
The Difference Between Laser carving, Etching And Marking
Laser technology has become an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing and marking. The versatility of lasers makes them suitable for many different applications, including laser engraving, etching, and marking. These three laser services are solutions for permanent laser marks to add characteristics to your products and parts.Although the three technologies look similar, they represent different processes and applications. This article will explore the differences between laser engraving, etching, and marking to help readers better understand their principles, applicability, and advantages and disadvantages.
Table of Contents

What is laser engraving?
Laser engraving is a modern precision processing technology that uses a laser beam to precisely score the surface of a material to create text and patterns. The basic principle is to focus a high-energy-density laser beam onto the surface of the material, causing the material to heat up. When the temperature rises to a certain level, the material melts or evaporates, ultimately creating extremely complex depth and detail. This is usually done very quickly, with the process material evaporating with each pulse, allowing for deeper marks to be achieved with repeated passes.
Best of all, the non-contact nature of laser engraving makes it suitable for use on a variety of sensitive materials, such as films, plastics, and glass, without causing physical damage or deformation. This makes laser engraving ideal for most personalized or custom projects.
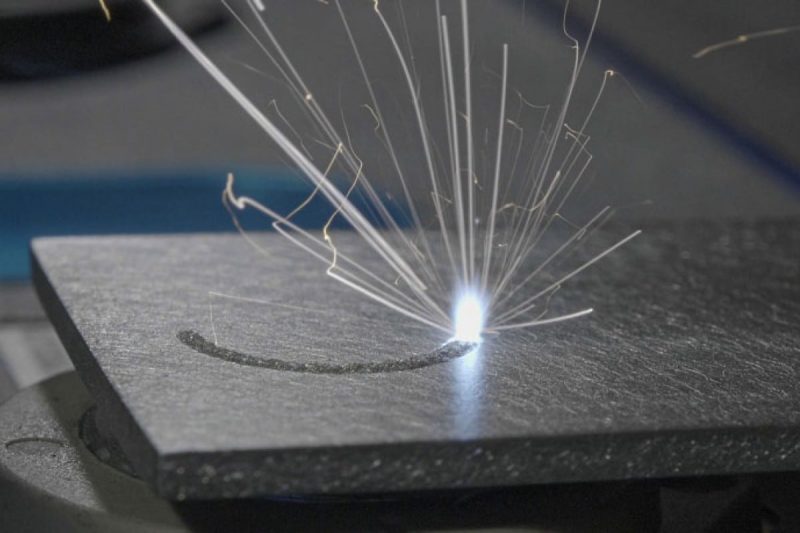
What is laser etching?
Laser etching is a high-precision material processing method that uses laser energy to non-contactly etch the surface of a material to create fine patterns, text, or depth. The principle of laser etching can be explained as a highly precise chemical or physical process. The energy of the laser beam is absorbed near the focal point, causing localized heating of the material. When etching, the material is heated and becomes ductile, which may eventually cause the surface to expand and deform, creating texture.
During the laser etching process, the laser beam is pulsed and releases energy suddenly at specific time intervals. Because lasers require less energy per unit area to etch metal than to engrave, the distance between pulses is greater. In one second, a 100-watt pulsed laser can deliver 100,000 pulses. Each pulse contains one millijoule of energy, with peak power reaching 10,000W. For high-quality marks, black and white provide the best contrast. Of course, the laser etching process is tuned to each application and therefore varies slightly

What is laser marking?
Laser marking, also known as laser coloring, carbonization, or laser dark marking, is a high-precision marking and imprinting technology. It uses a laser beam to operate non-contact on the material surface to create logos, labels, patterns, or text. The basic principle is to control the energy density and focus of the laser beam to interact with the material surface. A low-power beam is used to accomplish changes to the material’s surface without removing the material. These changes can include color changes, surface oxidation, permanent nicks, or deep markings.
There are four main types of laser marking technologies: foaming, annealing, carbon migration, and coloring. Laser marking can adjust laser parameters according to the desired effect, making it suitable for different materials and applications. This technology is widely used in signage, medical equipment, electronic components, and other fields to meet the high-precision needs of identification and marking.

The Difference Between Laser Engraving, Etching and Marking
Laser engraving, etching, and marking are different laser processing technologies, and each type of process has its own applications and properties. These distinctions are critical in selecting the appropriate laser processing technology, depending on the desired application and finished product requirements. Whether you are looking for high-precision engraving, etching of microstructures, or marking of lasting marks, there are different laser technologies to choose from.
Different working principles
- Laser carving work principle: Laser carving involves removing materials from the surface of the material to create permanent marks or designs. Its working principle is that the material is obscured, and the energy of the laser beam is concentrated in a small area, causing the material to evaporate or melt and remove from the surface.
- The principle of etching: Laser etching involves changing the surface of the material to create high contrast marks without removing the materials without significant removal. Its working principle is the surface texture or color change, where the laser beam changes the surface characteristics of the material.
- Playing work principle: Laser marking is a multifunctional process that changes the surface of the material through color changes or surface texture to create marks. It contains a variety of technologies, and the specific working principle depends on the selected technology.
Similarities and differences in applicable materials
- Laser engraving: Laser engraving works on a variety of materials, including wood, plastic, metal, glass, and ceramics. It is widely used in jewelry, gift manufacturing, sign making, art creation, and other fields.
- Laser etching: Etching is commonly used on materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and printing boards. It is mainly used in circuit board manufacturing, decoration, the printing industry, and other fields.
- Laser marking: Laser marking can be applied to a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, glass, and leather. It is used in signage, automotive parts, electronic components, aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, and more.
Comparison of finished product quality
- Laser engraving: Laser engraving has a deeper engraving degree and often produces deep and fine patterns after engraving. Therefore, it is often used to provide high-quality decorative effects in the fields of decorations, artworks, and jewelry.
- Laser etching: Provides high-precision surface treatment to ensure high accuracy and consistency, so etching is often used to manufacture products such as circuit boards that require fine structures.
- Laser Marking: Laser marking excels at providing durable and readable marks for signs and labels to ensure legibility. It can also be used to create ID cards and smart cards as it is fraud-proof.
Cost and efficiency comparison
- Laser engraving: Relatively high energy consumption and laser equipment costs, but generally high efficiency, with reasonable processing speeds, especially suitable for production environments.
- Laser etching: Relatively expensive because it may require multiple processing steps such as chemical treatments or etchants. Less efficient and longer, but still valuable in high-precision applications.
- Laser marking: Generally has a relatively low cost because it does not require large amounts of energy or multiple processing steps. It has an efficient marking speed and is suitable for high-volume marking on production lines.

How to choose the suitable laser engraving, laser etching and laser marking process
Choosing the right laser engraving, laser etching, or laser marking process for your business involves considering several key factors. Each of these processes has its own advantages and is suited to different applications. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
Understand your business needs
Before you can make a decision, you need to understand the specific requirements of your business. Consider factors such as:
- Materials: What materials will you be working with? Different materials may be better suited to one process over another.
- Applications: What are the primary applications for the marked or engraved products? For example, are you creating decorative items, labeling, branding, or identification marks?
- Volume: How many items do you need to process? Some processes are better suited to high-volume production, while others may be more suitable for lower volumes.
- Accuracy and precision: Consider the level of accuracy and precision required for your applications. Some processes offer finer details than others.
Material compatibility
The type of material you are working with plays a crucial role in the selection of the laser process. Different materials respond differently to laser energy. For instance:
- Laser engraving: Suitable for wood, glass, acrylic, and some metals.
- Laser etching: Works well with materials that change color or texture with surface heating, such as anodized aluminum.
- Laser marking: Offers flexibility and can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and textiles.
Ensure the chosen process is compatible with the materials you work with.
Depth of marking
Consider the depth of the mark or engraving you need. If you require deep, tactile engravings, laser engraving may be the best choice. For shallower, surface-level marks, laser etching and laser marking are more suitable. The depth of the mark is determined by the power and focus of the laser beam, as well as the specific settings and material properties.
Contrast and legibility
The contrast and legibility of the marks or engravings are vital, especially for applications like labeling and branding. Laser etching and laser marking often provide high-contrast marks that are easily readable. Evaluate the visual and tactile characteristics of the marks produced by each process.
Production volume
Consider your production volume and throughput requirements. Some processes are more suitable for high-volume production due to their speed and efficiency, while others are better for small-batch or customized production. For example, laser engraving can be time-consuming for high-volume production, while laser marking can be more efficient.
Cost considerations
Evaluate the cost of implementing the chosen laser process, including the equipment, maintenance, and material expenses. Laser marking systems can vary significantly in price, with more advanced systems often commanding higher costs. Factor in your budget constraints and long-term operational costs.
Regulatory compliance
For certain industries like medical devices or aerospace, there may be regulatory requirements for marking and engraving. Ensure that the chosen process complies with any industry-specific regulations or standards.
Flexibility and versatility
Consider the versatility of the laser system. Some systems are more versatile and adaptable to various materials and applications. Laser marking, due to its diverse techniques, offers a high degree of flexibility and adaptability.
User expertise
Assess the skill level and expertise of the personnel who will operate the laser system. Some processes may require more specialized knowledge and training, while others are more user-friendly. Ensure that your team can effectively use the chosen system.
Long-term viability
Consider the long-term viability and support for the chosen laser system. Research the manufacturer’s reputation, the availability of technical support, and the history of software updates. A reliable and well-supported system can ensure longevity and continuous operation.
User feedback and testing
Seek feedback from users in your industry who have experience with the laser process you are considering. Conduct tests and trials to determine the actual performance of the process on your specific materials and for your intended applications.
By carefully evaluating your business needs, material compatibility, volume, cost, and application-specific requirements, you can decide which laser engraving, etching, or marking process is best for your business. It may also be helpful to consult an expert in the field or the laser system manufacturer for additional insight and advice.
Summarize
In short, laser engraving, etching, and marking are different laser processing technologies, and they are different in principle, applicability, and application fields. Understanding their differences is critical to choosing the right technology to meet specific needs. Laser technology will continue to evolve in the future, providing more innovation and application opportunities in the manufacturing and marketing fields. Artists, manufacturers, and engineers alike can take full advantage of these technologies to achieve their creative and production goals.
Contact information
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
Get Laser Solutions

