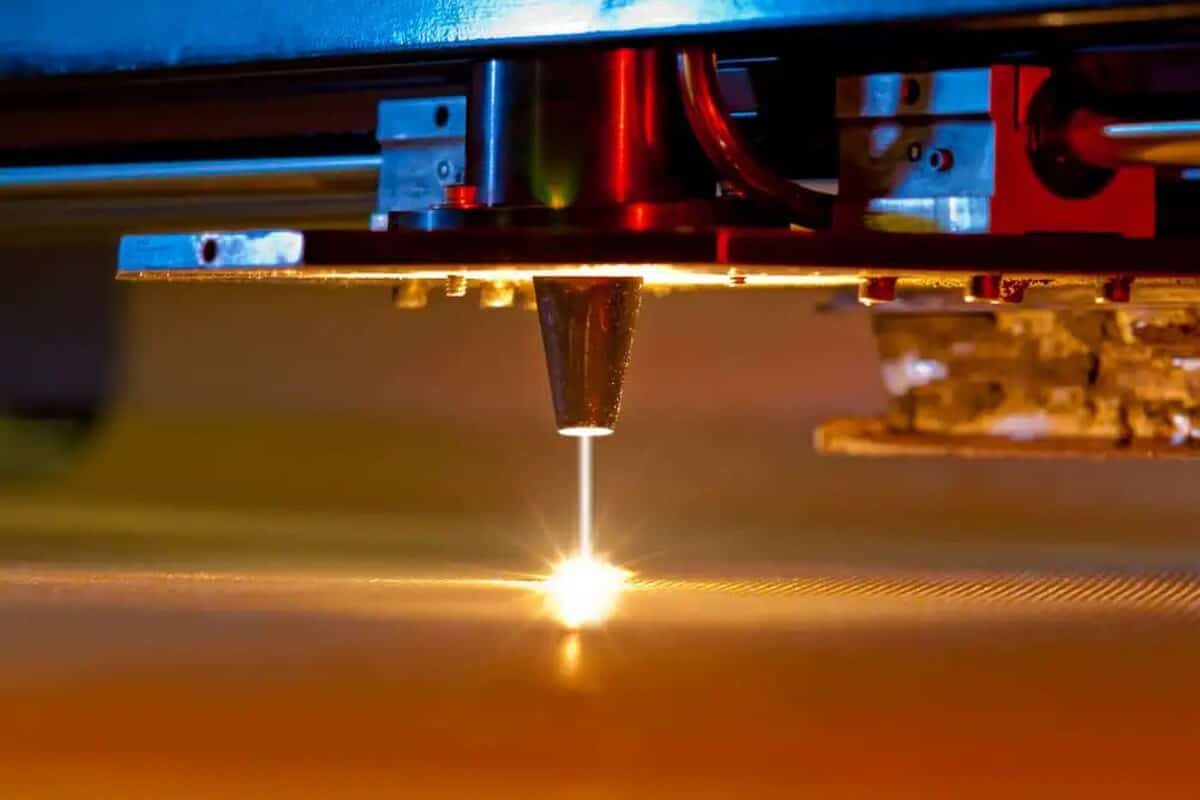
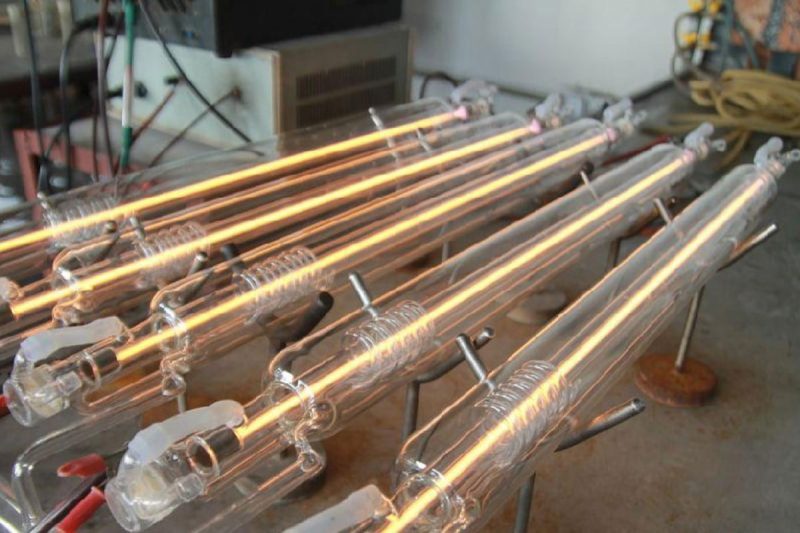


Working principle of CO2 laser cutting machine
Before we dive into what materials a CO2 laser cutting machine can cut, let’s first understand how a CO2 laser cutting machine works. The working principle of the CO2 laser cutting machine is based on the generation and utilization of the CO2 laser generator. The CO2 laser generates a high-energy CO2 laser beam by electrically exciting the gas mixture. Laser beams can focus energy into a very small area of the work area in a short period. When the laser beam irradiates the surface of the material, its high energy density can quickly heat, melt, or vaporize the material, thereby achieving cutting operations. CO2 laser cutting machine also has the following advantages:
- Efficient cutting: CO2 laser cutting has extremely high cutting speed, which can quickly complete cutting tasks of various materials and improve production efficiency.
- High precision: Due to the high focus of the laser beam, CO2 laser cutting machines can achieve very fine cutting and are suitable for applications that have strict requirements on cutting quality.
- Wide applicability: CO2 laser cutting is suitable for a variety of materials, including metals, organic materials, rubber, and ceramics. This makes it widely used in different industries such as manufacturing, medicine, and electronics.
- Non-contact processing: CO2 laser cutting is a non-contact processing technology, which reduces friction and wear with materials, helping to improve cutting quality and equipment life.
- Strong flexibility: CO2 laser cutting machines can adapt to the processing needs of different materials by adjusting cutting parameters, providing more flexible processing options.
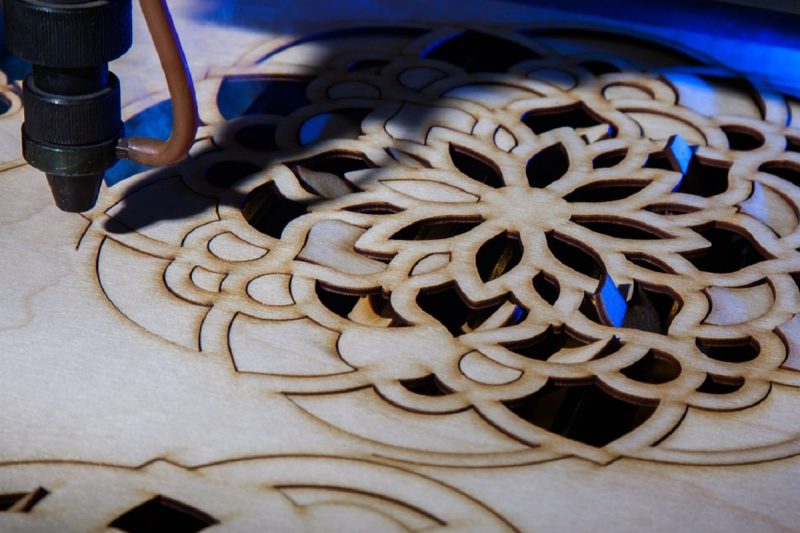

Materials compatible with CO2 laser cutting
Plastic
- Acrylic: CO2 laser cutting machines perform well on acrylic and can achieve high-precision cutting. Acrylic is a transparent and highly malleable material, and the high-focus characteristics of a CO2 laser cutter are ideal for cutting details and edges.
- PVC: CO2 laser cutting performs well on PVC, cutting efficiently and keeping edges flat. Common plastic PVC, its durability and versatility make it ideal for CO2 laser cutting.
- ABS: CO2 laser cutting performs well on ABS, enabling efficient and precise cutting. ABS is a strong and easy-to-process plastic, and CO2 laser cutting is often used to make models, prototypes, parts, toys, and electronic product casings.
- Polycarbonate: CO2 laser cutting enables efficient cutting of polycarbonate while maintaining high transparency of the material. Polycarbonate is a plastic with high strength and good heat resistance. CO2 laser cutting is often used to make eyeglass lenses, car lamp covers, etc.
Wood
- Hardwood: CO2 laser cutting has good adaptability to hardwood. Common types of hardwood such as oak, walnut, and cherry wood can be accurately cut by CO2 laser cutting machines. CO2 laser cutting can provide fine cuts and engravings on these hardwoods.
- Softwood: CO2 laser cutting is also suitable for softwood, such as pine, spruce, and cedar. Laser cutting can cut softwood quickly and can achieve detailed cuts.
- Plywood: CO2 laser cutting machines are efficient at cutting plywood, a material made from multiple layers of wood veneers glued together. Laser cutting can create complex designs and holes in plywood and is highly adaptable. Commonly used in furniture, construction, and craft manufacturing.
- MDF: CO2 laser cutters are ideal for processing MDF, a high-density board made of wood fiber and synthetic resin. Laser cutting enables smooth cut edges on MDF without the need for further processing.
Metal materials
- Stainless steel: CO2 laser cutting works very well on stainless steel. The high reflectivity and thermal conductivity of stainless steel make it challenging for laser cutting, but CO2 laser cutting machines can effectively overcome these problems by using nitrogen or oxygen as an auxiliary gas and adjusting cutting parameters.
- Aluminum: Aluminum material has better adaptability to CO2 laser cutting. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity results in a relatively small heat-affected area when cutting, helping to achieve crisp cutting edges.
- Copper: CO2 laser cutting has relatively weak adaptability to copper, because copper’s absorption of CO2 laser is weak, resulting in less significant cutting effects than other metals. Usually, higher power and higher purity oxygen are required as auxiliary gas to improve cutting results.
- Brass: Brass has good adaptability to CO2 laser cutting. Its copper content is relatively high and it can better absorb CO2 laser.
Textiles and Fabrics
- Cotton and linen: The CO2 laser cutting machine has a good cutting effect on cotton and linen materials. Cotton and linen are two natural fibers that can be laser cut to achieve detailed patterns and shapes and are widely used to make clothing, home textiles, and decorations.
- Synthetic fibers: Nylon and polyester are two common synthetic fibers used in a wide range of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial products. Laser cutting enables fine, crisp cuts in both synthetic materials.
- Leather: CO2 laser cutting has a superior cutting effect on leather. Because laser cutting is a non-contact processing method that can achieve smooth, clear cuts on leather, it is widely used to make leather clothing, footwear, and accessories.
Other materials
- Paper and cardboard: CO2 laser cutting machines cut paper and cardboard with fine and accurate results. This makes it widely used in the printing industry, packaging industry, and art design. Because laser cutting is non-contact, it can achieve high-precision cutting of thin paper and avoid physical pressure and deformation.
- Rubber: CO2 laser cutting has a better cutting effect on rubber sheets, and is especially suitable for making seals, seals, and rubber parts. Laser cutting produces smooth, fine cuts, making rubber products widely used in industrial and printing industries.
- Foam: CO2 laser cutting machine has excellent cutting ability on foam and is suitable for various foam types. Laser cutting’s high-precision, vibration-free cutting method for foam makes it widely used in packaging, model making, and artistic design. In addition, laser cutting can also achieve cutting of complex shapes, improving the design flexibility of foam products.
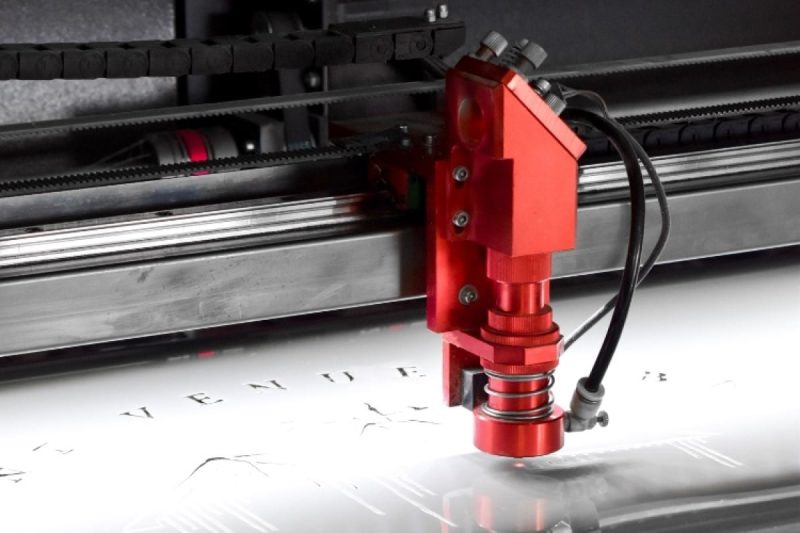

Specific considerations for different materials
Material thickness
- Metal materials: For metal materials, CO2 laser cutting machines are capable of cutting thinner sheets of metal, but for thicker metals, a higher-power laser may be required. Generally, using high-power laser generators is suitable for cutting thicker metal sheets, while low-power lasers are suitable for thin metals.
- Non-metallic materials: For non-metallic materials such as wood, plastic, and rubber, CO2 laser cutting machines are usually able to handle materials of different thicknesses. Adjusting the laser power and cutting speed can adapt to non-metallic materials of different thicknesses.
Reflectivity
- High reflectivity materials: High reflectivity materials, such as copper and aluminum, have weak absorption of CO2 laser cutting. Therefore, when cutting these materials, it is often necessary to use auxiliary gases, such as nitrogen or oxygen, to facilitate the cutting process.
- Low-reflectivity materials: Low-reflectivity materials such as wood and plastic have better absorption capabilities for CO2 lasers. It is easier to achieve high-quality cuts when cutting these materials.
Material composition
- Materials containing metal components: For materials containing metal components, CO2 laser cutting machines may face reflection and absorption problems. Laser parameters need to be adjusted according to the specific metal composition to obtain the best cutting effect.
- Organic materials: For organic materials, such as plastics and rubber, CO2 laser cutting machines can usually handle them effectively. However, different organic materials may have different cutting characteristics, so parameters need to be adjusted according to the specific material.
Laser power and focus position
- Laser power: Adjusting the laser power of the CO2 laser cutting machine can adapt to the cutting needs of different materials. For thicker or highly reflective materials, higher power may be required.
- Focus position: It is critical to ensure that the laser beam is focused near the material surface. Adjust the focus position to obtain the best cutting effect, ensuring that the beam can be fully absorbed and concentrated in the cutting area.
CO2 precautions and adjustments of laser cutting
Power and speed settings
- According to the type and thickness of the material, adjust the power and cutting speed of the CO2 laser cutting machine. For different materials, different power levels and cutting speeds may be required to achieve the best results.
Focus and beam alignment
- Keep the laser beam correctly in the working area and ensure that the focus is accurate. The position of the focus directly affects the cutting quality, so the focus position needs to be carefully adjusted to meet different materials and cutting requirements.
Auxiliary gas selection
- Choose proper auxiliary gases, usually including nitrogen, oxygen, or air. Different auxiliary gases can affect the way of cutting speed, cutting quality, and material absorption of the laser. Pay attention to the suggestions of the manufacturer to ensure a safe and efficient cutting process.
Alignment of beds and materials
- Maintain the level and cleaning of the working platform (bed) to ensure that the materials are installed and aligned correctly. The flatness of the material is essential to the section result.
Edge quality and smoothness
- For applications that require high-quality edges and surface smoothness, you may need to adjust the cutting speed and focus position. Slow laser cutting speed and shallow focus may improve the quality of cutting edges.
Maintenance and calibration
- Check and maintain the CO2 laser cutting machine regularly to ensure the cleaning and good state of all optical elements. Replace the worn parts promptly to prevent the cutting quality and equipment life.

Safety instructions for using CO2 laser cutting machine
Using CO2 laser cutting machines involves high-energy laser beams and potential hazards, so strict safety standards and operating procedures need to be followed. Here are some safety instructions when using a CO2 laser-cutting machine:
- Understand the equipment: Before using the CO2 laser cutting machine, carefully read the equipment’s operating manual and safety regulations. Make sure you understand how the equipment works, its functions, and safe operating procedures.
- Personal Protection Measures: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including laser safety glasses, protective clothing, and gloves. This can effectively reduce the potential damage to skin and eyes caused by the laser beam.
- Safe area setting: Set up a safe area around the CO2 laser cutting machine and ensure that only properly trained and authorized personnel can enter. Prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing the laser work area.
- Exhaust and Ventilation: Place the CO2 laser cutting machine in a well-ventilated area and ensure there is a proper exhaust system near the equipment. This helps eliminate harmful gases and dust generated and improves the safety of the working environment.
- Fire prevention: Since laser cutting may produce high temperatures, make sure there are no flammable items around the equipment. Fire extinguishing equipment should be installed near the equipment, and staff should be familiar with how to use it.
- Regular maintenance: Perform regular maintenance on the CO2 laser cutting machine, including cleaning the optical components, checking the laser source, and ensuring the stability of the machine. Regular maintenance helps reduce equipment failure and potential safety risks.
- Avoid direct exposure: Avoid direct exposure to the CO2 laser beam. Ensure that the work area has appropriate shielding facilities to prevent damage to the human body from laser radiation.
- Training and guidance: All operators who use CO2 laser cutting machines should receive professional training, and only trained and qualified personnel can operate them. Provide regular safety training to ensure operators understand the latest safety requirements and operating procedures.
- Emergency planning: Develop and train personnel to implement contingency plans in the event of an emergency. Including the steps to deal with equipment failure, fire, personal injury, etc.
- Comply with regulations and standards: Follow local regulations and laser safety standards to ensure that the use of CO2 laser cutting machines complies with relevant regulations and standards.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.

