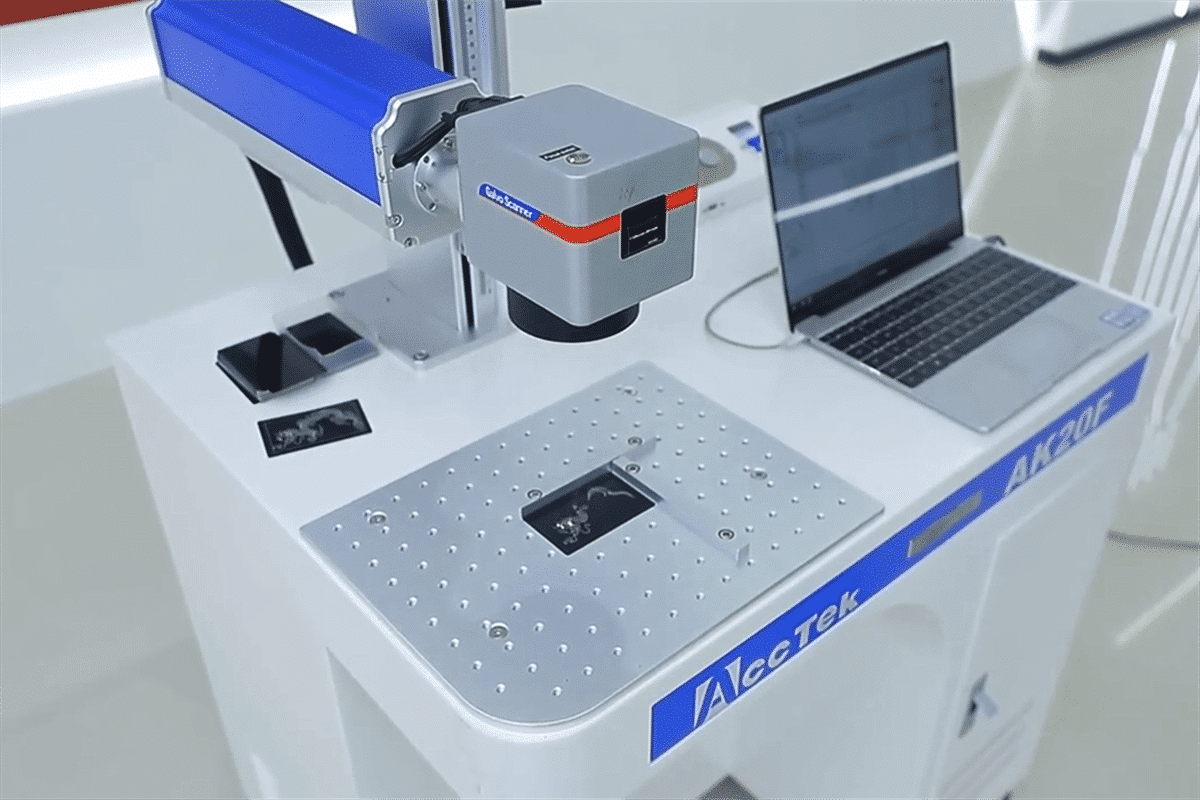


Why Choose Laser Marking?
What is laser marking?
The meaning of laser marking
The importance of choosing the right laser marking technology
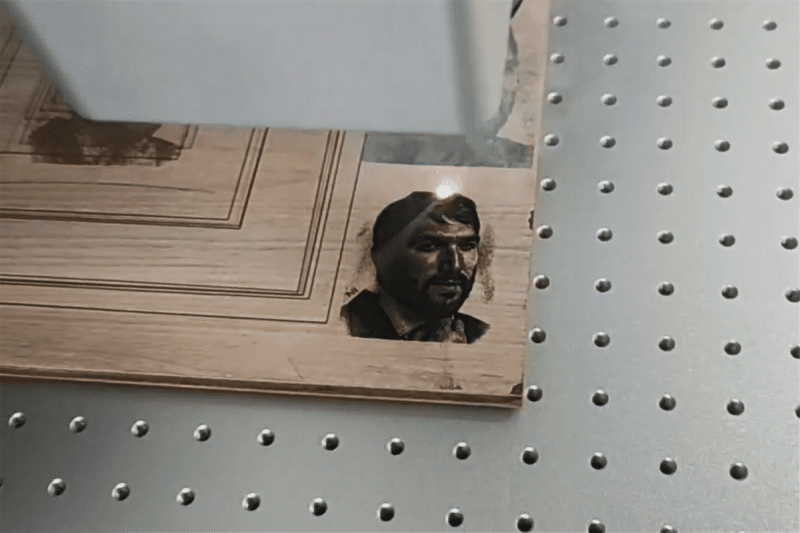

CO2 Laser Marking
How CO2 laser generator work
Applications and Advantages
CO2 laser marking stands out for its ability to mark a variety of non-metallic materials, including wood, acrylic, glass, textiles, plastics, foils, leather, and even stone. They are commonly used in areas such as food and pharmaceutical packaging, electronics, mobile communications, and building materials to mark products with intricate designs, logos, dates, or text. Essentially, CO2 laser has longer wavelengths and are highly adaptable, making them particularly suitable for use with organic materials and non-metallic substrates. Some key advantages of CO2 laser marking include:
- Deep engraving: CO2 laser excels at deep engraving applications, which involve removing a substantial volume of material to create a permanent mark. This is especially useful for applications that require longevity and visibility.
- Intricate graphics and text: CO2 laser is capable of marking intricate and detailed graphics and text, making them valuable for applications where precision is essential.
- Wavelength benefits: The longer wavelength provides benefits such as reduced heat-affected zones on certain materials and a reduced risk of melting or warping.
- Non-contact operation: CO2 laser marking is a non-contact process, eliminating the risk of tool wear and ensuring no direct contact with the material.
Limitations and Considerations
While CO2 lasers offer various advantages, they also come with certain limitations:
- Limited metal marking: CO2 laser is not well-suited for direct marking on most metals, as their longer wavelength is less effective at being absorbed by metal surfaces.
- Complex maintenance: The presence of mirrors and lenses in CO2 laser systems makes them more complex to maintain compared to a fiber laser, and requires CO2 laser tubes as consumables.
- Energy consumption: The photoelectric conversion efficiency of a CO2 laser generator is about 10-15%, which is much lower than that of a fiber laser generator, resulting in higher operating costs.
Fiber Laser Marking
How fiber laser generator work
Applications and Advantages
Fiber laser marking is widely used for product identification and traceability, with the ability to leave indelible barcodes, serial numbers, and graphics on a variety of metal materials. Fiber laser marking machines have become the first choice for marking in the metal industry due to their excellent accuracy, adaptability, and engraving durability. Some key advantages of fiber laser marking include:
- Metal marking superiority: Fiber laser is renowned for its exceptional performance in marking metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and other alloys. They create high-contrast, durable marks that are easily legible and scannable.
- Durable and low maintenance: Fiber laser generator has a reputation for its durability and longevity, requiring minimal maintenance. The absence of mirrors and complex gas mixtures simplifies upkeep.
- Energy efficiency: The electro-optical conversion efficiency of fiber lasers is about 30-50%, which means more energy saving, thus reducing operating costs.
- Compact design: Fiber laser systems are typically more compact and easy to integrate into production lines or small workspaces.
Limitations and Considerations
While fiber laser is well-suited for numerous marking applications, they also have limitations:
- Less effective on non-metals: Fiber laser is not as effective on non-metallic materials and may not provide the same level of marking quality or contrast.
- Reduced deep engraving: Achieving deep engraving with fiber laser can be challenging, especially on metals, as they tend to create more surface-level marks.
- Less versatile: Fiber laser is primarily designed for metal marking and may not be as versatile for marking a wide range of materials as CO2 lasers.
- Limited melting point: Fiber lasers can generate more heat in the marking process, which may affect materials with low melting points.
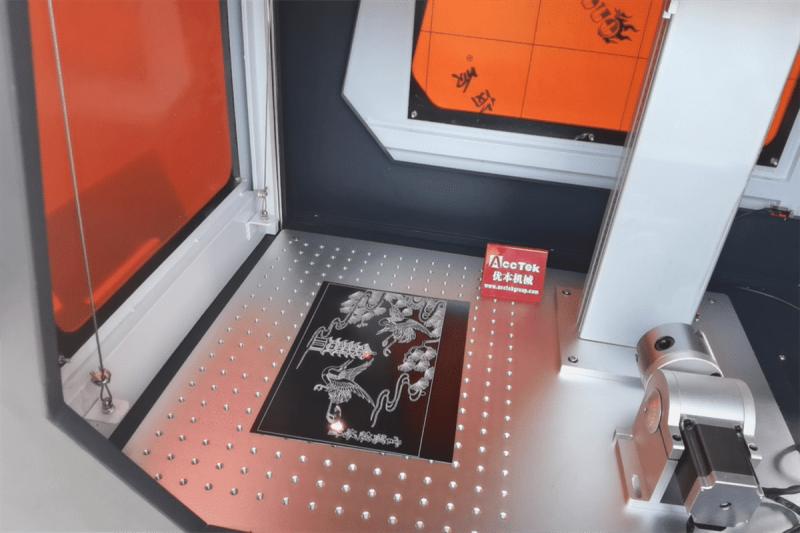

Key Factors in Laser Marking Selection
One of the pivotal decisions in adopting laser marking technology is the choice of the laser source itself. In choosing between CO2 and fiber laser for your laser marking needs, several key factors must be taken into account:
- Material Considerations. The primary material you intend to mark plays a decisive role in your choice. The CO2 laser is ideal for non-metallic and organic materials, while fiber laser excels at marking metals. Consider the materials you work with most frequently and prioritize a laser technology that caters to those needs.
- Marking Speed. The desired marking speed is another critical factor. If your application requires high-speed marking to maximize productivity, then you will need to choose more laser power, whether it is a fiber laser or a CO2 laser.
- Contrast and Marking Quality. Consider the maintenance requirements of your chosen laser technology. Fiber laser marking machines are known for their durability and minimal maintenance, while CO2 laser marking machines may require more complex maintenance due to the lifespan and environmental requirements of the CO2 laser tube. Long-term durability and ease of maintenance can significantly impact your operating costs.
- Maintenance and Durability. Consider the maintenance requirements of the chosen laser technology. Fiber lasers are known for their durability and minimal maintenance, while CO2 lasers may require more complex upkeep due to the presence of mirrors and lenses. Long-term durability and ease of maintenance can significantly impact your operational costs.
- Energy Efficiency. Efficient energy consumption is another crucial factor, as it directly affects operational costs. Fiber laser is highly energy-efficient, resulting in lower ongoing expenses compared to CO2 laser.
- Cost Considerations. Budget constraints often play an important role in the decision-making process. The initial cost of purchasing a laser system as well as the long-term operating costs must be considered. The price difference between fiber laser marking machines and CO2 laser marking machines is not large, but because laser marking machines have lower operating expenses, the investment can be balanced over time.

Choosing the Right Laser for Your Application
The decision between CO2 and fiber laser is not one-size-fits-all. It depends on your specific application, materials, and requirements. To make an informed choice, consider the following steps:
- Comparative Analysis. Perform a comprehensive comparative analysis of the advantages and limitations of both CO2 and fiber laser based on your specific marking needs. Identify the factors that are most critical for your application, such as materials, marking speed, contrast, and maintenance.
- Case Studies. Examine case studies and success stories related to your industry or applications. Learning from the experiences of others who have faced similar challenges can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of both laser technologies.
- Practical Considerations. Conduct practical tests and experiments using both CO2 and fiber laser systems if possible. Actual marking experience with your materials can help you determine which technology best meets your needs.
- Future Trends in Laser Marking. Consider the future trends and advancements in laser marking technology. Laser technology is continually evolving, and new developments may introduce solutions that address your specific requirements more effectively.
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
