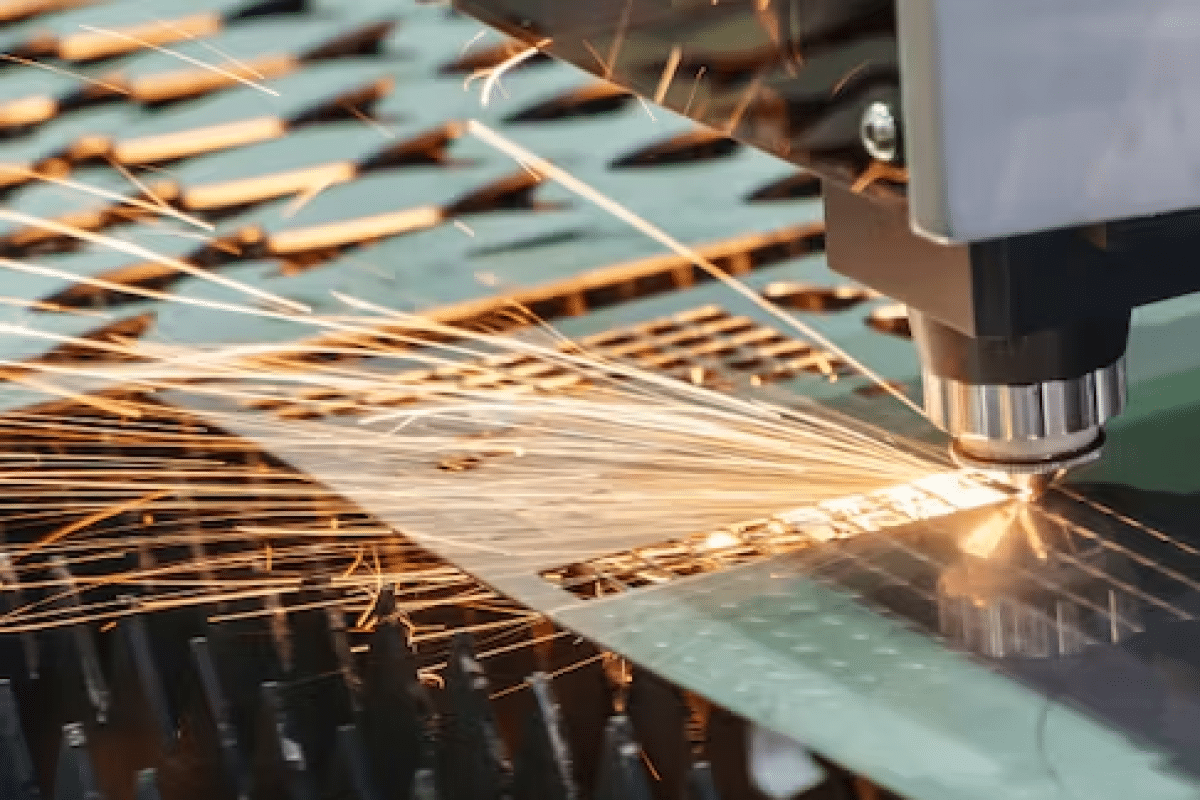
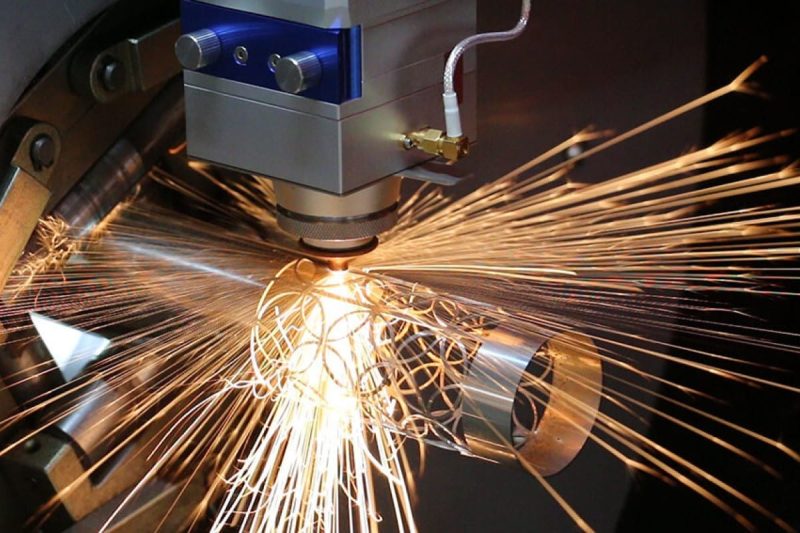


Laser cutting
How laser cutting works
The laser cutting machine is a machine tool that uses a high-energy laser beam to cut materials. Its principle is to convert electrical energy into light energy, and then concentrate the light energy into a high-energy laser beam, which is used to cut various materials. The working method of the laser cutting machine can be summarized as follows:
- Laser emission: The laser cutting machine contains a laser generator inside, which generates a high-energy laser beam.
- Laser beam transmission: Through the lens and lens system, the laser beam is focused into a highly concentrated light spot.
- Material cutting: The laser beam is precisely focused onto the surface of the workpiece, heating it to a temperature high enough to evaporate or melt the material in a short time. Control software translates the design and guides the movement of the laser head to trace the path of the desired pattern to achieve the cut.
Advantages of laser cutting
Laser-cutting technology offers several advantages over sawing, making it an ideal manufacturing solution for many projects. Some of the main advantages include:
- High precision: Laser cutting technology enables very high cutting precision. The diameter of the laser beam is small, so it can achieve precise and accurate cutting on the surface of the material. It is suitable for applications that have strict requirements on cutting accuracy, such as the electronics industry and precision component manufacturing.
- High efficiency: Compared with traditional sawing technology, laser cutting is faster. Laser beams can complete a large amount of cutting work in a short time, improving production efficiency. Especially for large-scale production and automated production lines, laser cutting is an efficient choice.
- Non-contact cutting: Laser cutting is a non-contact cutting technology. The laser beam acts directly on the surface of the material without physical contact. This means that there will be no vibration or force during the cutting process, which helps to reduce material deformation and damage and is especially suitable for situations with higher material requirements.
- Multi-material adaptability: Laser cutting technology has good adaptability to a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, wood, glass, etc. This multi-material adaptability enables laser cutting to be used in a wide range of industries and applications.
- No tool changes required: Compared with sawing technology that requires changing different types of saw blades according to different materials, laser cutting does not require tool changes, reducing downtime and labor costs during the production process.
- Flexibility: The laser cutting system has high flexibility and can be precisely controlled by computer numerical control to achieve the cutting of complex shapes. This flexibility makes laser cutting suitable for custom production and low-volume production.
Disadvantages of laser cutting
Although laser cutting technology excels in many ways, it also has some disadvantages. Here are some of the main disadvantages of laser cutting technology compared to sawing technology:
- High investment cost: Laser cutting equipment is relatively complex and uses high-power laser generators and sophisticated optical systems, making its equipment expensive. This makes the initial investment potentially a significant burden for some small businesses or those with limited budgets.
- High material requirements: Laser cutting requires high reflectivity and absorptivity of materials. Some materials may not be suitable for laser cutting or may require special handling to cut.
- Maintenance and operation skills required: Laser cutting systems require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure their performance and accuracy. This may require specialized skills and training, adding to operational complexity.
- Harmful gases and light radiation: Harmful gases and smoke, such as nitrogen oxides and organic waste gases, may be produced during the laser cutting process, which requires an effective ventilation system to deal with. In addition, laser cutting involves potential optical radiation risks and requires appropriate protective measures.
- Limited cutting thickness range: Compared to some traditional mechanical cutting methods, laser cutting may have some limitations when processing thicker materials. For some thicker materials, laser cutting may not be as effective as other methods.
- The tradeoff between complexity and flexibility: Programming and setting up a laser cutting system can be relatively complex and require specialized knowledge. This may cause some operators in small-scale production environments to face a learning curve and may require longer preparation time.
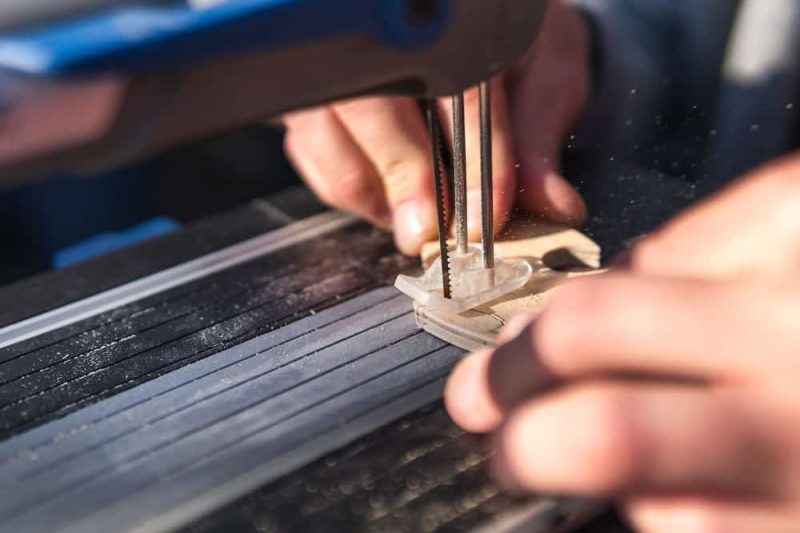

Sawing
How sawing works
The working principle of sawing is based on the rotational movement of the saw blade, which cuts through the material through the saw teeth. Here’s how sawing generally works:
- Selection of saw blades: Different types of saw blades can be selected for different materials and cutting requirements, including coarse saw teeth and fine saw blades.
- Rotary motion: The saw blade is usually mounted on a rotating shaft and can be manually operated or powered by an electric motor. The rotational motion of the saw blade enables its teeth to enter and cut through the material being cut.
- Sawtooth cutting: The sawtooth continuously enters the material during the rotation. Through the cutting motion of the sawtooth, the material is divided into the required shape and size.
- Feed motion: In some automated sawing systems, the workpiece is usually moved along a fixed path during the cutting process, which is called feed motion. This ensures that the material is cut evenly throughout the cutting process.
Advantages of sawing technology
Compared with laser cutting, sawing technology has some unique advantages, especially under specific application scenarios and material processing needs. Here are some of the advantages of sawing technology over laser cutting:
- Low cost: Sawing equipment is relatively simple, and compared with laser cutting equipment, investment and maintenance costs are lower. This makes sawing technology more practical for some businesses or individual craftsmen with limited budgets.
- Suitable for large size and thickness materials: Sawing technology has certain advantages when processing large and thick materials. For some wood or metal materials, sawing technology can make the cutting task easier.
- Relative to simple operation: Sawing equipment is usually relatively simple and easy to operate. In contrast, laser cutting technology may require a more complex setup and operation, so sawing is more user-friendly for some non-professional operators.
- Can be used on a variety of materials: sawing technology is widely applicable to different types of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, and more. Laser cutting has relatively high requirements on materials while sawing technology is more flexible in this regard.
- Suitable for some very thick materials: For some very thick materials, sawing technology may be more suitable. Laser cutting can have some limitations when working with extremely thick materials.
- Low technical threshold: operating sawing equipment is relatively simple and does not require excessive professional skills and training. This makes sawing technology easier to apply in some small and medium-sized enterprises or home workshops.
Disadvantages of sawing technology
Although sawing technology has advantages in certain applications, it also has some disadvantages compared to laser cutting. Here are some of the main disadvantages of sawing technology:
- Relatively low cutting accuracy: Cutting accuracy with sawing technology is often relatively low, especially when compared to laser cutting. This may not be suitable for applications that require high precision, such as electronic component manufacturing or cutting of precision mechanical parts.
- Slow cutting speed: The cutting speed of sawing is relatively slow, especially for large and thick materials. This may affect production efficiency, making sawing less suitable in some industrial environments where high throughput is required.
- More waste materials are generated during processing: During the sawing process, due to the characteristics of the saw teeth, more waste materials may be generated, including cut small pieces or shavings. This can increase the cost of cleaning up and disposing of scrap and create additional workload on the production environment.
- Weak ability to cut restrictive shapes: Sawing technology is less capable of cutting complex shapes and curves than laser cutting. Due to its non-contact nature, laser cutting can more easily cut complex shapes, while sawing has certain limitations in this regard.
- Not suitable for some special materials: Sawing technology may not be suitable for some special materials, such as composite materials, plastics glass, etc. In contrast, laser cutting technology can be applied to a wider variety of materials.
- Wear and Maintenance: Sawing tools (saw blades) are susceptible to wear and require regular replacement. Not only does this increase operating costs, but it can also cause production disruptions.
- Noise and vibration: The noise and vibration generated during the sawing process are relatively large, which may have a certain impact on the working environment and workers’ health. In comparison, laser cutting is generally quieter.
Sawing VS Laser Cutting Technology: How to Choose
Material type
- Sawing: Suitable for relatively thick, large, or composite materials, such as wood, large pieces of metal, etc.
- Laser Cutting: Suitable for thin and precise materials such as sheet metal, plastic, glass, etc.
Cutting accuracy requirements
- Sawing: If your requirements for cutting accuracy are not particularly high and your budget is limited, sawing may be a suitable option.
- Laser Cutting: In scenarios that require high-precision cutting, such as electronic parts manufacturing, precision machinery, etc., laser cutting can better meet the requirements.
Productivity and speed
- Sawing: Sawing speeds may be reduced when working with large and thick materials, but productivity can be increased by using more powerful sawing equipment.
- Laser Cutting: Laser cutting is faster in most cases and is particularly suitable for production environments that require high throughput.
Investment cost
- Sawing: Sawing equipment is usually simple, has relatively low investment costs, and is suitable for situations where the budget is limited.
- Laser Cutting: Laser cutting equipment is generally more expensive and requires a larger initial investment.
Material waste
- Sawing: Due to the characteristics of the saw teeth, more waste material may be generated during sawing. In some environments with high requirements for material waste, careful consideration is required.
- Laser Cutting: Laser cutting generally produces less scrap because it is a non-contact cutting method.
Operation and maintenance difficulty
- Sawing: The operation is relatively simple and the skill requirements for the operator are relatively low. Maintenance mainly involves saw blade replacement and equipment cleaning.
- Laser Cutting: Operation and programming may require a higher skill level, and equipment maintenance and calibration requirements are complex.
Safety and environmental impact
- Sawing: Sawing can produce noise and vibration due to the mechanical movement involved. In some cases where there are requirements for the working environment and operator health, these factors need to be considered.
- Laser cutting: usually produces less noise, but attention needs to be paid to the impact of laser radiation and exhaust gases on the environment and operators.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
