
What Factors Affect The Weldability of Laser Welding?
Laser welding has revolutionized modern manufacturing, offering high precision, minimal heat distortion, and the ability to join materials that are otherwise difficult to weld using traditional methods. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics rely heavily on laser welding for its speed and ability to deliver high-quality, strong joints with minimal post-weld treatment. Despite the numerous advantages of laser welding, achieving optimal weldability is not always straightforward. The success of a laser weld is determined by a variety of factors—material properties, laser parameters, equipment setup, environmental conditions, and post-weld treatments—all of which must be carefully controlled to ensure the production of a strong, durable, and defect-free weld.
In this article, we will explore in-depth the various factors that influence the weldability of materials in laser welding. These factors include base material composition, the geometry of the joint, laser power, speed, and beam quality, as well as external environmental factors such as temperature and contaminants. We will also examine common challenges encountered in laser welding and how they can be mitigated to achieve the highest possible weld quality. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the multiple variables involved in laser welding and how to optimize these factors for superior welding outcomes.
Table of Contents

Introduction to Laser Welding
Definition and Overview
Laser welding is a precision welding technique that uses a highly concentrated laser beam to melt and fuse materials, typically metals or thermoplastics. The laser beam, which is generated by a laser source, directs focused energy onto the material, creating a localized heat zone that melts the base material at the joint interface. As the molten material solidifies, it forms a weld. This process can be done using either continuous wave (CW) lasers, which provide steady heat, or pulsed lasers, which deliver energy in short bursts, often to prevent overheating and to provide controlled penetration.
Laser welding is highly versatile and can be used for a range of material types and thicknesses. It offers numerous advantages, including high welding speeds, narrow heat-affected zones (HAZ), minimal material distortion, and the ability to automate the process, which leads to increased production efficiency. The precision of the laser beam allows for welding in tight spaces and on delicate components, making laser welding ideal for high-precision applications, including the aerospace and electronics industries.
Importance of Weldability in Laser Welding
Weldability in laser welding refers to the ability of a material to form a strong, defect-free joint when subjected to the laser welding process. Achieving weldability depends on several interrelated factors, such as the material’s chemical composition, thermal properties, joint design, and how it responds to the localized heat input from the laser beam. If these factors are not optimized, the welded joint may be prone to defects such as porosity, cracking, distortion, or weak bonding.
The concept of weldability is particularly crucial in laser welding because the high-energy concentration of the laser beam can have a significant impact on the material’s microstructure and mechanical properties. For instance, rapid heating and cooling cycles can lead to issues like residual stress, cracking, or undesirable phase transformations in certain materials. To overcome these challenges, manufacturers must carefully select and control the various parameters involved in laser welding.
Comparison with Traditional Welding Methods
While laser welding is known for its precision and efficiency, it differs significantly from traditional welding methods such as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding in several important ways. Traditional welding methods use electric arcs to generate heat, which heats a larger area of the material and generally results in wider heat-affected zones. These methods also tend to involve slower welding speeds and higher material distortion. On the other hand, laser welding is characterized by a highly concentrated beam of energy, which allows for faster welding speeds, narrower heat-affected zones, and minimal distortion.
However, laser welding is more sensitive to changes in material properties, joint design, and laser settings than traditional methods. For example, traditional methods can be more forgiving when welding thicker materials or joints with irregular geometries, while laser welding requires more precise control of parameters such as laser power, beam focus, and welding speed. As such, laser welding may not be the ideal solution for all applications, particularly when dealing with materials or geometries that are challenging for the process.

Material Properties
The material being welded plays a significant role in the success of a laser welding operation. Key material properties that influence weldability include base material composition, thickness and geometry, melting point, thermal conductivity, and the presence of alloying elements or additives.
Base Material Composition
The chemical composition of the base material is one of the most important factors affecting weldability. Different materials have different melting points, thermal conductivities, and solidification behaviors, all of which influence the laser welding process. For example, high-carbon steels tend to form hard and brittle phases during cooling, increasing the likelihood of cracking in the weld. Similarly, materials with high levels of certain alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum may be more susceptible to phase transformations, which could lead to weld defects or reduced mechanical properties.
Some materials, such as aluminum and copper, are particularly challenging to weld using laser welding due to their high thermal conductivity and low melting points. These materials require higher laser power to achieve adequate penetration, but the risk of burn-through is also much higher. Materials with a high coefficient of expansion, such as titanium alloys, may experience thermal distortion during welding, requiring precise control of the laser parameters.
Understanding the composition of the material being welded is essential for determining the optimal laser parameters. The alloying elements and impurities in the material can influence how the material responds to heat and the formation of the weld, making it necessary to adjust parameters like laser power, beam focus, and shielding gas.
Thickness and Geometry
Material thickness and joint geometry directly affect the energy required for welding and the heat distribution within the material. For thin materials, lower laser power is generally sufficient, but careful control is needed to avoid excessive heat input that could cause burn-through. For thicker materials, higher laser power and slower welding speeds are necessary to ensure full penetration and a sound weld.
The geometry of the joint also influences how the laser interacts with the material. Simple butt joints are relatively easy to weld because they provide a direct connection between the two surfaces. However, more complex joints, such as T-joints, fillet joints, or lap joints, may require special attention. The angle and alignment of the joint will influence the laser’s ability to properly penetrate and fuse the materials.
Materials with complex geometries may also introduce additional challenges for laser welding due to difficulties in aligning the beam with the joint, and variations in thickness along the joint. Optimizing the joint design and ensuring proper alignment of the laser beam are critical steps in achieving strong, high-quality welds.
Melting Point and Thermal Conductivity
The melting point of a material determines how much energy is required to melt it. Materials with high melting points, such as tungsten, titanium, or high-alloy steels, require significantly more energy to reach their melting point and require careful management of laser power. On the other hand, materials with low melting points, such as aluminum or zinc, can melt too easily under a laser beam and may require fast welding speeds or pulsed laser techniques to prevent excessive melt-through.
Thermal conductivity—the ability of a material to conduct heat—also impacts weldability. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper, dissipate heat quickly, meaning the laser beam must provide sufficient energy to overcome this heat loss and achieve proper penetration. Conversely, low thermal conductivity materials, such as stainless steel, retain heat more effectively, which can lead to a larger heat-affected zone (HAZ) and potential thermal distortion if not managed properly.
Alloying Elements and Additives
The presence of alloying elements and additives can have a profound impact on the weldability of a material. Common alloying elements like manganese, silicon, and chromium can improve a material’s mechanical properties but may also introduce challenges during welding. For instance, manganese can make the weld more susceptible to cracking, while excessive silicon can lead to the formation of brittle phases in the weld zone.
Additives such as flux may be used to enhance surface bonding, prevent oxidation, or modify the weld pool behavior. The selection of flux and other additives should be made carefully, as they can influence the final quality and mechanical properties of the weld.

Laser Parameters
The laser parameters, including laser power, focus, speed, beam quality, and others, are fundamental to the weldability of materials. These parameters control how the laser beam interacts with the material, the energy delivered to the weld pool, and the rate of solidification.
Laser Power
Laser power directly influences the depth of penetration, speed of welding, and the amount of heat generated during the process. Higher laser power leads to deeper penetration, but it also increases the risk of burn-through or excessive heat-affected zones. Lower power settings may not provide sufficient energy to achieve full penetration in thicker materials, resulting in weak joints or incomplete fusion.
The optimal laser power setting depends on the material being welded, its thickness, and the desired weld characteristics. In general, a balance must be struck between sufficient power to melt the material and avoid excess heat that could distort the workpiece.
Laser Focus
Laser focus controls the size and intensity of the laser beam. A tightly focused beam results in a small, high-energy spot on the material, which allows for deeper penetration and narrower welds. However, too tight a focus can increase the risk of burn-through, especially with thinner materials. In contrast, a defocused beam will spread the energy over a larger area, reducing the risk of burn-through but also leading to shallower penetration and wider welds.
The optimal focus depends on the material, thickness, and geometry of the joint. For precise control, laser systems typically feature adjustable focus, allowing operators to fine-tune the beam according to specific welding requirements.
Pulse Duration
In pulsed laser welding, the laser beam is delivered in short, intense bursts of energy. The duration of these pulses—pulse duration—can significantly impact the penetration depth, cooling rate, and overall quality of the weld. Shorter pulses allow for more controlled energy input and can help prevent overheating, while longer pulses provide more energy for deeper penetration.
Pulse duration must be carefully adjusted based on the material and thickness being welded. Longer pulses are typically used for thicker materials, while shorter pulses are used for thin materials to avoid thermal distortion.
Beam Quality
Beam quality refers to the distribution of energy within the laser beam and is an essential factor in determining how effectively the laser can focus on the material. A high-quality beam has a uniform energy profile, allowing for consistent energy delivery and a more stable weld. Low-quality beams, on the other hand, can lead to uneven energy distribution, resulting in poor weld quality and inconsistent joint formation.
Laser welding systems with high beam quality typically produce cleaner, more precise welds with fewer defects.
Welding Speed
Welding speed affects the time during which the laser is applied to the material. Faster welding speeds typically result in lower heat input, leading to smaller heat-affected zones and reduced distortion. However, if the speed is too high, there may not be enough time for proper penetration, resulting in weak joints. Slower speeds can increase heat input, leading to larger heat-affected zones and potentially more distortion, but they may be necessary for welding thicker materials.
The optimal welding speed is determined by the material type, thickness, and desired weld characteristics.
Shielding Gas
Shielding gas is used in laser welding to protect the weld pool from contamination by the surrounding atmosphere, which could lead to oxidation or other defects. The type of shielding gas used, such as argon, nitrogen, or a mixture of gases, can affect the quality of the weld, including its strength, appearance, and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, shielding gas can influence the heat dissipation and cooling rate of the weld pool, which in turn affects the weld’s microstructure.
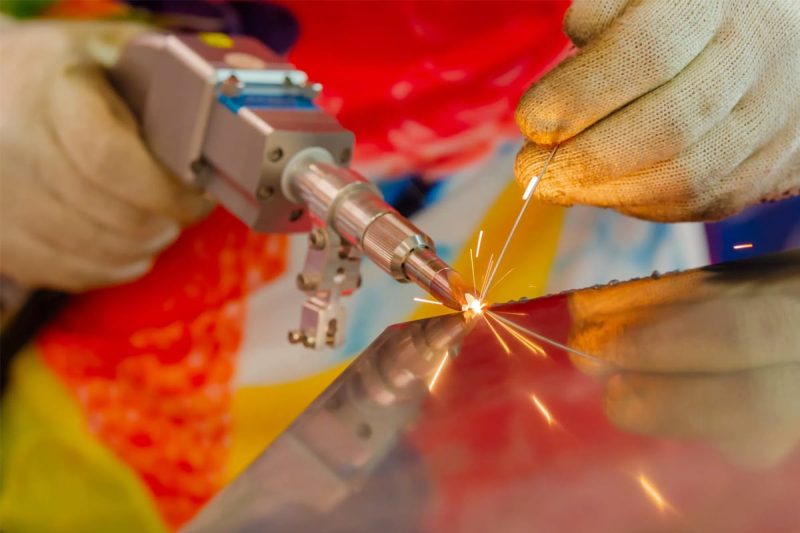

Material Thickness and Joint Design
In laser welding, material thickness and joint geometry significantly impact the welding process, energy required, and ultimately the quality of the weld. A deep understanding of these factors is critical to achieve optimal welds with minimal defects.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the material being welded has a direct impact on the laser welding process. Thicker materials require higher laser power to achieve full penetration and create a strong bond. When welding thicker materials, it’s necessary to manage the heat input carefully to prevent overheating and distortion. A higher power setting allows for deeper penetration but can also increase the size of the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which may affect the mechanical properties of the base material.
For thin materials, lower laser power is typically used to avoid burn-through, as these materials require less energy to melt. The key challenge in welding thin materials with a laser is balancing the laser power to avoid excessive heat input, while still achieving sufficient penetration without damaging the material. The fast cooling rate of laser welding helps in minimizing the heat-affected zone for thinner materials.
Joint Geometry
The geometry of the joint—such as butt joints, T-joints, lap joints, and fillet joints—plays a crucial role in the success of a laser weld. Laser welding typically works best with butt joints, as the direct alignment of the material edges ensures a consistent weld pool. However, more complex joints such as lap joints or T-joints require careful beam alignment, as the laser needs to ensure penetration on all sides of the joint, including any gaps that may exist between the materials.
When the joint geometry involves complex shapes or variations in material thickness, adjustments to the welding parameters are needed. For example, lap joints require precise control of the laser focus and beam angle to ensure that the upper material fuses effectively with the lower material. Fillet welds also require careful control of the laser beam’s interaction with the joint’s surfaces, as the angles and material proximity can influence heat distribution.

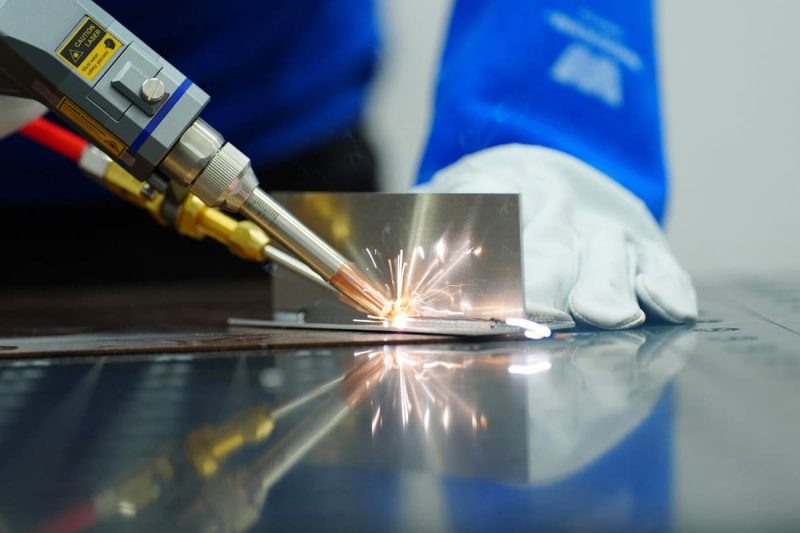
Heat Management and Cooling Rate
Effective heat management is crucial in laser welding to control material properties, minimize distortion, and prevent weld defects. Key aspects of heat management include the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and the cooling rate.
Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
The heat-affected zone (HAZ) is the region of the material that is not melted but experiences a change in microstructure due to the high temperatures during welding. The size and extent of the HAZ are determined by the laser power, welding speed, and material type. In laser welding, the HAZ tends to be smaller compared to traditional welding methods due to the concentrated heat of the laser beam. However, even a small HAZ can impact material properties, especially for high-strength steels or materials that are sensitive to thermal cycles.
For certain materials, such as high-carbon steels or titanium alloys, a larger HAZ can lead to reduced mechanical properties, such as brittle behavior or stress corrosion cracking. As a result, careful control of the laser parameters, especially the power and speed, is essential to minimize the HAZ while still achieving adequate fusion at the joint interface.
Cooling Rate
The cooling rate, or the speed at which the molten weld pool solidifies, is a critical factor in determining the final microstructure and mechanical properties of the weld. Laser welding typically results in very fast cooling rates due to the small heat-affected zone and the rapid solidification of the molten pool. Faster cooling rates can result in a finer microstructure, which may improve the strength of the weld. However, this rapid cooling can also introduce residual stresses, potentially leading to cracking or distortion in certain materials, especially those with high hardenability, such as high-carbon steels.
A slower cooling rate may reduce the risk of cracking, but it can result in the formation of larger grains, which may reduce the overall strength of the weld. Managing the cooling rate is vital for balancing these factors. Techniques such as post-weld heat treatment (e.g., annealing) can be employed to relieve residual stresses and improve the final material properties.

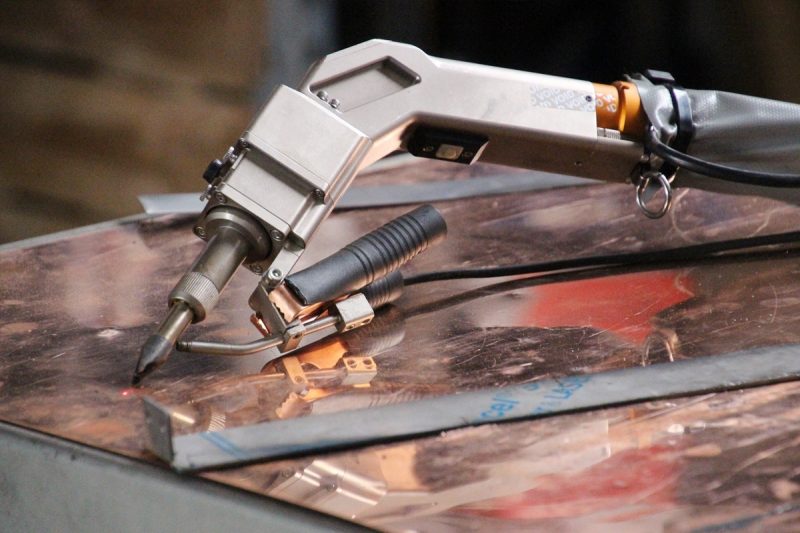
Laser Welding Equipment and Setup
The quality of the laser weld is heavily influenced by the type and configuration of the laser welding equipment. Key components of the equipment include the laser source, focusing lens, optics, and the welding head.
Laser Source Type
The type of laser used in the welding process affects several aspects of the operation, including beam quality, power, and focus. Common laser types for welding include CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and disk lasers:
- CO2 lasers: These are the most widely used lasers in industrial welding due to their high power and versatility. CO2 lasers are ideal for welding thicker materials and provide a stable beam quality.
- Fiber lasers: These lasers are known for their high beam quality and efficiency, making them particularly effective for thin-sheet metal welding. Fiber lasers offer faster welding speeds and can achieve higher precision than CO2 lasers, especially on materials with low thermal conductivity.
Choosing the right laser source depends on the material type, thickness, and application requirements.
Focusing Lens and Optics
The laser beam must be focused onto the workpiece to achieve the desired weld size and penetration. The quality and alignment of the focusing lens and optics play a critical role in beam accuracy and weld quality. A high-quality optical system ensures that the laser beam remains stable and focused, which is particularly important for high-precision applications.
The focal length of the lens, the aperture size, and the positioning of the lens can all influence how the energy is distributed over the material’s surface. Poorly aligned optics can lead to defocusing, which results in inconsistent energy delivery and potentially weak or defective welds.
Welding Head and Focusing Optics
The welding head is responsible for directing the laser beam onto the material. The setup of the welding head, including its position, tilt, and movement, affects the uniformity and quality of the weld. The welding head must be aligned precisely with the material to ensure that the laser beam remains focused on the joint throughout the welding process.
In addition to the welding head, the focusing optics, which shape and direct the beam, need to be properly maintained and calibrated. Any misalignment or degradation in these optics can lead to inconsistent beam delivery and poor weld quality.
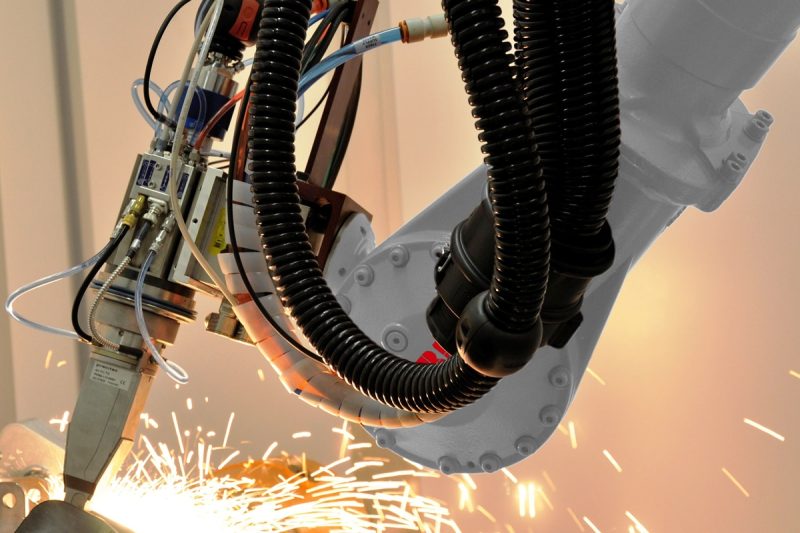

Environmental Conditions
The environmental conditions under which laser welding takes place can have a significant effect on the quality and consistency of the weld. Key environmental factors to consider include ambient temperature and airflow.
Ambient Temperature
Extreme temperatures can affect the material’s response to the laser welding process. For example, materials may become brittle at low temperatures, which can increase the likelihood of cracking during welding. Conversely, high ambient temperatures can lead to excessive material distortion or thermal expansion, which may affect joint alignment and weld consistency. Maintaining a stable ambient temperature is crucial for ensuring that the material responds predictably to the welding process.
Airflow and Contaminants
The presence of contaminants such as dust, oil, moisture, or fumes can affect the welding process in several ways. Contaminants in the air can absorb some of the laser energy, reducing the efficiency of the process. In addition, impurities on the material surface can lead to oxidation, corrosion, or other defects that compromise the quality of the weld.
Controlling the welding environment through proper ventilation, clean surfaces, and an enclosed welding chamber can help reduce the risk of contamination and ensure more consistent welds.
Post-Weld Treatment
Once the laser welding process is completed, post-weld treatments may be necessary to improve the mechanical properties, relieve residual stresses, and ensure the weld meets the required specifications.
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process where the welded material is heated to a specific temperature and then slowly cooled. This process is used to relieve residual stresses that may have been introduced during the rapid heating and cooling phases of the welding process. Annealing helps to restore the material’s ductility and reduce the risk of cracking.
In laser welding, materials that experience rapid cooling rates may require annealing to prevent embrittlement and improve weld toughness. The exact annealing temperature and duration depend on the material type and the specific requirements of the weld.
Surface Finish and Cleaning
After welding, the surface of the weld may have oxidation, scale, or other contaminants that need to be removed. Cleaning and finishing the weld surface is essential to ensure a smooth, defect-free appearance and to enhance the corrosion resistance of the welded area.
Cleaning can involve techniques such as mechanical polishing, chemical pickling, or abrasive blasting. Proper surface finish is particularly important in industries where weld aesthetics and material integrity are paramount, such as in medical devices or consumer electronics.

Challenges in Laser Welding
While laser welding offers many advantages, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Common issues include porosity, cracking, distortion, and inconsistent weld quality.
Porosity
Porosity occurs when gas pockets form within the weld pool, leading to voids in the weld. This is often caused by trapped gases such as nitrogen or oxygen that get trapped during the solidification process. Porosity can weaken the weld and affect its performance. Proper shielding gas, careful control of the welding parameters, and ensuring clean surfaces before welding can help minimize porosity.
Cracking and Distortion
Cracking is a significant issue in laser welding, particularly in materials with high carbon content or low ductility. The rapid cooling rates of laser welding can create high residual stresses, which may lead to cracking, especially in the heat-affected zone.
Distortion can also occur due to uneven heating and cooling, which causes the material to warp or deform. Managing the heat input through optimal laser parameters and using clamping techniques can help reduce distortion.
Inconsistency in Weld Quality
Inconsistent weld quality can arise from variations in material properties, laser parameters, or environmental factors. Fluctuations in the laser power or focus, joint misalignment, or changes in shielding gas flow can all contribute to inconsistent welds. To minimize these inconsistencies, it is essential to maintain tight control over the welding process and regularly calibrate equipment to ensure uniformity across all welds.

Summary
In laser welding, the weldability of materials depends on a wide range of factors, from material composition and thickness to laser parameters and external environmental conditions. By understanding these factors and optimizing them, manufacturers can produce high-quality welds that meet stringent requirements for strength, durability, and appearance. While challenges such as porosity, cracking, and distortion may arise during the welding process, careful control and selection of welding parameters, equipment, and post-weld treatments can mitigate these issues and improve the consistency and reliability of laser welding across a variety of materials and applications.

Get Laser Welding Solutions
For businesses seeking high-quality, reliable welds, AccTek Laser offers cutting-edge laser welding solutions designed to meet diverse industrial needs. As a professional manufacturer of laser cutting, welding, cleaning, and marking machines, AccTek Laser provides state-of-the-art equipment tailored to optimize weldability. Whether you’re working with metals, plastics, or composites, our laser welding machines offer precision, speed, and efficiency for even the most challenging applications.
AccTek Laser’s laser welding machines are engineered to handle various materials and thicknesses, with customizable settings for laser power, pulse duration, focus, and welding speed, ensuring that your welds meet the highest standards. Our team of experts can help you select the right equipment, configure the system for your specific needs, and offer ongoing support to ensure optimal performance throughout the production process.
By choosing AccTek Laser, you gain access to advanced technology and a partner committed to enhancing your welding quality and productivity, ultimately helping you achieve flawless, durable welds every time.
Contact information
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
Get Laser Solutions
