire risks.
- Certification standards: Obtain and maintain equipment certifications, including but not limited to ISO certification, CE certification, etc. These certifications indicate that the equipment meets international standards and safety requirements, helping companies improve the market competitiveness and reputation of their products. Certification agencies will conduct strict audits and tests to ensure the safety and environmental performance of the equipment.
Follow Industry Best Practices and Standard Operating Procedures
- Best Practices: Follow the best practices in the industry to ensure that the use and maintenance of laser cutting equipment meet the highest safety and environmental standards. This includes adopting advanced technologies and materials, implementing effective safety measures, and optimizing operating procedures. Industry associations and professional organizations usually publish relevant best practice guidelines, which companies should actively refer to and adopt.
- Standard Operating Procedures: Establish and implement standard operating procedures (SOPs) covering equipment operation, maintenance, safety inspections, and emergency response. Standard operating procedures should detail operating steps, precautions, and emergency measures to ensure that operators follow them to reduce human errors and fire risks. Train operators regularly to ensure that they are familiar with and follow these procedures.
Continuous Improvement and Updates
- Continuous improvement: Companies should continuously evaluate and improve safety management systems, incorporate new technologies and standards, and enhance the safety of equipment and operations. By implementing continuous improvement measures, companies can effectively respond to changing regulatory requirements and industry challenges, and maintain the efficiency, safety, and environmental performance of equipment.
- Technology updates: Track new technologies and developments within the industry, and update and upgrade equipment in a timely manner to improve safety and efficiency. New technologies can provide more advanced safety protection and environmental protection features, helping companies maintain their leading position in the field of laser cutting.

Fire Incident Mitigation Strategies
Stop running immediately
- Emergency stop: Once signs of fire are found, the operator should immediately press the emergency stop button or turn off the power of the equipment to stop the operation of the laser cutting machine. The laser cutting machine will generate high temperature and high energy during operation. Stopping the work quickly can reduce the continuous release of fire source and heat and prevent the fire from spreading.
Implement Emergency Procedures
- Emergency response plan: Operators should act quickly according to the fire emergency procedures established by the company. Emergency procedures usually include steps such as alarm, evacuation, and fire extinguishing. Ensure that all employees are familiar with and understand the emergency procedures and can take quick and effective actions in the event of a fire.
- Alarm: Immediately activate the fire alarm system and notify all personnel to evacuate. The alarm system should have sufficient volume and warning signs to ensure that every employee can hear and take action in time.
Prioritize Personnel Safety
- Evacuate people: Evacuate all people on site quickly but in an orderly manner, and ensure that all employees and visitors leave the fire scene quickly. Do not try to rescue objects during the evacuation process to prevent people from being trapped or increase the risk of fire.
- Evacuation routes: Ensure that evacuation routes are unobstructed and clearly marked to avoid smoke or flames from the fire hindering the evacuation of people. Regularly inspect and maintain evacuation routes to ensure their normal function.
Use Appropriate Fire Extinguishing Equipment
- Fire extinguishing equipment selection: In the early stage of a fire, fire extinguishing equipment suitable for laser cutting machine fires should be used. Common fire extinguishing equipment includes carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, dry powder fire extinguishers, etc. These fire extinguishers can effectively extinguish electrical fires or material fires.
- Fire extinguishing skills: The operator should be familiar with the use of fire extinguishers, select appropriate fire extinguishers according to the size and type of fire, and use correct fire extinguishing skills. Avoid using water to extinguish fires, as water may cause electric shock risks to electrical equipment.
Regularly Inspect and Maintain Fire-Fighting Equipment
- Equipment inspection: Regularly inspect fire extinguishing equipment, including the pressure, expiration date, and operating status of the fire extinguisher. Ensure that the fire extinguisher can be used normally in an emergency. Check all parts of the fire extinguishing system, such as sprinklers, pumps, and water sources, to ensure that they are functioning properly.
- Maintenance records: Keep detailed maintenance records of fire extinguishing equipment, recording each inspection and repair. Regularly maintain and replace equipment to ensure that the fire extinguishing system is always in good working condition.
Training and Drills
- Employee training: Regularly conduct fire safety training for employees, including fire identification, emergency response, fire extinguisher use and evacuation procedures. The training should cover all possible emergency situations to ensure that employees have the necessary knowledge and skills.
- Emergency drills: Regularly conduct fire emergency drills to simulate actual fire scenarios and improve employees’ ability to respond to fires. The drills should include the complete process from fire alarm to personnel evacuation, fire extinguishing and reporting.

Addressing Common Problems and Misunderstandings
Fire Risk Control of Laser Cutting Equipment
- Actual risk level: Although laser cutting equipment operates in a high temperature environment, its design and operating specifications are committed to reducing the risk of fire. Modern laser cutting equipment is equipped with a variety of safety features, such as automatic shutdown devices and efficient cooling systems, which can effectively prevent overheating and potential fires. The internal channels and airflow design of the equipment are carefully calculated to ensure that heat can be properly dissipated during the cutting process.
Optimize Operating Procedures
- Material selection and preparation: Select suitable cutting materials and ensure that the materials have been cleaned before cutting. Removing oil, dust and other combustible impurities can significantly reduce the risk of fire. Proper stacking of materials to avoid stacking them too high or impeding heat dissipation is also a key measure to reduce the risk of fire.
- Setup and Monitoring: Correctly setting the parameters of your laser cutting machine, such as laser power, cutting speed, and air flow, can effectively control the heat during the cutting process. Operators should strictly follow the equipment manual and monitor the cutting process in real time to detect and handle abnormal situations in a timely manner.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
- Equipment maintenance: Regularly maintain and inspect laser cutting equipment, including electrical systems, cooling systems, ventilation and exhaust systems. Ensure that all components are working properly to avoid fires caused by equipment aging or failure. Regularly clean the cutting head and filter of the equipment to prevent dust and waste accumulation, which is also an important measure to prevent fires.
- Fault detection: Regularly detect faults on the equipment, especially the status of electrical circuits and laser generators. Early detection of potential problems and repairs can effectively reduce the risk of fire caused by equipment failure.
Training and Education
- Operator training: Train operators on fire safety and equipment operation to ensure they understand how to safely operate the laser cutting machine. Training should include fire prevention measures, emergency procedures, and the use of fire extinguishers. Good training can improve operators’ safety awareness and emergency response capabilities.
- Emergency drills: Conduct fire emergency drills regularly to familiarize operators with emergency procedures and evacuation routes. Drills can help employees take quick and orderly action when a fire actually occurs, reducing the damage caused by the fire.
In summary, although laser cutting equipment operates in a high-temperature environment, fire risks can be controlled to the lowest level by optimizing operating procedures, regular equipment inspections, and training and education. Understanding the characteristics of the equipment and taking effective safety measures can significantly reduce the occurrence of fires during laser cutting, thereby ensuring the safety of equipment and personnel.

Summarize
Get Laser Solutions
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.

