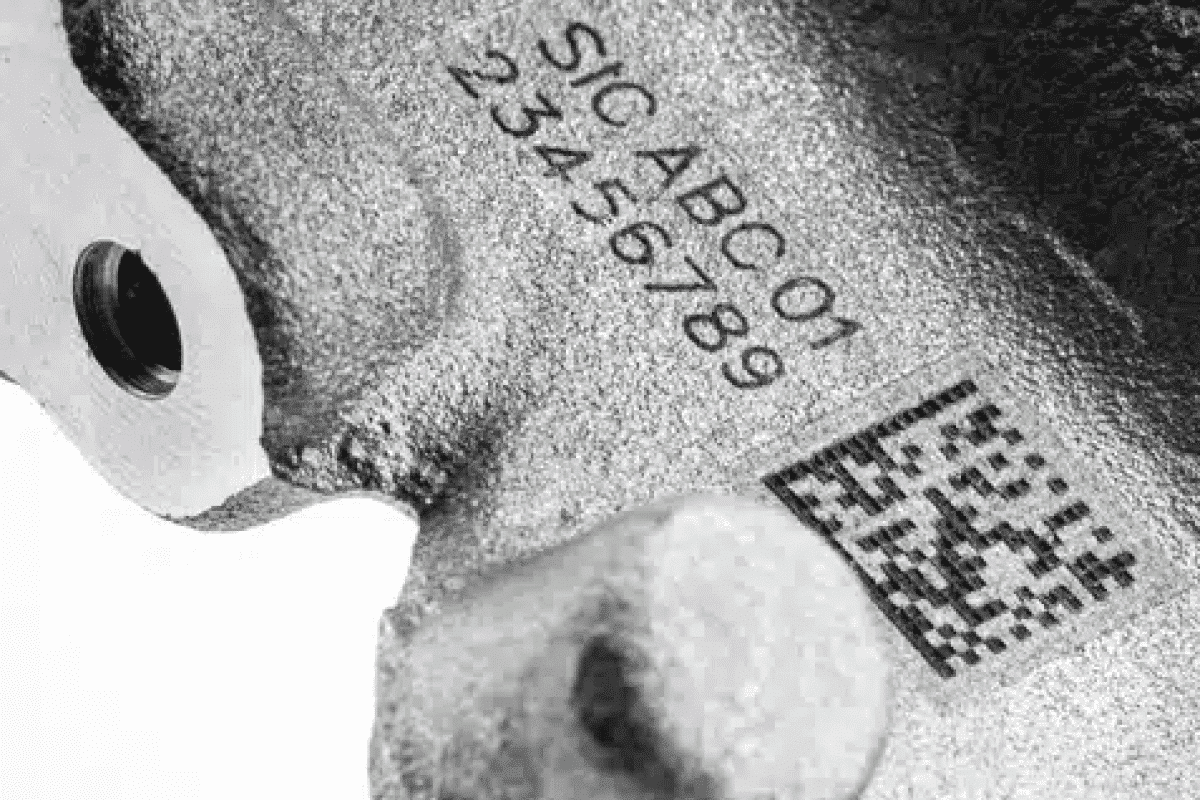

How Laser Parameter Selection Shapes Marking Precision
As a high-precision and high-efficiency marking method, laser marking technology is widely used in industrial manufacturing, medical machinery, electronic products, and other fields, such as marking, engraving, patterns, and other processing on product surfaces. Laser marking can realize various markings. High-quality marking of various materials. However, the quality of laser marking results also depends on the choice of laser parameters.
This article will deeply explore the impact of the selection of laser parameters in laser marking on the marking effect, including factors such as laser power, marking speed, laser wavelength, pulse power, etc., consider the response of different materials to laser parameters, and understand the optimization of laser parameters. The method is designed to provide effective parameter selection guidance for laser marking operators.
Table of Contents
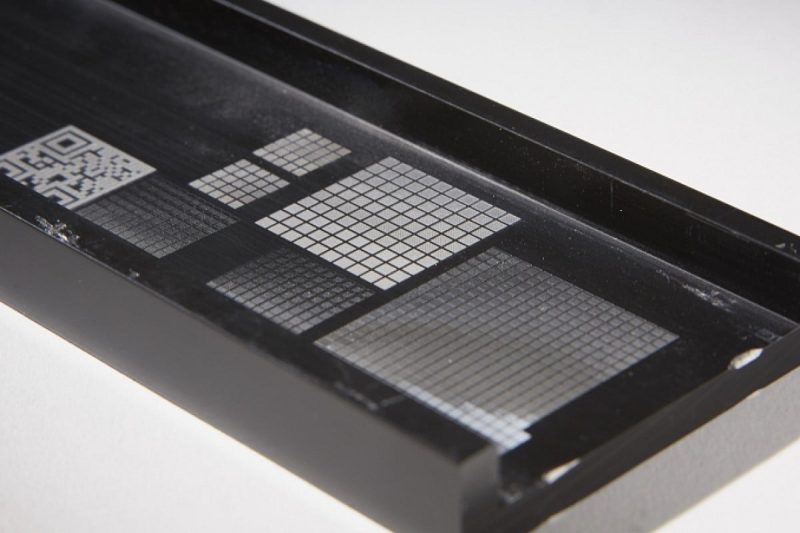
Basic principles of laser marking
Laser marking is a high-precision processing technology that uses laser beams to mark the surface of objects. Its basic principles involve key steps such as laser emission, focusing, and acting on the surface of the object. The specific principles are as follows:
- Laser emission: Laser generation usually uses gas laser generators, solid laser generators, or semiconductor laser generators as laser sources. The laser beams generated by these laser generators are highly monochromatic and coherent, providing a stable and controllable light source for subsequent marking.
- Laser modulation: In laser marking, the intensity of the laser beam needs to be modulated. Modulation can be achieved through light interference, gratings, or modulators to ensure that the laser can accurately mark according to the required pattern.
- Beam focusing: The laser beam is focused through optical elements such as lenses or mirrors to minimize the spot on the surface of the object, thereby increasing the energy density. The focused laser spot can act on the object surface more accurately to achieve high-resolution marking.
- Energy effect: When the laser beam acts on the surface of an object, its high energy density will cause local heating of the material. This action can have different effects on different materials, including scoring, melting, or vaporizing to create clear marks.
- Control system: The laser marking system is equipped with a sophisticated control system, which can accurately control the trajectory of the laser beam on the surface of the object according to the preset pattern, text, or code. Through computer control, a high degree of automation and flexibility can be achieved to adapt to various marking needs.
The basic principles of laser marking have been widely used in industrial manufacturing, medicine, electronics, and other fields. Its high precision and high efficiency make it an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.
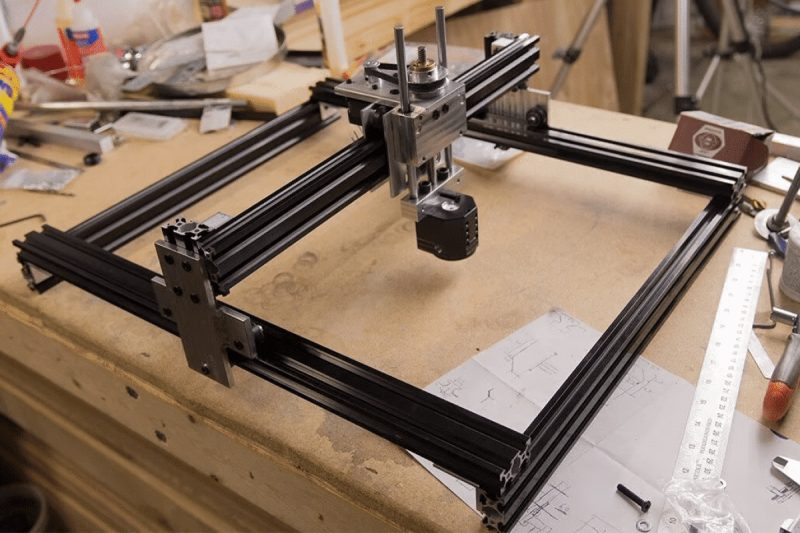
Laser parameters that affect marking results
The quality of laser marking results directly depends on the selection of several key laser parameters. These parameters have a complex relationship with each other, and a reasonable choice can achieve high-quality marking, while an inappropriate choice can lead to blurred, ablated, or insufficient depth of marks. The following are the main laser parameters that affect the laser marking effect:
Laser power
Laser power is one of the key parameters that affect mark depth and speed in laser marking. If the laser power is too low, the mark may be unclear, while if the power is too high, the material may be excessively ablated. When selecting laser power, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the characteristics of the material and marking requirements, and find the optimal power range through experiments and experience.
Marking speed
Marking speed refers to the speed at which the laser beam moves on the surface of the object. The choice of marking speed will affect the time for the laser to interact with the object, thus affecting the quality of the mark. A marking speed that is too fast may cause the laser beam to be unable to fully act on the material surface and the marking effect is unclear, while a marking speed that is too slow may cause excessive ablation. Therefore, choosing the appropriate marking speed is critical to achieving clear, consistent marks.
Laser wavelength
Laser wavelength is the wavelength range of the laser beam, which affects the transmission and absorption of laser in different materials. In addition, different materials have different absorption characteristics for lasers of different wavelengths. For example, for metallic conductive materials, near-infrared lasers are more easily absorbed; while for non-conductive materials, visible light or ultraviolet lasers may be more suitable. Therefore, choosing the appropriate laser wavelength can improve the marking effect.
Pulse frequency and pulse width
Pulse frequency refers to the number of pulses emitted by the laser per second, which directly affects the action time of the laser on the material. Reasonable selection of pulse frequency can control the depth and accuracy of marking. Generally, for hard materials, a higher pulse frequency can be selected to improve marking accuracy; while for soft materials, the pulse frequency can be moderately reduced to avoid excessive ablation.
Focus position
The choice of laser focus position directly affects the focusing of laser energy. A reasonable focus position can ensure that the laser energy is fully concentrated on the workpiece surface, thereby improving the clarity and accuracy of marking. When adjusting the focus position, you need to pay attention to the light absorption characteristics of different materials and the relationship between the laser beam diameter and the focus position.
To sum up, the quality of the laser marking effect is comprehensively affected by multiple laser parameters. Only through reasonable selection and adjustment of laser parameters can high-quality and high-efficiency laser marking be achieved.

Response of different materials to laser parameters
The application of laser marking on metal and non-metal materials has different characteristics. Therefore, there are some unique considerations in the selection of laser parameters for these two types of materials.
Special requirements for metal materials
- High laser power: Metallic materials are generally more sensitive to high-power lasers. The high-power laser can provide enough energy in a short time to melt and vaporize the metal surface, producing clear marks.
- Relatively slow marking speed: Metal materials require a long time of laser action to ensure sufficient energy is transferred to the surface, so a relatively slow marking speed is usually chosen.
- Near-infrared laser: Metal absorbs near-infrared laser better, so near-infrared laser is usually more suitable for metal materials.
- High pulse frequency: Higher pulse frequency helps improve marking accuracy, but needs to be adjusted based on the thermal conductivity of the metal to avoid overheating.
- Surface focus position: The focus position on the metal surface is usually selected on the surface of the material to ensure that the laser can be fully concentrated on the surface.
Considerations for non-metallic materials such as plastics and glass
- Relatively low laser power: For non-metallic materials, too high a laser power may cause excessive ablation and thermal damage, so a relatively low laser power is usually chosen.
- Faster marking speed: Since the absorptive capacity of non-metallic materials is relatively low, a faster marking speed can be selected to prevent excessive ablation.
- Visible light or ultraviolet laser: Non-metallic materials are more sensitive to visible light or ultraviolet laser, so choosing the appropriate wavelength can improve the marking effect.
- Frequency Pulses and Pulse Widths for Humidity: Non-metallic materials are generally more adaptable to lower pulse frequencies and moderate pulse widths to avoid excessive ablation and damage.
- Focus position at the surface or a moderate depth: The focus position for non-metallic materials is chosen depending on the material type, usually at the surface or at a moderate depth to ensure that the laser can act effectively.

Methods for optimizing laser parameters
Cutting speed and material thickness
Optimizing laser parameters is a key step to achieving high-quality laser marking results. Here are some common ways to optimize laser parameters:
Experimental verification
Conduct small-scale experiments and observe the marking effects under different parameter combinations by adjusting parameters such as laser power, marking speed, pulse frequency, and pulse width. Through experimental verification, the optimal parameter combination is found to meet the requirements of different materials and pricing depths.
Material Property Analysis
Different materials have different sensitivities to laser parameters, so the characteristics of the marked material, including light absorption coefficient, thermal conductivity, melting point, etc., need to be considered when optimizing parameters. A thorough analysis of the material properties allows targeted selection and adjustment of laser parameters.
Focus position adjustment
Adjust the laser focus position according to the properties of the material being marked. For metal materials. The focus is usually chosen on the surface. For non-metallic materials, you can choose to work on the surface or at a moderate depth to ensure that the laser can effectively act.
Optimization of pulse frequency and pulse width
Optimize pulse frequency and pulse width according to different materials and marking requirements. By adjusting these two parameters, the action time and energy transfer of the laser to the material can be controlled to obtain clear and fine marking effects.
Marking speed control
Select an appropriate marking speed to ensure that the laser remains on the surface for sufficient time while avoiding problems caused by overheating. Typically, slower marking speeds improve mark depth and clarity.
Laser wavelength selection
For different materials, choose the appropriate laser wavelength to increase the absorption rate of the laser. Metals are generally more sensitive to near-infrared lasers, while non-metallic materials are more adaptable to visible or ultraviolet lasers.
Online monitoring and feedback system
An advanced online monitoring system is introduced to monitor the marking effect during the laser marking process in real time, and the laser parameters are adjusted in real-time through the feedback system. Such a system increases production efficiency and ensures consistent mark quality.
Operator experience accumulation
The operator’s experience in actual work is also an important factor in optimizing laser parameters. By continuously accumulating practical experience, operators can become more proficient in adjusting parameters according to different situations and improve the consistency and effect of marking.
Summarize
The selection of laser parameters in laser marking has a great impact on the marking effect. By rationally selecting parameters such as laser power, pulse frequency, focus position, etc., and taking into account actual operating experience and material characteristics, high-quality, high-efficiency laser marking can be achieved to meet the marking and decoration needs of different industries.
Need more information about laser marking and laser engraving processes? Contact the experts at AccTek Laser! As a leading manufacturer of laser marking machines and laser engraving machines, we can answer and resolve any questions you may have about these processes. To learn more about our laser capabilities, contact us today. Work with us on your next project, and request a quote.
Contact information
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
Get Laser Solutions
