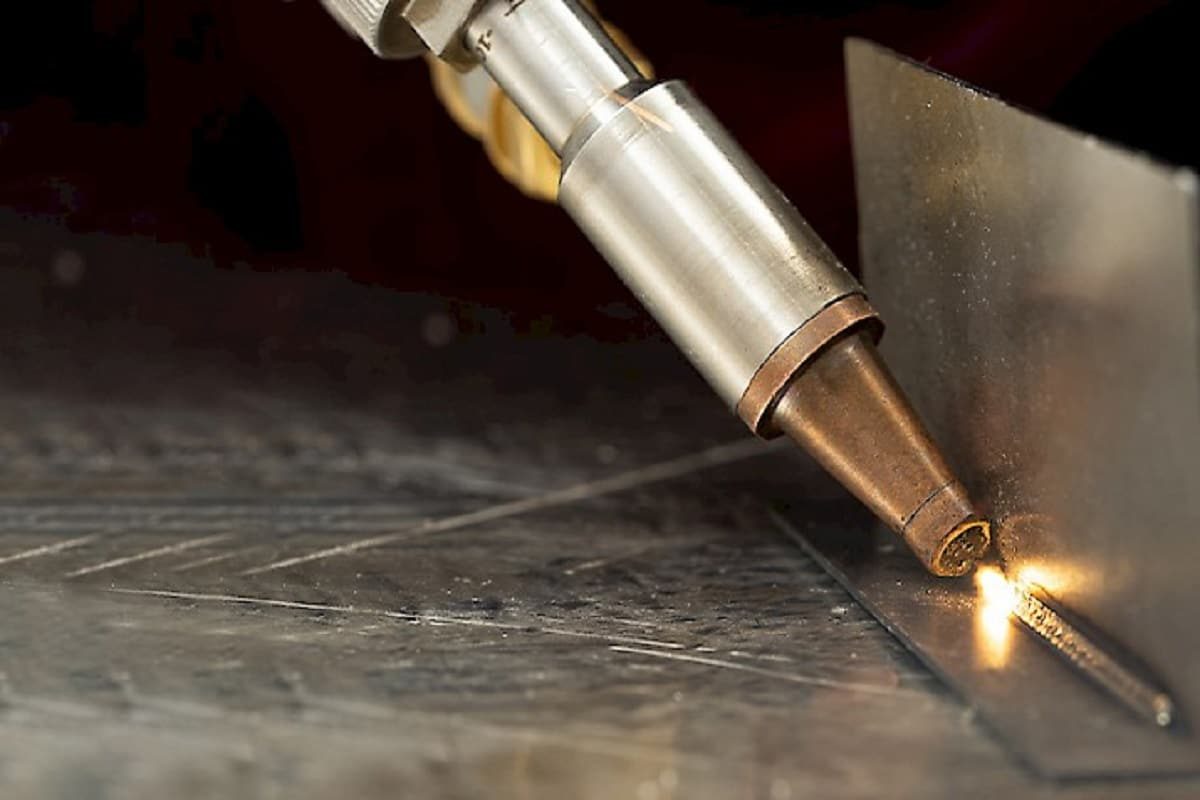
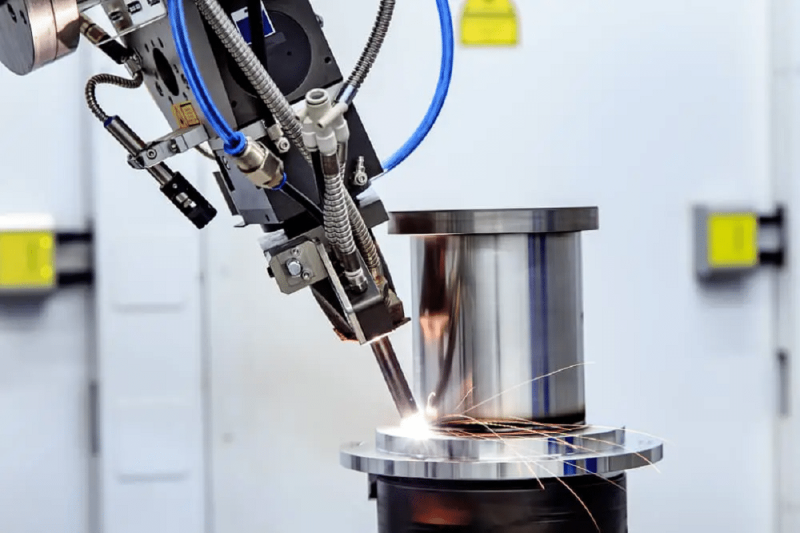


Basic Knowledge of Laser Welding
Laser welding is an efficient, precise welding technology that uses a highly focused laser beam to join materials together. The laser beam generates intense heat that melts and fuses the edges of the workpiece, creating a strong and precise weld. The technology is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. The versatility of laser welding lies not only in its ability to weld different materials but also in the variety of accessories and functions that can be integrated into a laser welding machine. These accessories and features play a vital role in improving the welding process, ensuring high-quality welds, and increasing overall operational efficiency.
Laser welding offers several advantages over traditional welding methods such as TIG (tungsten inert gas) welding and MIG (metal inert gas) welding:
- Precision and control: Laser welding provides unparalleled precision and control of the welding process. The focused laser beam can be guided precisely to the required welding point, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
- Minimum heat affected zone: Laser welding generates less heat than other welding methods, thus reducing the risk of material deformation and improving weld quality.
- High welding speed: Laser welding is much faster than traditional welding methods, and the concentrated heat source can achieve fast welding, increase productivity, and shorten production time.
- Clean welding: Because there is no physical contact between the welding tool and the workpiece, laser welding produces clean, spatter-free welds.
- Non-contact welding: There is no direct contact between the welding tool and the workpiece, reducing wear and helping to extend the service life of the equipment.
Laser Welding Machine Accessories
Beam delivery system
One of the main accessories of a laser welding machine is the beam delivery system. Different types of beam delivery systems are used depending on the specific application and requirements, each with its unique advantages.
- Articulated arms: Articulated arms are a common choice for beam delivery in laser welding. These robotic arms are highly flexible and can articulate in multiple directions, allowing the laser beam to reach hard-to-reach welding areas. Articulated arms provide high precision and are often used in applications that require mobility, such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- Fiber optic cable: Fiber optic cable is another popular choice for transmitting laser beams. These cables transmit laser energy over long distances with minimal loss. Fiber optics are suitable for applications where the laser source needs to be located away from the welding area. The ability to deliver the laser beam precisely makes it suitable for welding tasks in tight spaces and remote welding applications.
Smoke exhaust system
Vision system
Vision systems play a key role in laser welding, especially when processing complex or small welds that require high precision. These systems typically involve cameras, sensors, and software to monitor and guide the welding process.
- Cameras: Cameras are often integrated into laser welding machines to provide real-time visual feedback to the operator. High-speed cameras capture the welding process at a microscopic level, allowing precise monitoring and adjustment. This visual feedback helps control weld bead shape, size, and quality.
- Sensors: Sensors help ensure the accuracy of laser welding. It can detect changes during the welding process, such as the distance between the welding head and the workpiece, the temperature of the material, and the position of the workpiece. This data is used to make real-time adjustments to keep the welding process within specified parameters.
- Vision software: Vision software analyzes data collected by cameras and sensors to enable real-time control and feedback. The software automatically adjusts the laser’s power output, beam focus, and welding speed to optimize weld quality. It also helps in detecting defects and anomalies in welds, ensuring that the final product meets the required standards.
Wire feeder
Gas delivery system
Laser welding often requires the use of a shielding gas to protect the weld and control the process. These gases may include argon, helium, nitrogen, or mixtures of these gases. Gas delivery systems provide a controlled atmosphere around the welding area, providing the following benefits:
- Shielding: The primary purpose of the assist gas is to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, which prevents oxidation and ensures a clean, defect-free weld.
- Cooling: Shielding gases, such as helium, also have cooling properties, and they can help control welding temperatures to prevent overheating and material damage.
- Arc stabilization: In processes such as laser beam welding using filler wire, airflow helps stabilize the welding arc, resulting in a stable and consistent weld.
Power and pulse control
In laser welding, controlling the laser’s power output and pulse duration helps accommodate different materials and thicknesses. The laser welding machine is equipped with an advanced control system that allows the operator to adjust the following parameters:
- Pulse duration: Pulse duration can be adjusted to control heat input and penetration depth, making it possible to weld thin or heat-sensitive materials.
- Laser power: Laser power can be adjusted to control welding speed and depth of penetration, ensuring optimal results for every material and joint configuration.
- Pulse shaping: Some advanced laser welding machines allow for pulse shaping, which allows for customized energy distribution during the welding process, thereby increasing control over the weld.
This level of control is beneficial for the following reasons:
- Material compatibility: Different materials require different levels of energy to achieve optimal weld penetration and quality. The ability to adjust the laser generator power output ensures compatibility with a wide range of materials.
- Weld depth and width: Operators can control the depth and width of the weld by fine-tuning pulse duration and power settings. This level of precision helps achieve the desired welding characteristics.
- Minimize heat input: In applications where minimizing heat input and heat-affected zone size is critical, the ability to control power and pulse settings is essential.
Cooling system
The laser welding process generates large amounts of heat, which can cause the laser generator and other critical components to overheat. To ensure machine longevity and consistent performance, cooling systems are often integrated into laser welding machines to effectively manage temperature levels. Generally, two main types of cooling systems are used:
- Water cooling: A water cooling system circulates water through the laser generator and related components to absorb and dissipate heat. It has high heat dissipation efficiency and is mainly used in high-power laser generators and industrial applications.
- Air cooling: Air cooling systems use forced air to cool the laser generator and components. Its more compact design makes it suitable for lower-power laser generators, but also makes it more convenient in certain applications.
Automation and robotics integration
To maximize efficiency and consistency, laser welding machines can be integrated with robotic arms and automation systems. Automation has several advantages:
- Precision and repeatability: The robotic arm can precisely control the position and movement of the welding head to ensure repeatability and consistency of the welding process.
- High productivity: Automation can significantly increase production throughput, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing.
- Operator safety: Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, minimizing hazards to operators and improving safety.
Welding monitoring and quality control
Welding monitoring and quality control help ensure that welds meet required standards and maintain consistency. Therefore, laser welding machines can integrate a variety of sensors and software, including:
- Infrared sensor: The infrared sensor can detect temperature changes and abnormalities during the welding process. It is particularly useful for detecting defects such as porosity, cracks, or lack of fusion.
- Control software: Advanced software can accurately control welding parameters and quality standards, detect deviations from specified standards, and automatically adjust the welding process to correct any problems that may arise.
- Optical inspection: Optical inspection systems use cameras to capture images of welds and analyze defects to ensure quality standards are adhered to.
Remote control and programming
Modern laser welding machines come with user-friendly interfaces and software that enable remote control, programming, and data storage. These features enhance the machine’s usability and versatility in a variety of ways:
- Remote operation: Remote control enables operators to remotely adjust welding parameters and monitor the process, increasing safety and convenience.
- Pre-programmed setups: Machines with programming capabilities can store welding parameters and configurations for specific jobs, simplifying setup and reducing the possibility of human error.
- Data logging: Data logging capabilities allow operators to record and analyze welding data, promoting process optimization and quality assurance.
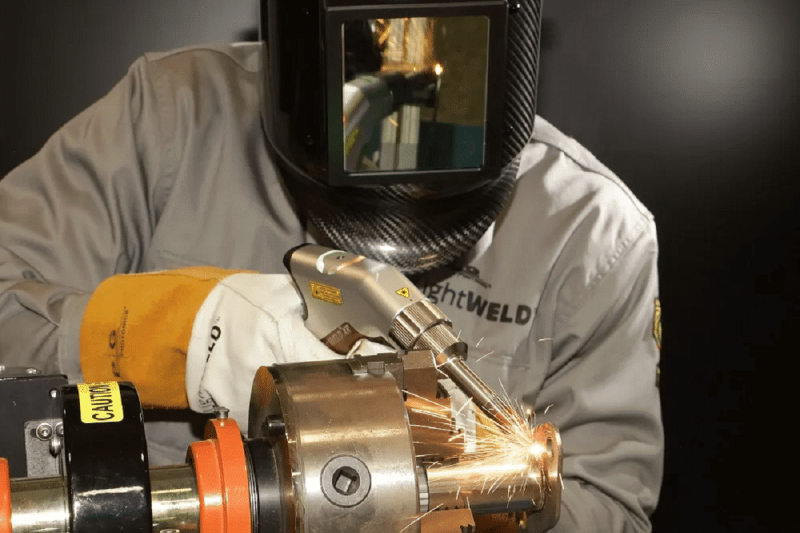

Application And Functions of Laser Welding Accessories
Laser welding is used in a wide range of industries with its enhanced accessories and advanced capabilities:
- Automotive industry: The automotive industry uses laser welding extensively to join components ranging from body panels to exhaust systems. Accessories such as articulated arms and automation systems can increase the efficiency of production lines. Vision systems and quality control measures ensure the structural integrity of welds, helping to improve the overall safety and durability of the vehicle.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, precision and reliability are critical. Laser welding with articulated arms and automation is critical for the manufacture of complex components such as turbine blades and structural components. Quality control and non-destructive testing systems help ensure welds meet strict safety and quality standards.
- Electronics and microelectronics: The electronics industry relies on laser welding to create complex connections on microelectronic components. An advanced fiber optic beam delivery system is ideal for working in confined spaces, while vision systems and sensors ensure the precision required for welding.
- Medical device manufacturing: Laser welding plays a vital role in the production of medical devices, where precision and freedom from contaminants are crucial. Wire feeders for adding biocompatible filler materials as well as vision systems and quality control measures ensure the reliability and safety of medical implants and devices.
- Jewelry & precision engineering: Laser welding is a staple technology in the jewelry industry, used to create intricate designs and seamless joints. Fiber optic transmission systems, power and pulse control, and vision systems contribute to the production of high-quality work. The ability to handle delicate and small items is a testament to the precision of laser welding in this field.
- Shipbuilding and heavy industry: In shipbuilding and other heavy industries, laser welding is used to join thick metal plates and components. A beam delivery system with long-distance capability is required. In addition, the cooling system helps maintain the continuous operation of large laser welding machines.
Challenges And Thoughts
While laser welding machines and their accessories and features offer numerous advantages, there are still some challenges and things to be aware of:
- Initial investment: Laser welding machines can be expensive, and the cost increases as advanced accessories and features are added. To determine the economic feasibility of these enhancements, a careful cost-benefit analysis is required.
- Training: Operators require adequate training to effectively use laser welding machines, especially when integrating accessories and advanced features.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure the continued functionality of your laser welding machine. In particular, cooling systems must be well maintained to prevent overheating.
- Material compatibility: Compatibility with welding materials is an important consideration, not all materials are suitable for laser welding.

Choose The Right Accessories For Your Laser Welding Machine
When considering accessories and features to enhance your laser welding machine, it is important to evaluate your specific application and requirements. The choice of accessories should be consistent with the materials you are using, the quality of welding required and the workspace available. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right accessories:
- Material compatibility: Different materials require different laser welding methods. Certain materials may require specific fittings or gas delivery systems to achieve the desired weld quality.
- Accuracy and tolerance: If your application requires the highest levels of accuracy and tolerance, accessories such as vision systems and wire feeders may be essential.
- Throughput: For high-volume production, automation and robotic integration can significantly improve efficiency and consistency.
- Operator safety: Consider the safety of the welding operator. Smoke extraction systems and automation can help minimize hazards faced by operators.
- Budget constraints: Assess your budget and weigh the cost of the accessory against the potential benefits it provides for your specific application.
- Long-term goals: Consider your long-term goals and how your chosen accessories can support scalability and future growth.

Future Trends And Developments
The world of laser welding is constantly evolving. As technology advances, so will the accessories and features that enhance the welding process. Some noteworthy trends and developments in laser welding include:
- Increased automation: The integration of laser welding machines with robotics and automation is expected to continue to grow. This trend will further increase efficiency, reduce human error, and improve the repeatability of welding processes.
- Advances in vision systems: Vision systems will improve the ability to recognize and analyze complex images, allowing for better control of the welding process and better detection of defects.
- Enhanced remote control and connectivity: Laser welding machines will be equipped with more advanced software and have remote monitoring and control capabilities, which will help industries that deploy machines in remote or hazardous locations.
- Environmental sustainability: There is an increasing focus on developing environmentally friendly welding processes. Laser welding has a minimal heat-affected zone and efficient energy use, making it ideally suited to sustainability goals. Enhancements may include the use of green laser sources and more efficient cooling systems.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
