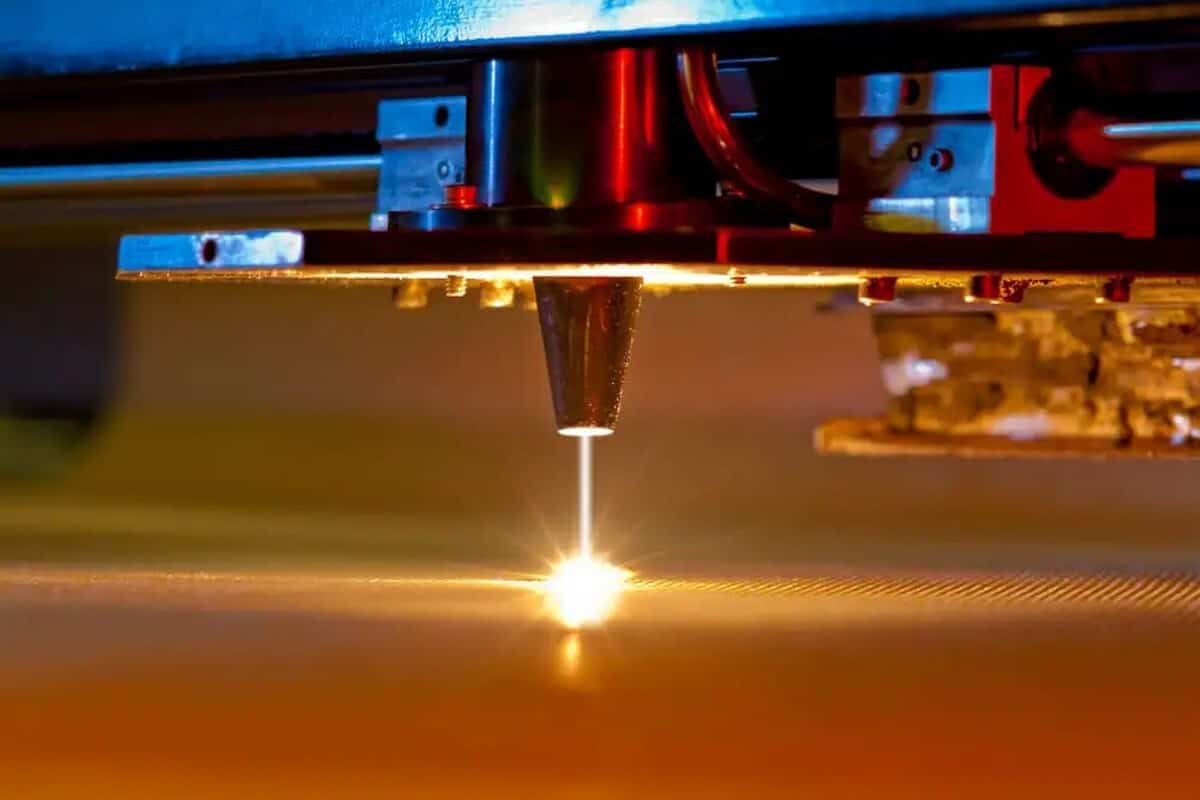
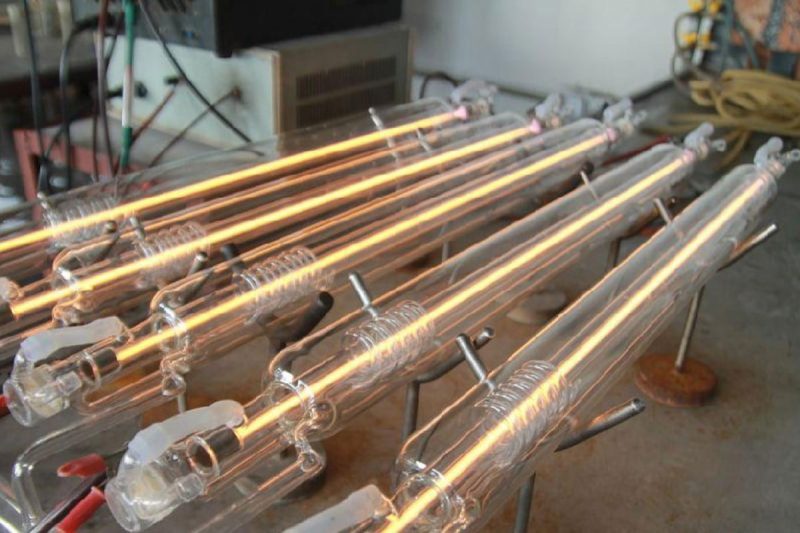


Basic Knowledge of CO2 Laser Technology
What is a CO2 laser generator?
Working principle of CO2 laser generator
CO2 laser generators work based on the principle of stimulated emission. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Laser medium: The active medium in a CO2 laser generator is a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and other gases. This medium is excited using an external energy source, usually an electrical discharge, to produce a population inversion in which more atoms are in the excited state than in the ground state.
- Resonator: An optical resonator consists of mirrors at either end of the laser tube that confine the photons and reflect them back and forth, which further stimulates the excited atoms, thereby emitting coherent light.
- Laser beam formation: A mirror in the resonator is partially reflective, allowing some light to escape. The escaping light forms a laser beam, which can then be focused and directed.
CO2 laser wavelength
Composition of CO2 laser cutting machine
A CO2 laser cutting machine contains several basic components:
- Laser generator: This is where the laser beam is generated and it contains a mixture of carbon dioxide gas and components responsible for exciting the gas and producing the laser beam.
- Optics: Laser optics, including mirrors and lenses, are used to precisely focus and direct the laser beam onto the workpiece. Proper alignment and focus help complete precise cuts, and the quality and efficiency of the optics also play a vital role in the cutting process.
- Power supply: The power supply provides the electrical energy required to excite the gas mixture in the CO2 laser tube, thereby determining the power output of the laser.
- Cooling system: To prevent overheating and maintain stable laser performance, the CO2 laser cutting machine integrates a cooling system.
- Worktable: The workpiece is usually mounted on a movable worktable that can be positioned in the XY plane. The ability to move the workpiece enables complex and precise cuts.
- Gas assist system: Some laser cutting machines use gases such as oxygen or nitrogen to assist the cutting process. This gas blows away molten material and increases cutting efficiency.
- Control system: A computer control system manages the power, speed, and other parameters of the laser generator. Also, it guides the movement of the laser head and controls the cutting process.

Power Output of CO2 Laser Generator
Power control
Factors affecting power output
Several factors affect the power output of a CO2 laser system. Some major determining factors include:
- Laser tube design: The physical design and structure of a laser tube play a vital role in determining its power output, with more advanced and efficient designs tending to provide higher powers.
- Gas mixture: The composition of the carbon dioxide gas mixture affects the efficiency of the laser generator and therefore its power output.
- Current: The amount of current applied to the laser tube will affect the degree of excitation of the CO2 gas, which in turn affects the power output of the laser generator.
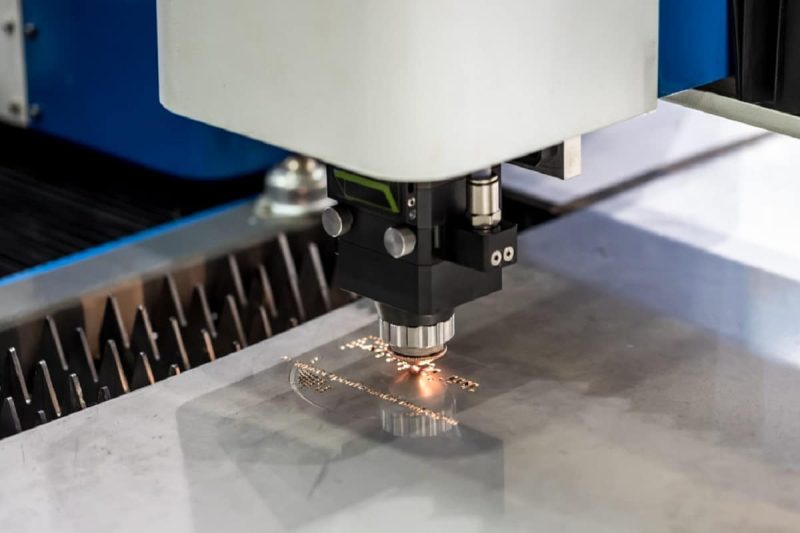
Effect of power output on cutting ability
Cutting speed
One of the most obvious effects of increasing laser power is increased cutting speed. In laser cutting, cutting speed refers to how fast the laser head or workpiece moves when the laser is activated. Typically, higher laser power allows for faster cutting speeds. This relationship can be understood through several key factors:
- Material thickness: The thickness of the material being cut will have a significant impact on cutting speed. In general, thicker materials can only be stably cut using a higher-power laser, which will also affect the laser cutting speed.
- Beam intensity: Higher power means higher beam intensity. Higher strength results in more efficient material absorption and faster vaporization or melting, thus speeding up the cutting process.
- Optimum balance: Achieving the best balance between power and cutting speed is crucial. Excessively increasing power may result in material damage, excessive kerf width (cutting width), and a greater risk of deformation, especially with thinner materials.
- Cutting speed considerations: While increasing power can increase cutting speed, it is also important to balance speed and quality. Excessive power can cause material burning, excessive melting, and deformation. Finding the right balance helps achieve high-speed cutting without compromising cut quality.
Cutting quality
Laser power output can significantly affect cutting quality. Higher power levels generally produce smoother, cleaner cuts with fewer defects. Cut quality is evaluated based on factors such as edge roughness, heat-affected zone, and the presence of dross (re-solidified material) on the cut edge.
- Smooth, precise cuts: Higher power helps achieve smoother, more precise cuts. With more power, the laser can stay focused and deliver energy evenly across the surface of the material, resulting in clean, straight, and defined cuts.
- Heat-affected zone: The heat-affected zone (HAZ) is the area around the cut where the temperature increases during the cutting process. Higher-power lasers may produce larger heat-affected zones (HAZ) at the edges of the material due to increased energy input. This is important to consider, especially in applications where the minimum heat-affected zone is critical.
- Slit width: The width of the slit (called the kerf) is affected by power. Higher power may slightly widen the cut, which is advantageous for some applications because it reduces the chance of material sticking together during the cutting process.
- Punching and perforating: Punching and perforating are the processes of creating holes or openings in materials. Higher power is beneficial for punching and piercing because it creates holes faster and cleaner. This is particularly important for applications where punching or perforation is an integral part of the final product, such as when creating formwork or filtration systems.
Material compatibility
The power output of a CO2 laser generator directly affects the range of materials that can be effectively processed. Higher-power laser generators can handle a wider range of materials, including thicker and more heat-resistant substances. This versatility is especially beneficial for job shops and manufacturers working with a variety of materials.
- Multi-material cutting: High-power CO2 laser generators are capable of cutting multiple materials on one machine, eliminating the need for multiple setups and equipment changes.
- Expanded application areas: The increase in power expands the application areas, from precision cutting of thin materials to heavy-duty cutting of thick metals.
Processable material range
Laser cutting is suitable for a variety of materials, each with its characteristics and requirements. The power output of a CO2 laser generator greatly affects the range of materials that can be effectively cut. Different materials require different power levels for efficient cutting:
- Low-power applications: For thin and relatively low-density materials such as paper, cardboard, and some plastics, lower-power CO2 laser generators are sufficient for clean and precise cuts.
- Medium power applications: Materials such as acrylic, wood, and thinner metals require moderate power levels to cut effectively, and laser power can be adjusted to optimize speed and quality.
- High-power applications: Thicker metals, ceramics, and composite materials often require a high-power CO2 laser generator to effectively cut the material. The ability to produce higher power broadens the range of materials that can be processed.
Relationship Between Material Type And Laser Power
Material absorption
Material thickness
Material density
Material reflectivity
Material reflectivity
Material thermal conductivity
Material melting point and vaporization point
Material response to heat
Material damage
Material accuracy
Material safety

Factors Affecting The Selection of CO2 Laser Generator
Material type
Material thickness
Reduce quality requirements
Yield
Budget constraints
Energy efficiency
Maintenance and serviceability

Safety Precautions
Laser safety is critical in any environment in which CO2 laser-cutting machines operate. Higher-power laser cutters may pose greater risks to operators, bystanders, and the equipment itself.
- Eye protection: Laser beams, especially high-power laser beams, can cause serious eye damage or even blindness. All persons near CO2 laser cutting machines should wear appropriate eye protection, such as laser safety glasses or goggles.
- Material safety: Certain materials can produce harmful fumes or particles when cut or engraved with a CO2 laser cutting machine. High-power laser systems may require more space and better ventilation due to increased heat and gas production. Adequate ventilation and air filtration systems help ensure the safety of operators and the work environment.
- Equipment safety: Laser-cutting machines should be equipped with safety features such as interlocks and emergency stop buttons to prevent accidents and protect the operator.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
