Metal Laser Cutting Machine
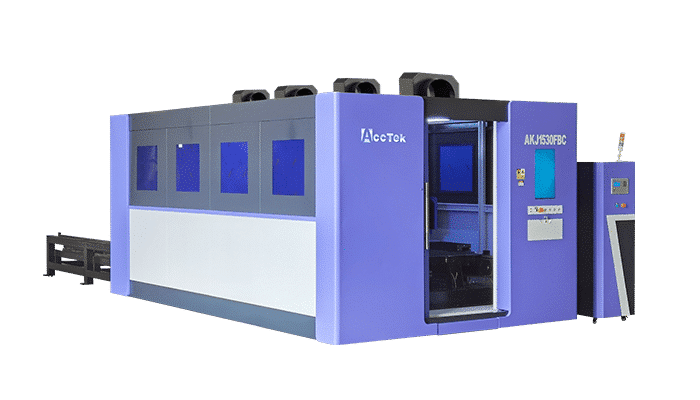

Product Range
Laser Cutting VS. Other Methods
Laser Cutting vs. Plasma Cutting
Laser cutting delivers superior precision and cleaner cuts compared to plasma cutting. It produces less heat-affected zones, minimizing material distortion. While plasma cutting is faster for thicker materials, laser cutting excels in accuracy and fine detail, making it ideal for intricate designs and thinner metals.
Laser Cutting vs. Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting is effective for thick materials and provides a clean edge without heat. However, laser cutting is faster, more energy-efficient, and capable of cutting thinner metals with higher precision. Water jet cutting can also struggle with highly reflective materials, whereas laser cutting handles them effortlessly.
Laser Cutting vs. Mechanical Cutting
Mechanical cutting methods, such as sawing or shearing, involve physical force that can cause material stress and require frequent tool maintenance. In contrast, laser cutting uses no contact, reducing wear on tools and offering higher precision. It is also faster and more suitable for complex, detailed cuts.
Why Choose AccTek Laser
Cutting-Edge Technology
AccTek Laser machines utilize the latest fiber laser technology, ensuring high precision and fast cutting speeds. Our systems provide unmatched accuracy and efficiency, ensuring the best quality cuts across various materials with minimal distortion.
Custom Solutions
We understand that every business has unique requirements. That's why we offer customizable options, including power ranges, work area sizes, and cutting speeds, allowing you to tailor our machines to fit your specific production needs and material types.
Exceptional Energy Efficiency
Our laser cutting machines are designed for maximum energy efficiency. With lower power consumption and optimized performance, AccTek Laser machines help reduce operational costs, making them a cost-effective solution for both small and large-scale manufacturing.
Durability and Reliability
AccTek Laser cutting machines are engineered for long-term durability, with high-quality components and precision manufacturing. Our machines are designed to provide consistent, reliable performance, reducing maintenance needs and extending the lifespan of your equipment.
After-Sales Support
We believe in building long-term relationships with our customers. AccTek Laser provides exceptional after-sales support, including installation, training, and ongoing technical assistance. Our team is always ready to help you optimize machine performance and resolve any issues quickly.
Competitive Pricing and Value
At AccTek Laser, we offer high-performance laser-cutting machines at competitive prices, ensuring that you get the best value for your investment. Our machines deliver outstanding quality at an affordable cost, making us a trusted partner for your manufacturing needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does Metal Laser-Cutting Machines Cost?
The cost of a metal laser cutting machine can vary greatly depending on a variety of factors, including the machine’s specifications, power, size, and brand. Here are the general price ranges for metal laser-cutting machines:
- Low-Power Metal Laser Cutting Machine (1000w-3000w): This type of machine is a compact machine suitable for small businesses and workshops. It usually has a lower power rating and a smaller cutting area. The price of a 1000w laser cutting machine ranges from $12,500 to $30,000, while the price of a 3000w laser cutting machine ranges from $20,000 to $45,000.
- Medium-Power Metal Laser Cutting Machine(6000w-12000w): This machine is designed for medium-sized manufacturing operations and provides higher power and a larger cutting area. Prices for mid-range laser cutting machines range from $35,000 to $180,000.
- High-Power Metal Laser Cutting Machine(20000w-30000w): The cost of large high-power metal laser cutting machines designed for heavy-duty and high-speed cutting ranges from $160,000 to $320,000. This type of machine is used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery manufacturing.
It’s important to note that these are general price ranges, and the actual cost of a metal laser cutting machine can vary greatly based on factors such as laser power, cutting area, automation features (such as automated loading and unloading devices), and more. If you would like the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information, you can contact us at any time. AccTek Laser’s engineers will provide you with complete solutions and quotations based on your specific needs. We can also provide you with details of any additional costs associated with installation, training, and maintenance.
What Type of Laser Can Cut Metal?
Many types of laser generators can be used to cut metal, but the most common types used in metal-cutting applications are fiber laser generators, CO2 laser generators, and Nd: YAG laser generators. Each laser generator has its advantages and limitations, making it suitable for different metal-cutting scenarios.
- Fiber Laser Generator: Fiber laser generators are popular in metal cutting applications due to their high efficiency and precision. This laser generator uses fiber optics to deliver a concentrated laser beam to the laser head. Fiber laser generators typically operate in the near-infrared range (approximately 1.06 microns) and are particularly suitable for cutting metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Fiber laser generators are known for their high power and excellent beam quality, which can cut metal materials of various thicknesses accurately and quickly.
- CO2 Laser Generator: The CO2 laser generator is one of the most widely used types of laser generators used for cutting metal. It operates in the infrared range (wavelength of approximately 10.6 microns) and is ideal for cutting metals (e.g. steel, stainless steel, aluminum, etc.) and non-metallic materials (e.g. plastics, wood, etc.). The working principle of the CO2 laser generator is to project the high-power CO2 laser beam onto the metal surface through a series of mirrors and focusing lenses to complete the cutting of thin metal sheets.
- Nd: YAG Laser Generator: The Nd: YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser generator is another type of laser used for metal cutting. They operate in the near-infrared spectrum and are suitable for cutting a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, and some non-ferrous materials. Nd: YAG lasers are typically used for precision cutting and are capable of cutting thicker materials than CO2 laser generators, but have less cutting capabilities than fiber laser cutters.
The choice of laser type for metal cutting depends on a variety of factors, including the thickness and type of metal being cut, the cutting speed required, the accuracy required, and cost considerations. Additionally, advances in laser technology continue to improve the performance and capabilities of these laser generators in metal-cutting applications. The appropriate laser generator type and configuration must be selected based on the specific requirements of your metal-cutting project.
What Are The Disadvantages of Laser Cutting Metal?
While laser cutting metal has many advantages, it also has some disadvantages and limitations that should be considered when choosing this method for your application. Here are the main disadvantages of laser cutting metal:
- High Initial Investment: Purchasing a laser cutting machine, especially a high-quality one, can be expensive. Initial capital costs include the laser cutting system, associated equipment (such as cooling and exhaust systems), and installation. For small businesses or those with a limited budget, the higher initial investment cost can be a hindrance.
- Energy Consumption: Laser cutting is energy-intensive, especially when using high-power lasers to cut thick metals. This results in higher energy costs, but it is worth noting that fiber laser generators are more energy efficient than CO2 laser generators.
- Maintenance Requirements: Laser-cutting machines require regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and accurately. Over time, components such as lenses, mirrors, and airflow systems need cleaning and replacement. Maintenance increases operating costs and downtime.
- Surface Finish: While laser cutting generally produces clean edges, the process can sometimes leave a heat-affected zone (HAZ) and slight surface discoloration, especially on thicker materials. Additional processes may be required to resolve these issues.
- Limited Material Thickness: Laser cutting may not be the most efficient way to cut extremely thick materials. Thicker metal sheets require higher laser power, which slows down the cutting process and increases operating costs. For very thick materials, other methods such as plasma cutting or waterjet cutting may be more suitable.
- Material Limitations: While laser cutting can handle a variety of metals, it may not be suitable for all types. Some specialty or specialty alloys may be difficult to cut, or the process may adversely affect material properties.
- Warping and Deformation: The heat generated during the laser cutting process may cause some materials to warp or deform, especially when cutting thin sheets or complex patterns, which can affect the accuracy and flatness of the cut parts.
- Environmental Concerns: While laser cutting is generally more environmentally friendly than some other cutting methods, it is not completely free of environmental impacts. The use of high-power laser generators and the disposal of waste materials still have environmental impacts.
- Noise and Smoke: Laser cutting can produce noise and smoke, depending on the material being cut and the cutting parameters. Adequate ventilation and noise control measures may be necessary to ensure a safe and comfortable working environment.
- Security Question: Laser cutting involves the use of high-intensity laser beams, which can pose safety risks to operators if not handled properly. Proper training and safety measures can help prevent accidents, such as eye injuries from direct exposure to the laser beam.
Despite these shortcomings, laser cutting remains a highly versatile and efficient method of cutting metals, especially for applications that require precision, intricate designs, and minimal material waste. When evaluating whether laser cutting is right for your particular project, you must weigh these disadvantages against its many advantages and consider your unique requirements and budget constraints.
How Accurate is laser cutting of metal?
Laser cutting is known for its exceptional accuracy and precision, making it one of the most precise metal-cutting methods. The accuracy of laser cutting of metal can vary depending on a variety of factors, including the type of laser, the quality of the laser system, the material being cut, and the expertise of the operator. Here are some general guidelines for laser cutting accuracy:
- Focus and Beam Quality: Proper focusing of the laser beam and maintaining good beam quality contribute to high-precision cutting. Smaller beam diameter allows for finer cuts and greater accuracy. Laser cutters with advanced optics and beam control systems tend to produce more precise cuts.
- Material Thickness: The thickness of the material being cut affects accuracy. Thinner materials tend to have higher accuracy levels, while thicker materials may have slightly larger tolerances due to factors such as beam divergence and heat dissipation.
- Laser Power: The power of the laser used also has an impact on accuracy. Higher-power laser generators can cut thicker materials but may produce a wider kerf (cutting width) and a larger heat-affected zone, which may affect accuracy.
- Cutting Table Stability: The stability of the cutting table and mechanical parts of the machine helps improve accuracy. A sturdy and well-maintained machine helps achieve precise cutting.
- Cutting Path Planning: The path followed by the laser during the cutting process will affect the cutting accuracy. Optimized cutting paths minimize errors and increase cutting accuracy.
- Material Properties: The accuracy of laser cutting may be affected by the material being cut. Certain metals, such as stainless steel and aluminum, cut more accurately than others due to their characteristics, while highly reflective materials, such as copper, can present challenges in achieving high accuracy.
- Machine Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration and maintenance of your laser cutting machine are critical to achieving and maintaining accuracy. Proper alignment and routine maintenance of optics help ensure accurate cuts.
- Operator Skills: Operator expertise plays an important role in achieving precise cuts. Skilled operators understand how to optimize cutting parameters, select the appropriate focus point, and manage factors such as beam quality and heat-affected zone to maintain accuracy.
- Cutting Complexity: The complexity of the cutting pattern or design affects accuracy. Simple geometries often cut more accurately than complex or highly detailed designs, while more complex and detailed cuts may require additional attention to achieve precise results.
Laser cutting is a high-precision metal cutting method capable of achieving tight tolerances, but high accuracy can vary depending on a variety of factors. To achieve the highest level of accuracy, it is essential to use a well-maintained, high-quality laser cutter and choose the appropriate laser type for your material. In addition, it is important to hire skilled operators who can optimize the cutting parameters according to your specific requirements to achieve the required cutting accuracy.
Do Metal Laser-Cutting Machines Consume A Lot of Power?
The power consumption of a metal laser cutting machine can vary widely depending on a variety of factors, including the machine’s power rating, specific cutting parameters, and the material being processed. Here are rough estimates of power consumption as a general guideline:
- The 12kw laser cutting machine may consume 58.8kWh (kilowatt hours) of electricity per hour of operation.
- The 15kw laser cutting machine may consume 63.8kWh of electricity per hour of operation.
- The 20kw laser cutting machine may consume 82.8kWh of electricity per hour of operation.
Keep in mind that these estimates are very rough and may vary depending on the machine’s design, efficiency, and how it is configured for your specific cutting task. Additionally, power consumption can fluctuate during the cutting process, especially when the machine operates at different speeds and power levels for different parts of the job.
If you want to get accurate information about the power consumption of a specific fiber laser cutting machine, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and user manual. Laser-cutting machine manufacturers often provide detailed information about the machine’s power requirements and energy efficiency.
How To Maintain Metal Laser Cutting Machines?
Maintaining your metal laser cutting machine ensures its longevity, efficiency, and safety. Here are some general tips for maintaining such a machine:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the machine regularly to prevent dust, debris, and metal shavings from accumulating. Use a soft brush, compressed air, or a vacuum cleaner to remove particles from the cutting area, lenses, mirrors, and other components.
- Inspect Optics: Check the condition of the laser optics (lenses and mirrors) frequently. Clean them gently with appropriate lens cleaning solutions and lint-free wipes to remove any residue or dirt that may affect the quality of the laser beam.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the laser beam is properly aligned. Misalignment can lead to poor cutting quality and premature wear of components. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for alignment procedures or consult a technician if necessary.
- Monitor Gas Supply: Make sure the gas supply (usually oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air) is sufficient and free of contaminants. Replace gas filters as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain the quality of the laser cut.
- Inspect and Replace Consumables: Regularly inspect consumable parts such as nozzles, lenses, and protective windows for signs of wear or damage. Replace them as needed to maintain cutting quality and protect sensitive components.
- Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This includes linear guides, bearings, and drive systems. Use the appropriate lubricants to prevent excessive wear and ensure smooth operation.
- Software Updates: Keep the machine’s control software up to date to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with newer operating systems. Check for updates from the manufacturer periodically
- Calibration: Periodically calibrate the machine to ensure accuracy and repeatability in cutting dimensions. This may involve checking the accuracy of the cutting head positioning system and adjusting parameters as necessary.
- Safety Checks: Regularly inspect safety features such as emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and safety guards to ensure they are functioning correctly. Replace any damaged or malfunctioning safety components immediately.
- Training and Documentation: Ensure that operators are properly trained in the safe operation and maintenance of the laser cutting machine. Provide access to documentation such as user manuals, maintenance schedules, and troubleshooting guides.
- Professional Service: Schedule regular maintenance checks by qualified technicians or service personnel according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. They can perform more in-depth inspections, adjustments, and repairs to keep the machine in optimal condition.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure that your metal laser-cutting machine operates efficiently, reliably, and safely for years to come.
What Safety Measures Do Metal Laser Cutting Machines Have?
Metal laser cutting machines incorporate various safety measures to protect operators, bystanders, and the equipment itself. Here are some common safety features found in metal laser-cutting machines:
- Enclosures: Laser cutting machines are typically enclosed to contain the laser beam and prevent radiation exposure. Enclosures may have interlocking doors that automatically shut off the laser when opened.
- Safety Interlocks: Interlocks are mechanisms that prevent the laser from operating if certain conditions are not met, such as the enclosure doors being open or the machine covers being removed. This helps prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam.
- Emergency Stop Button: Laser cutting machines are equipped with emergency stop buttons that immediately shut down the machine in case of an emergency or when safety concerns arise. These buttons are easily accessible to operators.
- Beam Containment: Laser cutting machines use beam containment systems to prevent the laser beam from escaping the cutting area. This may include beam traps, beam blocks, or other measures to absorb or redirect the laser energy.
- Fume Extraction: Laser cutting generates fumes and smoke that can be hazardous to health. Machines are equipped with fume extraction systems to remove these pollutants from the cutting area and vent them safely outside the machine.
- Automatic Shutdown: Some laser cutting machines have sensors that detect abnormalities such as overheating, excessive vibration, or power fluctuations. These sensors can trigger an automatic shutdown to prevent damage to the machine or potential safety hazards.
- Safety Glasses: Operators and personnel working near the laser cutting machine should wear appropriate safety glasses or goggles to protect their eyes from direct or reflected laser radiation.
- Training and Certification: Operators should receive proper training on the safe operation of laser cutting machines. Training programs cover topics such as machine operation, maintenance, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. Certification may be required to operate the machine.
- Warning Signs and Labels: Laser cutting machines are equipped with warning signs and labels indicating potential hazards and safety precautions. These help operators and bystanders understand the risks associated with the machine and how to operate it safely.
- Remote Monitoring: Some laser cutting machines feature remote monitoring capabilities that allow operators to monitor the machine’s operation and performance from a distance. This can help identify potential safety issues or malfunctions early on.
By incorporating these safety measures, metal laser cutting machines ensure safe operation and minimize the risk of accidents or injuries in industrial environments.
Is There Risk of Deformation When Laser Cutting Metal?
Yes, there is a risk of deformation when laser cutting metal, especially with certain metals and under certain conditions. Deformation can occur due to several factors:
- Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): Laser cutting generates intense heat, which can cause a heat-affected zone (HAZ) in the metal surrounding the cut. In some cases, this heat can lead to localized melting or warping, resulting in deformation along the cut edge.
- Material Thickness: Thicker metal materials are more prone to deformation during laser cutting, especially if the laser power and cutting speed are not optimized for the material thickness. Higher laser power and slower cutting speeds can increase the amount of heat transferred to the material, increasing the risk of deformation.
- Material Composition: The composition of the metal being cut can influence its susceptibility to deformation. For example, metals with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, can dissipate heat more quickly, reducing the risk of deformation compared to materials with lower thermal conductivity, such as stainless steel.
- Fixturing and Clamping: Proper fixturing and clamping of the metal sheet during laser cutting are essential to minimize the risk of deformation. Securely holding the material in place helps prevent movement or vibration during cutting, which can contribute to distortion or warping.
- Preheating and Post-Cutting Cooling: In some cases, preheating the metal sheet before laser cutting or implementing post-cutting cooling techniques can help reduce the risk of deformation. Preheating can minimize thermal shock, while controlled cooling can help alleviate residual stresses in the metal.
- Machine Calibration and Settings: Proper calibration of the laser cutting machine and optimization of cutting parameters such as laser power, cutting speed, and auxiliary air pressure can help achieve clean, precise cuts with minimal distortion.
To mitigate the risk of deformation when laser cutting metal, it’s essential to carefully consider these factors and adjust the cutting parameters accordingly. Additionally, selecting the appropriate laser cutting method and equipment for the specific metal and application can help minimize deformation and ensure high-quality results.
Related Resources

Understanding the Smells Associated with Laser Cutters
This article mainly discusses the causes, common types, and impacts of odors produced by laser cutting machines during processing, and proposes effective methods to reduce odors and improve the working

A Comprehensive Guide to Determining Laser Power for Laser Cutting Machines
This article mainly introduces how to determine and optimize the laser power of the laser generator to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and stability of laser cutting and welding.

Laser Cutting Machine Nozzle Guide
This article mainly introduces nozzle types, sizes, materials, and factors affecting performance, helping you choose the right nozzle and improve cutting accuracy and efficiency.