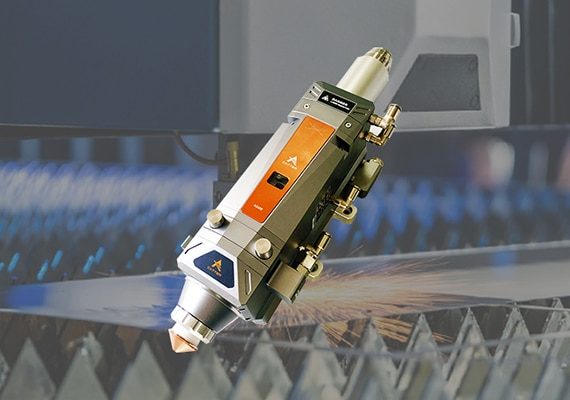

The high-quality laser cutting head delivers precision and efficiency, featuring advanced optics for superior beam focus and accuracy. Designed for durability and versatility, it ensures clean cuts on various materials, minimizing waste. With user-friendly adjustments and high-speed performance, it’s the perfect component for professional-grade laser cutting applications.

The ultra-stable laser generator is the heart of cutting-edge performance, delivering consistent power output for flawless cutting and engraving. Engineered for reliability, it ensures precision even during extended operations. Its advanced design minimizes fluctuations, enhances efficiency, and maximizes material compatibility, making it essential for professional-grade laser cutting applications.
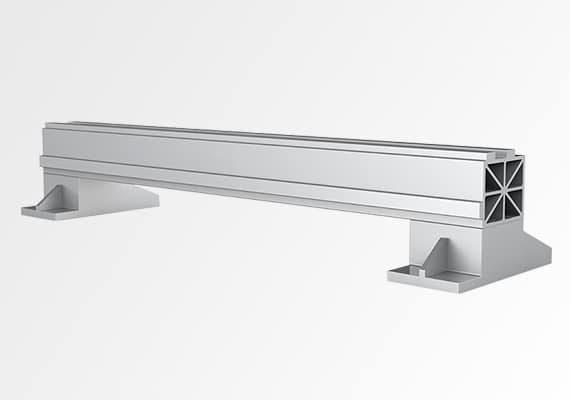

The aviation aluminum beam combines lightweight design with exceptional strength, ensuring stability and precision during high-speed operations. Crafted from aerospace-grade aluminum, it enhances cutting accuracy while resisting deformation. Its corrosion-resistant and durable structure reduces vibration, enabling smooth, efficient performance, making it a cornerstone of advanced laser cutting technology.
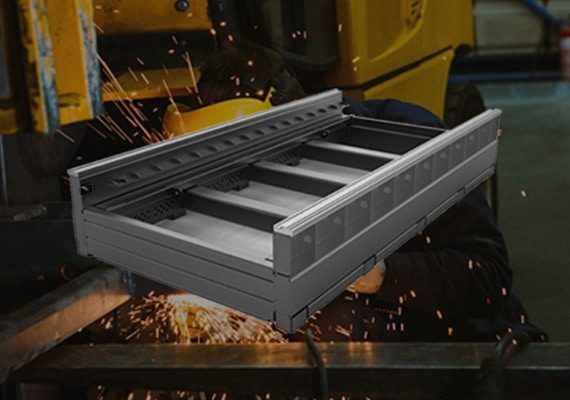

The Sturdy Cutting Bed is built for durability and precision, providing a stable platform for flawless laser cutting. Its robust construction resists wear and deformation, ensuring long-term reliability. Designed to support heavy workloads and various materials, it enhances cutting accuracy and efficiency, making it indispensable for industrial-grade performance.
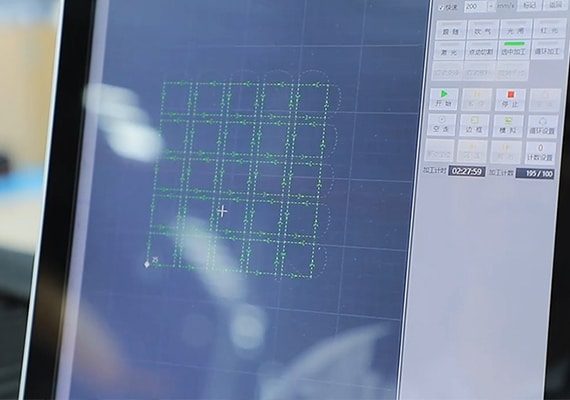
The friendly CNC control system offers intuitive operation with a user-focused interface, simplifying laser cutting processes. Equipped with advanced programming capabilities, it ensures precise control and seamless execution of complex designs. Compatible with various file formats, it boosts productivity while providing an effortless experience for professionals and beginners alike.
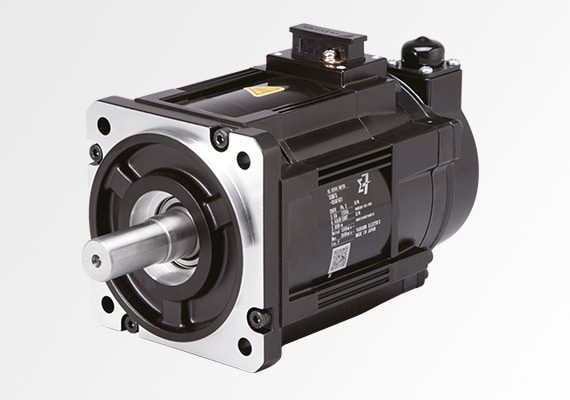

The high-precision servo motor ensures unmatched accuracy and smooth motion control for laser cutting operations. Its advanced design delivers rapid response and stable performance, enabling intricate cuts with exceptional detail. Built for durability and efficiency, it minimizes errors and enhances speed, making it essential for professional-grade cutting precision.
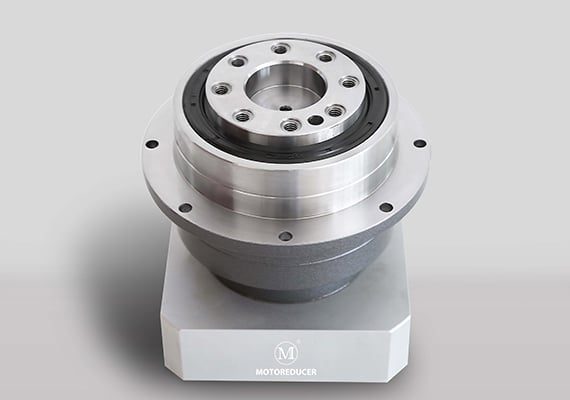

The high-performance reducer optimizes torque transmission for smooth and efficient laser-cutting operations. Engineered for durability, it minimizes vibration and ensures stable performance under high workloads. Its precision design enhances cutting accuracy and extends machine life, making it an indispensable component for achieving consistent, high-quality results.
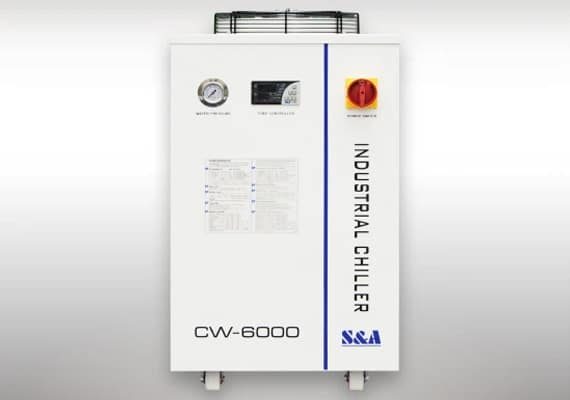

The high-efficiency water chillers provide reliable cooling to maintain optimal laser performance during intensive operations. Designed for energy efficiency, they regulate temperature precisely, preventing overheating and ensuring consistent output. With a durable build and user-friendly controls, these chillers enhance system longevity and productivity, making them essential for peak laser-cutting efficiency.
| Model | AKJ-1325F | AKJ-1530F | AKJ-1545F | AKJ-2040F | AKJ-2560F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Range | 1300*2500mm | 1500*3000mm | 1500*4500mm | 2000*4000mm | 2500*6000mm |
| Laser Type | Fiber Laser | ||||
| Laser Power | 1-40KW | ||||
| Laser Generator | Raycus, Max, IPG | ||||
| Control Software | Cypcut, Au3tech | ||||
| Laser Head | Raytools, Au3tech, Boci | ||||
| Servo Motor | Yaskawa, Delta | ||||
| Guide Rail | HIWIN | ||||
| Maximum Moving Speed | 100m/min | ||||
| Maximum Acceleration | 1.0G | ||||
| Positioning Accuracy | ±0.01mm | ||||
| Repeat Positioning Accuracy | ±0.02mm | ||||
Achieves exceptional accuracy with advanced laser technology, delivering clean, intricate cuts on a variety of materials.
Combines powerful laser generators and optimized components to ensure fast, reliable performance for large-scale operations.
Features a sturdy cutting bed, aviation aluminum beam, and robust components designed for long-lasting, industrial-grade use.
Equipped with a friendly CNC control system, simplifying complex processes with intuitive controls and seamless integration.
Capable of cutting a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, for diverse applications.
High-efficiency water chillers maintain optimal system performance while minimizing energy consumption.
High-precision servo motors and high-performance reducers ensure smooth, stable motion for flawless results.
Maximizes productivity with minimal material waste and maintenance costs, providing excellent value for businesses of all sizes.
| Laser Power | Thickness (mm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) | Focus Position (mm) | Cutting Height (mm) | Gas | Nozzle (mm) | Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000W | 0.8 | 18 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 1 | 10 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 | |
| 2 | 5 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 14 | |
| 3 | 1.5 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 1500W | 1 | 18 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 2 | 6 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 14 | |
| 3 | 2.5 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 4 | 0.8 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 2000W | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 2 | 10 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 4 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 14 | |
| 4 | 1.5 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 5 | 0.9 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 6 | 0.6 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 3000W | 1 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 2 | 15-18 | 0 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 7.0-8.0 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 14 | |
| 4 | 5.0-6.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 5 | 2.5-3.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 6 | 1.5-2.0 | -3.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 8 | 0.6-0.7 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 16 | |
| 4000W | 1 | 25-30 | 0 | 0.6 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 2 | 16-20 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 10-13 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 14 | |
| 4 | 6.0-7.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 5 | 4.0-5.0 | -2.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 6 | 2.5-3.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 8 | 1.0-1.3 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 10 | 0.8 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 16 | |
| 6000W | 1 | 30-45 | 0 | 1 | N2 | 1.5S | 12 |
| 2 | 20-25 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 14-16 | -1.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 4 | 8.0-10.0 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 5 | 5.0-6.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 14 | |
| 6 | 3.5-4.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 8 | 1.5-2.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 16 | |
| 10 | 1.0-1.2 | -4.5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 18 | |
| 12 | 0.6-0.7 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 4.0S | 18 | |
| 14 | 0.4-0.6 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 4.0S | 18 | |
| 16 | 0.3-0.4 | -8 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0S | 20 | |
| 8000W | 1 | 40-45 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 |
| 2 | 25-30 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 22-25 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 4 | 12-15 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 5 | 8.0-10.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 6 | 6.0-7.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 8 | 3.5-4.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 2.0-2.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 14 | |
| 12 | 1.6-2.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 1.0-1.2 | -6 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 0.8-1.0 | -7 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 0.7-0.8 | -8 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.5-0.6 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 25 | 0.4-0.5 | -10 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 30 | 0.2 | +7 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 10KW | 1 | 45-50 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 |
| 2 | 25-30 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 20-25 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 4 | 18-20 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 5 | 14-16 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 6 | 8.0-9.0 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 8 | 5.0-6.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 4.0-4.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 14 | |
| 12 | 1.6-2.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 1.2-1.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 1.0-1.2 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 0.8-1.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.6-0.8 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 25 | 0.5-0.6 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 30 | 0.25-0.45 | +7 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 40 | 0.15-0.2 | +8 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 12KW | 1 | 45-50 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 |
| 2 | 30-35 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 20-25 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 4 | 18-20 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 5 | 14-16 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 6 | 10-12 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 8 | 6.0-8.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 4.0-6.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 14 | |
| 12 | 2.0-3.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 1.5-2.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 1.3-2.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 1.0-1.6 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.8-1.2 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 25 | 0.5-0.7 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 16 | |
| 30 | 0.25-0.3 | +7 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 40 | 0.15-0.2 | +8 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 15KW | 1 | 48-52 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 |
| 2 | 35-38 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 3 | 25-27 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 4 | 20-22 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 12 | |
| 5 | 15-17 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 6 | 12-14 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 8 | 8.0-9.0 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 5.0-7.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 14 | |
| 12 | 2.5-3.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 2.0-3.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 1.5-2.5 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 1.3-1.8 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 0.8-1.2 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 25 | 0.5-0.7 | -5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 18 | |
| 30 | 0.4-0.5 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 40 | 0.25-0.3 | +8 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 50 | 0.2-0.25 | +9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8.0B | 20 | |
| 20KW | 1 | 55-60 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 8 |
| 2 | 40-45 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 8 | |
| 3 | 30-35 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 10 | |
| 4 | 25-30 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 12 | |
| 5 | 18-20 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 14 | |
| 6 | 16-18 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 14 | |
| 8 | 10-12 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 9.0-10.0 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 14 | |
| 12 | 5.0-6.0 | -6 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 4.0-5.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 3.0-4.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 2.0-3.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 1.5-2.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 6.0B | 18 | |
| 25 | 1.0-1.2 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6.0B | 18 | |
| 30 | 0.8-1.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 40 | 0.5-0.8 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 50 | 0.4-0.6 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8.0B | 20 | |
| 60 | 0.2-0.3 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8.0B | 20 | |
| 30KW | 1 | 55-60 | 0 | 0.8 | N2 | 2.0S | 8 |
| 2 | 40-45 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.0S | 8 | |
| 3 | 30-35 | -1 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 10 | |
| 4 | 25-30 | -2 | 0.5 | N2 | 2.5S | 12 | |
| 5 | 18-25 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 14 | |
| 6 | 18-20 | -3 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.0S | 14 | |
| 8 | 15-18 | -4 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 14 | |
| 10 | 12-15 | -5 | 0.5 | N2 | 3.5S | 14 | |
| 12 | 10-12 | -6 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 14 | 8.0-10.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 16 | 6.0-8.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 18 | 3.0-4.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 5.0B | 16 | |
| 20 | 2.0-3.0 | -7 | 0.3 | N2 | 6.0B | 18 | |
| 25 | 1.5-2.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 6.0B | 18 | |
| 30 | 0.8-1.0 | -7.5 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 40 | 0.5-0.8 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 7.0B | 20 | |
| 50 | 0.4-0.6 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8.0B | 20 | |
| 60 | 0.2-0.3 | -9 | 0.3 | N2 | 8.0B | 20 |

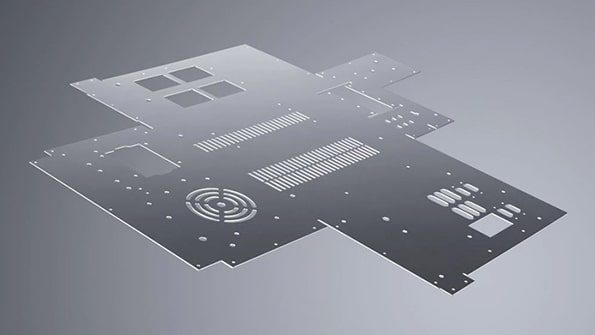
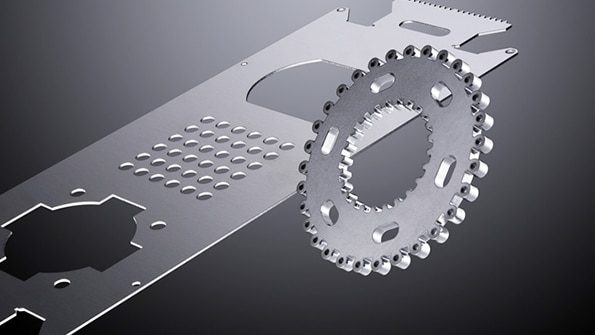

Aluminum laser cutting speeds can vary depending on several factors, including the thickness of the aluminum sheet, the power of the laser cutting machine, the desired cut quality, and specific cutting process parameters. Laser cutting speeds are typically measured in inches per minute (IPM) or meters per minute (m/min).
For thin aluminum sheets (1mm–10mm thick), laser cutting speeds can range from a few meters per minute to tens of meters per minute. The speed depends largely on the power of the machine and the specific cutting conditions. Thicker aluminum sheets, however, require slower speeds to ensure clean cuts and to prevent issues like overheating, melting, or the formation of burrs. This is due to the increased material density and the higher laser power needed to effectively cut through the material.
The optimal cutting speed is determined by the capabilities of the laser cutting machine and the desired cut quality, including factors like edge finish, precision, and accuracy. Higher-power laser generators designed specifically for metal cutting can achieve faster speeds, delivering superior results.
If you need more information on aluminum laser cutting, feel free to contact us. Our engineers will recommend the ideal cutting speed based on your chosen machine and specific requirements. We also offer guidance on cutting speeds for different aluminum thicknesses, assist with gas options, and help make test cuts to fine-tune parameters for optimal results.
Operating costs for laser cutting aluminum can vary significantly based on factors such as job size, design complexity, aluminum thickness, energy consumption, labor costs, and other overhead expenses. These costs can fluctuate due to market conditions and location, but here’s an approximate breakdown of each item involved:
These are general estimates and can vary greatly depending on your specific setup. For more precise information tailored to your needs, it’s recommended to consult local suppliers, manufacturers, or industry experts to obtain detailed, location-specific operating cost data.
Various laser cutting machines are capable of cutting aluminum, but the choice of machine depends on factors such as material thickness, required precision, and the specific application. Below are the most common laser-cutting machines used for aluminum:
Generally, fiber lasers are preferred for aluminum cutting due to their higher efficiency, faster speeds, and ability to produce narrower kerfs. When selecting a laser cutting machine, it’s important to consider the power output based on the desired thickness, as well as the machine’s overall capabilities and the reputation of the manufacturer to ensure high-quality, reliable cutting results.
While laser cutting is a safe and effective method for processing aluminum, several potential risks need to be addressed with proper safety measures. Here are some of the key risks associated with laser-cutting aluminum:
To minimize these risks, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s safety guidelines, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), ensure proper ventilation, and establish comprehensive safety protocols. Consulting with a laser safety expert and adhering to local safety regulations will further enhance the safety of laser-cutting aluminum.
Aluminum and its alloys are commonly processed using laser cutting due to their excellent properties. While most aluminum alloys can be effectively cut with a laser, some are better suited than others based on factors like material thickness, cutting speed, and the type of laser machine used. Here are some of the most common aluminum alloys that can be laser cut:
When laser cutting aluminum alloys, it’s important to consider the material’s specific composition and thickness, as these factors influence the laser’s power, cutting speed, and assist gas requirements. Consulting with the laser cutting machine manufacturer or service provider is recommended to ensure the best results for your particular application.
The most commonly used gas for laser cutting aluminum is nitrogen (N2). Nitrogen is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with aluminum during the cutting process. This helps prevent oxidation, which can affect the quality of the cut. Using nitrogen as an assist gas offers several benefits for laser cutting aluminum:
While nitrogen is the preferred assist gas for laser cutting aluminum, other gases like compressed air or oxygen can also be used based on the application. Compressed air is cost-effective for cutting thinner sheets, while oxygen may offer higher cutting speeds but can lead to increased oxidation and rougher edges. Choosing the right assist gas depends on factors like desired edge quality, cutting speed, material thickness, and machine capabilities. For optimal results, consult with the laser cutting machine manufacturer or a cutting specialist to select the best gas for your specific needs.
Aluminum poses several challenges when it comes to laser cutting due to its unique properties. Here are the key reasons why aluminum can be difficult to cut:
To overcome these challenges, specialized techniques and optimized parameters are necessary. These include using higher laser power, selecting appropriate assist gases, adjusting the focal length and beam quality, and employing cooling or air assist systems. With the right equipment and parameters, laser cutting aluminum can be achieved efficiently and with high precision.
Laser-cutting aluminum can be safe when proper safety precautions and operating procedures are followed. Adhering to safety guidelines significantly reduces potential risks and ensures a safe working environment. Below are key safety considerations for laser cutting aluminum:
To ensure the safety of laser-cutting aluminum, it’s important to follow local regulations and guidelines, perform regular risk assessments, provide appropriate safety equipment, and maintain a safe working environment. Consulting a laser safety expert or occupational health and safety specialist can provide additional insights tailored to your specific situation.

With years of experience in laser cutting technology, we have honed our expertise to provide cutting-edge solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our team of skilled engineers and technicians has the in-depth knowledge to ensure you get the perfect laser-cutting machine for your specific application.

At AccTek Laser, we build strong relationships with our clients. Our dedicated support team provides prompt assistance and after-sales service to keep your laser-cutting machine running at its best for years to come. Your satisfaction is our top priority and we will help you every step of the way.

Quality is the cornerstone of our manufacturing process. Every laser-cutting machine is rigorously tested and adheres to strict quality control standards, ensuring that the product you receive meets the highest industry benchmarks. Our dedication to quality ensures you get a machine that performs consistently and delivers perfect cuts every time.
We understand the importance of cost efficiency in today’s competitive landscape. Our laser-cutting machines can provide excellent value for your investment, minimizing downtime and reducing operating costs while maximizing productivity and efficiency.
4 reviews for Aluminum Laser Cutting Machine
Patricia –
Efficient and reliable, the aluminum laser cutter handles thin aluminum sheets with ease, ensuring consistent cutting quality.
Martina –
The machine’s precision is exceptional, providing clean and accurate cuts for our aluminum fabrication projects.
Bence –
The laser cutting machine stability during cutting operations ensures reliable performance, enhancing our productivity.
Hassan –
Precision and speed converge in an aluminum laser cutting machine, offering efficient and consistent results for our aluminum cutting needs.