
Revealing the Depth of Laser Marking: Discovering Maximum Laser Marking Depth
Laser marking is a versatile and precise technology that plays a key role in various industries, ensuring product traceability, enhancing aesthetic appeal, and providing valuable information. Laser marking harnesses the power of coherent light to provide precision and durability unmatched by traditional marking methods. Its applications span countless industries from automotive to medical, leaving an indelible mark both literally and figuratively. As industries seek ways to enhance product traceability, aesthetic appeal, and information encoding, the depth of laser marking becomes a critical parameter.
Marking depth is more than just a technical specification, it is a key parameter that determines the longevity, visibility, and functionality of the marking material. In industries where durability and traceability are critical, such as aerospace and healthcare, the ability to control and maximize marking depth is a key consideration. This article will fully reveal the complexities of laser marking maximum depth. From understanding the basics of laser technology to exploring the factors that affect mark depth, we take a deep dive into the various applications of laser marking and examine the technological advancements shaping its future.
Table of Contents
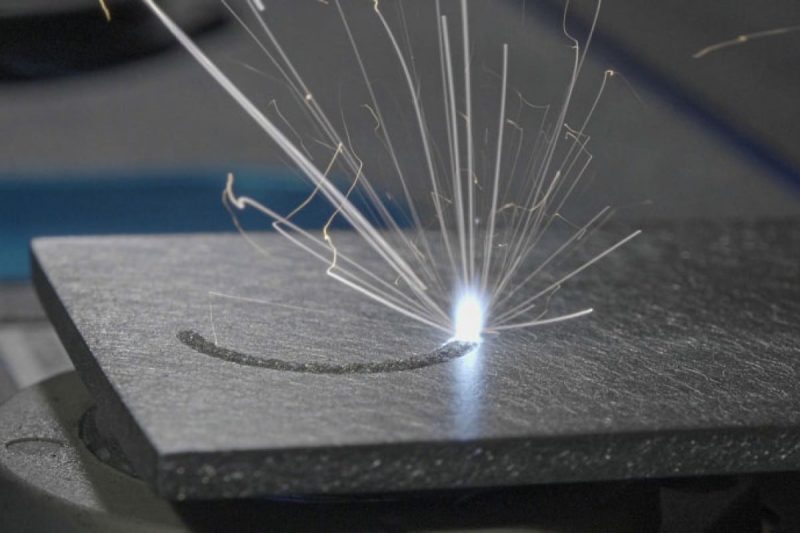
Laser Marking Basics
Lasers, an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, operate on the principles of stimulated emission and optical amplification. Laser devices produce coherent and focused beams through a process of stimulated emission, providing unparalleled precision. There are many types of lasers used in laser marking, such as CO2 laser, Nd: YAG laser, fiber laser, etc. Each laser has its unique characteristics and applications.
Laser marking processes can be roughly divided into thermal and non-thermal methods. During thermal processing, materials are heated, causing changes in color or composition, whereas non-thermal methods, such as ablation, rely on the energy of a laser to remove or change material without generating large amounts of heat. In addition, the pulse duration, power density, and beam quality of the laser further affect the marking process. Longer pulses may generate more heat and affect the material differently than shorter intense pulses. Beam quality represents how focused the laser beam is and plays a key role in achieving the accuracy required for different marking depths.
Factors Affecting Marking Depth
Material Properties
The diversity of materials used in manufacturing creates unique challenges for laser marking. Different materials have unique properties, and some materials are more receptive to laser energy, while others may be resistant to transformation. Metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and wood exhibit different properties that affect their response to laser energy. Factors such as thermal conductivity, melting point, and absorption properties also affect the maximum mark depth achievable on different materials.
Laser Wavelength
The wavelength of the laser beam also affects the depth of reach. Different materials absorb different wavelengths of light, and choosing the right wavelength can make the marking process more efficient. A harmonious interplay between material properties and laser wavelength helps achieve optimal marking depth.
Power Dynamics
The power of the laser (expressed in watts) determines the amount of energy delivered to the material. While higher power can facilitate deeper marks, finding the delicate balance between depth and precision is an ongoing challenge. It requires a detailed understanding of the material’s response to different power levels.
Pulse Duration And Power Density
Pulse duration (in seconds) affects the temporal aspect of energy transfer. Ultra-short femtosecond pulses minimize heat transfer to the material, allowing for precise marking with minimal collateral damage. However, fine precision is required within the pulse duration to achieve the desired marking depth without compromising material integrity.
Laser Beam Quality
The quality of a laser beam is represented by parameters such as beam divergence and focusability. A well-focused, high-quality beam ensures that laser energy is concentrated on the target area, contributing to marking accuracy and uniformity.
Marking Speed And Frequency
Marking speed and frequency are key considerations, especially in industrial applications. The balance between speed and depth is a delicate one, and faster marking may come at the expense of depth, so careful calibration is required based on the specific requirements of the application.

Maximum Achievable Marking Depth For Various Materials
Due to different material properties and responses to laser energy, the maximum marking depth that can be achieved with laser marking also varies. In addition, laser parameters and application-specific requirements also affect laser marking depth. Here are the maximum depths achievable with various common materials:
Metal
- Steel: Laser marking on steel can typically achieve a depth of 10 to 50 microns (μm), depending on the steel’s composition, surface finish, and laser parameters.
- Aluminum: Compared to steel, aluminum has reflective properties that typically result in shallower marks, ranging in depth from approximately 5 to 30 μm. Anodized aluminum surfaces can sometimes provide deeper marks due to their enhanced surface reaction with the laser.
- Titanium: Titanium is known for its hardness and enables marking depths between 20 and 60 μm. Due to its high reflectivity, achieving deeper marks may require specific laser settings and techniques.
Plastic
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Laser marking depth on ABS can typically reach between 20 and 150 μm, depending on the ABS type, color, and presence of additives. Additionally, ABS has a low melting point, requiring a delicate balance to achieve mark depth without causing excessive material damage.
- Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate materials can reach depths of 10 to 100 μm, depending on the material composition and additives used for UV protection or reinforcement. In addition, the transparency of polycarbonate affects laser absorption, requiring precise control of laser parameters.
- PVC (polyvinyl chloride): Laser marking depth on PVC is typically 20 to 20 μm, depending on the PVC formulation and expected surface finish. It is important to note that the versatility of PVC requires careful adjustment of laser parameters to balance depth and avoid material degradation.
Ceramic
- Alumina: Laser marking depth on ceramic materials such as alumina can reach 10 to 50 μm. However, due to its hardness and brittleness, marking ceramics often requires careful control of laser parameters to achieve the required depth without causing cracks.
- Zirconia: Zirconia is known for its high strength and biocompatibility, and can reach depths of 10 to 40 μm, although this may vary depending on the specific zirconia composition. The brittleness of zirconia requires precise laser control to avoid material breakage.
Glass
- Transparent glass: Affected by transparency, the marking depth is usually between 10 and 100 μm. Specific laser wavelengths may be required to produce marks on clear glass.
- Ceramic glass: Ceramic glass is similar to alumina ceramic and has marking depths ranging from 10 to 50 μm. Ceramic composition affects interaction with laser energy.
Wood
- Hardwoods (e.g. oak, walnut): Laser marking on hardwoods such as oak or maple can achieve depths between 50 and 200 μm, but this can vary significantly depending on wood density and moisture content.
- Softwoods (e.g. pine, cedar): The depth of marking on softwoods is similar to that on hardwoods and is also affected by the wood composition and laser parameters.
Note
- Achieving maximum marking depth relies on precise control of laser parameters such as laser power, marking speed, frequency, and focus.
- The actual depth achieved may vary due to material variations, surface treatment, laser type, and specific application.
- These depth ranges are indicative and may vary depending on the specific laser system used and the desired mark quality or application requirements.
- Make a test mark on the target material and adjust the laser settings accordingly to achieve the desired depth without compromising material integrity.

Application of Laser Marking
Industrial Applications
Laser marking has become an integral part of various industries. In the automotive sector, laser marking ensures traceability and quality control of parts. The electronics industry relies on laser marking for product branding and serialization, while aerospace applications require durable and high-precision marking to ensure strict safety and regulatory standards.
Medical Applications
In the medical field, laser marking ensures the traceability and authenticity of surgical instruments and medical devices. Surgical instruments and medical equipment bear markings that must withstand the sterilization process without compromising their structural integrity. The medical field requires a delicate balance between achieving maximum marking depth and retaining the functionality of the marking instrument. Laser marking can achieve maximum marking depth while meeting strict biocompatibility standards.
Consumer Goods
From complex packaging to personalized merchandise, consumer products benefit from the versatility of laser marking. Laser marking technology can create detailed designs, barcodes, and serial numbers to enhance product aesthetics and traceability.

Challenges And Limitations
Overcoming Depth Limitations
Although laser marking technology has come a long way, overcoming depth limitations remains an ongoing challenge. Researchers and engineers continue to explore innovative approaches, from fine laser parameters to new materials, to push the boundaries of achievable marking depth.
Material-Specific Challenges
From the reflective nature of metals to the brittleness of ceramics, different materials present unique challenges. Tailoring laser parameters to specific materials and developing adaptive technologies are key steps to address these challenges and achieve maximum marking depth on different materials.
Cost Considerations And Affordability
While laser marking offers unparalleled accuracy, the cost of implementing and maintaining a laser marking system can be a limiting factor, especially for smaller businesses. Amid the widespread adoption of laser marking technology, striking a balance between affordability and technical complexity remains an ongoing consideration.
Summarize
The exploration of the maximum marking depth of laser marking provides an understanding of the fundamentals of laser technology, the nuances of material interaction, and its diverse applications across industries. From achieving precision in industrial marking to solving challenges in the medical and consumer goods sectors, laser marking has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. As we address the complexities of achieving maximum mark depth, laser marking is not only a tool for creating indelible marks on materials but also a catalyst for innovation and growth. Continuous advancements in technology, its integration with artificial intelligence, and the exploration of nanotechnology have opened up new frontiers, indicating that in the future laser marking will continue to shape industries, products, and even cultural heritage with unparalleled precision and depth.
For those seeking the pinnacle of laser marking technology, AccTek Laser is ready to help. Whether it’s learning about the depths our machines can reach or purchasing a machine for your business, our team is dedicated to guiding you every step of the way. Contact us today to explore the huge potential of laser marking and experience the difference AccTek Laser can bring.
Contact information
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
Get Laser Solutions
