

What Is Laser Marking?
Types of Laser Marking
There are many types of laser marking processes, each with its unique advantages and suitable for specific materials and applications. The most common types of laser marking include:
- Laser engraving: In laser engraving, a laser beam removes material to create deep and highly visible marks. This method is typically used in applications that require durability and legibility, such as serial numbers on metal parts.
- Laser etching: Laser etching is a non-ablative process (possibly removing the smallest amount of material) that discolors the surface of the material, creating light marks. This method is ideal for delicate materials, such as certain plastics and ceramics, and is often used for branding and decorative purposes.
- Laser ablation: Laser ablation involves removing the surface layer of material to create high-contrast marks on a variety of surfaces.
- Laser annealing: Laser annealing uses laser light to cause color changes on the surface of the material. It is suitable for marking stainless steel, titanium, and other metals and is commonly used in the medical device and automotive industries.
- Laser foaming: Laser foaming is a specialized method of creating high-contrast marks on plastics by inducing localized foaming, creating contrast without removing the material.
Laser Marking Accuracy
The accuracy of laser marking is a key factor in determining its effectiveness for a specific application. To understand the accuracy of laser marking, we need to consider the following aspects:
- Resolution: Laser marking systems are capable of high resolution, typically measured in microns (μm) or millimeters (mm). Resolution determines how fine the mark detail can be, allowing the creation of intricate designs, small characters, and intricate patterns.
- Marking speed: The speed at which the laser beam travels through the material plays an important role in determining accuracy. Faster marking speeds will affect the quality and depth of the mark, so finding the right balance can help achieve the desired marking results.
- Focus and spot size: The focus and spot size of the laser beam are key factors in achieving accurate marking. Smaller spot sizes allow for more precise and detailed marking, while larger spot sizes may be suitable for applications where speed is a priority but fine details are less important.
- Material properties: The type of material being tagged can also affect accuracy. Materials with different properties, such as hardness, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity, can affect the laser’s interaction with the surface, thus affecting the quality and accuracy of the mark.
- Repeatable results: Laser marking technology consistently delivers precise results over time. The repeatability of lasers aids in manufacturing processes that require uniform marks on numerous products.
Factors Affecting Laser Marking Accuracy
Laser System Quality
The quality of the laser system used for laser marking is a key factor in determining the accuracy and accuracy of the mark. An advanced and well-maintained laser system can significantly impact the results of your laser marking process.
- Optics: High-quality laser systems feature top-of-the-line optics, including high-performance lenses, mirrors, and beam expander modules. These components play a vital role in maintaining the focus and quality of the laser beam, ensuring that it remains pointed precisely and accurately at the marking surface.
- Beam quality: The beam quality of laser systems varies and is often quantified using parameters such as the M² (M squared) value. Lower M² values indicate higher beam quality, resulting in a more focused and accurate laser beam. Premium laser systems are designed to provide low M² values, ensuring laser energy is tightly focused and capable of producing precise marks.
- Pulse control: Control of laser pulses is another aspect of laser system quality. High-quality systems provide precise control of pulse duration, frequency, and energy. This level of control is critical to achieving precise marking, especially when working with different materials that may require specific pulse settings to optimize accuracy.
- Beam stability: Laser beam stability is a key consideration for accurate marking. High-quality laser systems are designed to minimize beam fluctuations, ensuring consistent intensity and position of the beam during the marking process. Beam instability may cause changes in mark quality and accuracy.
- Advanced cooling system: Laser systems must operate within a specified temperature range to maintain optimal accuracy. High-quality laser systems often employ advanced cooling systems to keep the laser generator and optical components at the right temperature. This helps prevent laser beam fluctuations caused by temperature changes.
- Maintenance and calibration: Regular maintenance and calibration of your laser system is critical to ensuring long-term accuracy. High-quality laser systems typically come with comprehensive maintenance and calibration protocols to keep the system in optimal condition. Routine maintenance addresses issues such as dust and debris buildup, ensuring your laser system continues to deliver precise results.
- Longevity and durability: The longevity and durability of the laser system are critical factors. High-quality systems are built to withstand the rigors of industrial use, ensuring they maintain accuracy and performance over an extended period. This longevity is critical for industries that rely on consistent marking accuracy.
Material Properties
One of the key factors affecting laser marking accuracy is the material being marked. Due to their unique properties, different materials exhibit different responses to laser energy, and understanding these material considerations can help achieve accurate and high-quality laser marking.
- Material thickness: The thickness of the material to be marked will affect the accuracy of laser marking. Thicker materials may require adjustments to the laser parameters to ensure the mark reaches the desired depth without causing damage to the surrounding material. Thin materials, on the other hand, may require lower power settings to prevent excessive marking or perforation.
- Surface finish: The surface finish of the material also plays a vital role in laser marking accuracy. Smooth and polished surfaces tend to produce more accurate and high-contrast marks, while rough or irregular surfaces may cause variations in mark quality. In some cases, surface treatment techniques such as sandblasting or chemical treatments may be required to achieve accurate marking on challenging surfaces.
- Material color and reflectivity: Material color and reflectivity significantly affect laser marking accuracy. For example, dark-colored materials absorb more laser energy and generally produce sharper, higher-contrast marks. Light-colored or reflective materials may require more precise control of laser parameters to achieve the same level of accuracy. Additives or coatings can sometimes be applied to a material to enhance its suitability for laser marking.
- Transparency and absorption: Transparent materials, such as some plastics and glasses, may not respond well to direct laser marking due to their limited absorption of laser energy. In this case, laser marking can be performed on a layer of contrasting material or additives applied to the surface to improve accuracy.
- Material reaction to heat: How the material reacts to the heat generated by the laser is a key consideration. Certain materials may melt, vaporize, or deform under the influence of a laser beam. Accurate laser marking on such materials requires careful control of laser parameters, including power, speed, and pulse duration, to avoid unexpected changes in material properties.
Environmental Factors
The environment in which laser marking occurs plays an important role in determining the accuracy of the mark. Various environmental factors can affect the accuracy of the laser marking process. Understanding and managing these factors helps ensure consistent and accurate marking results.
- Temperature: Temperature is a key environmental factor that affects laser marking accuracy. Laser systems are designed to operate within a specific temperature range. Temperature fluctuations can affect the performance of laser systems, causing changes in mark quality. High temperatures can cause thermal drift and affect the focus of the laser beam, while low temperatures can slow down or damage system components.
- Humidity: Humidity in the working environment can also affect laser marking accuracy. Excessive humidity can cause some materials to absorb moisture, affecting their performance and laser marking quality. Conversely, low humidity can cause static electricity to build up, which can lead to surface contamination or damage to laser optics.
- Air quality and particulate matter: The air quality and presence of particulate matter in the environment can have a direct impact on laser marking accuracy. Airborne dust and particles can deposit on the optical components of a laser system, causing lens contamination. This contamination can scatter the laser beam and reduce its accuracy.
- Vibration and mechanical stability: Vibrations from nearby equipment, machinery, and even foot traffic can affect the accuracy of laser marking. Even slight vibrations can disrupt the focus of the laser beam and cause markings to be inaccurate.
- Lighting conditions: Ambient lighting conditions in the marking area can affect the visibility of laser marks and the accuracy of their placement. Inconsistent lighting can make it difficult for operators to monitor the laser marking process and verify the quality of the mark. Proper lighting conditions allow operators to assess marking accuracy in real time.
- Air turbulence and airflow: Air turbulence and airflow in the marking environment can affect the trajectory of the laser beam. Changes in airflow can cause the beam path to distort, resulting in inaccurate mark placement.

Materials That Can Be Laser Marked
Metal
Plastic
Ceramic
Glass
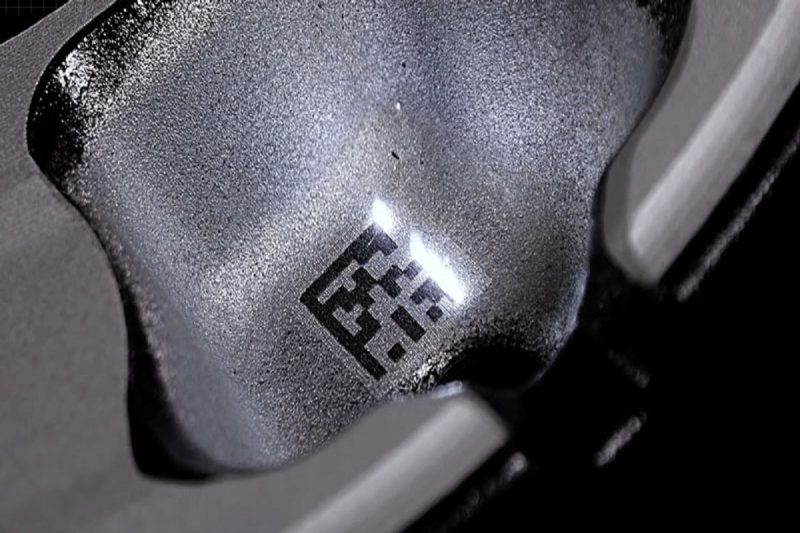

Challenges And Limitations of Laser Marking
While laser marking is a highly accurate and versatile technology, it does have some challenges and limitations that need to be considered:
- Material limitations: Certain materials, such as clear plastics, can be difficult to accurately mark with a laser due to their low absorption of laser energy. Specialized techniques or additives may be required to improve accuracy.
- Surface inconsistencies: Irregular surfaces, curved shapes, or uneven textures can pose challenges for laser marking, as maintaining consistent focus and achieving uniform mark depth can be difficult.
- Cost: High-quality laser marking systems can be expensive, which can be a limitation for small businesses or applications with limited budgets.
- Heat: Laser marking generates heat, which may affect the material being marked. With some materials, such as plastics, this heat can cause discoloration or deformation. The correct settings and laser type must be chosen to minimize these effects.
- Quality control: Implementing a strong quality control process helps identify and correct marking issues early in the production process, ensuring accurate results for the final product.
- Specialized systems: Certain applications may require specially designed laser systems to handle specific materials and challenges. These systems often include additional features such as high-speed galvanometer scanners to improve accuracy.

Application of Laser Marking
The accurate and accuracy of laser marking makes it widely used in various industries:
- Manufacturing: Laser marking is widely used in the manufacturing process to mark product information, logos, barcodes, etc. Its accuracy ensures that important information is permanently marked on the product, thereby enhancing traceability and quality control.
- Automotive: In the automotive sector, laser marking marks engine components, chassis components, and safety-related information on vehicle surfaces for part identification, traceability, and branding. Given the challenging conditions the car faces, markings must be accurate and permanent.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, laser marking is integral for component marking, serialization, and part identification. The high accuracy and durability of laser marking contribute to safety, maintenance, and traceability in this critical area.
- Medical devices: Due to the critical nature of its products, the medical device industry relies heavily on laser marking. Laser marking is used to mark surgical instruments, implants, and medical packaging. accurate helps improve the safety and traceability of medical devices.
- Electronics: Laser marking is widely used to mark electronic components, circuit boards, connectors, and even consumer electronics. High-accurate accuracy ensures parts fit perfectly and product information is marked for reference.
- Jewelry: In the jewelry world, laser marking offers a highly precise method of engraving intricate designs, text, and even images on precious metals and gemstones. accurate and customization options are highly sought after in the jewelry industry.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.

