

What is pad printing?
How Pad Printing Works
The working principle of pad printing involves the use of special printing tapes and inks. The pattern or text on the printing tape is printed on the surface of the tape, and then in the printing process, through a certain pressure and transmission mechanism, the ink pattern and text are transferred to the surface of the material. After the ink is cured or dried, it combines with the surface of the material to form a durable mark. Its technological process includes the following steps:
- Prepare the printing tape: First, prepare the printing tape with the desired pattern or text, usually using a flexible elastic or silicone plate.
- Coloring and printing: Apply ink or pigment on the pattern part of the printing tape, then contact the printing tape with the surface of the target material, and transfer the ink from the printing tape to the surface of the material through a certain pressure and transfer method.
- Curing and handling: After the ink has been transferred, it needs to be cured, usually by means such as heat pressing or UV radiation. The cured ink will form a strong bond with the surface of the material.
Advantages of Pad Printing
As a printing technology, pad printing has many advantages in modern manufacturing, making it widely used in various fields. Here are some key advantages of pad printing technology compared to laser marking:
- Strong adaptability: Pad printing is suitable for many types of materials, including plastic, rubber, metal, glass, etc., so it has been widely used in many industries, such as electronics manufacturing, toy production, decoration manufacturing, etc.
- The surface is not damaged: During the pad printing process, there will be no direct physical or chemical changes on the surface of the material. In contrast, laser marking can cause minor surface changes on some materials.
- Variety of colors: Pad printing uses inks for printing, which can achieve a variety of colors and effects, including transparent, glossy, and matte. This opens up more possibilities for pad printing in terms of decoration and identification.
- Low cost: Pad printing setup costs are fairly low, and pad printing equipment doesn’t take up much space. Compared with some high-precision printing technologies, pad printing usually has lower manufacturing costs.
- Production speed: For some mass production situations, pad printing can print a large number of products in a shorter time, because it does not require the fine focusing of the laser beam like laser marking.
- Various printing effects: Pad printing can realize complex patterns, logos, texts, etc., and has high decorative and personalized customization capabilities.
- Coping with irregular surfaces: Pad printing technology can be used for different shapes and uneven objects. In contrast, laser marking may require more adjustment and adaptation to complex shapes.
Disadvantages of pad printing
As a surface printing technology, pad printing has some disadvantages and limitations in addition to its many advantages. Here are some of the main disadvantages of pad printing technology:
- Limited precision: Pad printing technology is limited in terms of pattern and text precision. Due to the elasticity and manufacturing process of the printed tape, the details of the pattern may not be as good as the laser marking technology.
- Insufficient durability: Compared to laser marking technology, its durability may be lower. Prolonged exposure to the outside environment may cause fading, fraying, or peeling.
- Preparation and replacement of printing tape: Pad printing requires special printing tape, and when using pad printing, only one color of ink can be printed at a time. Therefore, when printing different patterns on different materials, it takes a certain amount of time and resources to replace the printing tape.
- Relatively low productivity: Compared with some laser marking, the productivity of pad printing is relatively low. Each printing process can take a certain amount of time, which can be a limiting factor in mass production.
- Hazardous Waste Disposal: Waste generated during the pad printing process, including used printing tape, and waste ink that may contain hazardous substances. Disposal of these wastes may require special environmental protection measures.

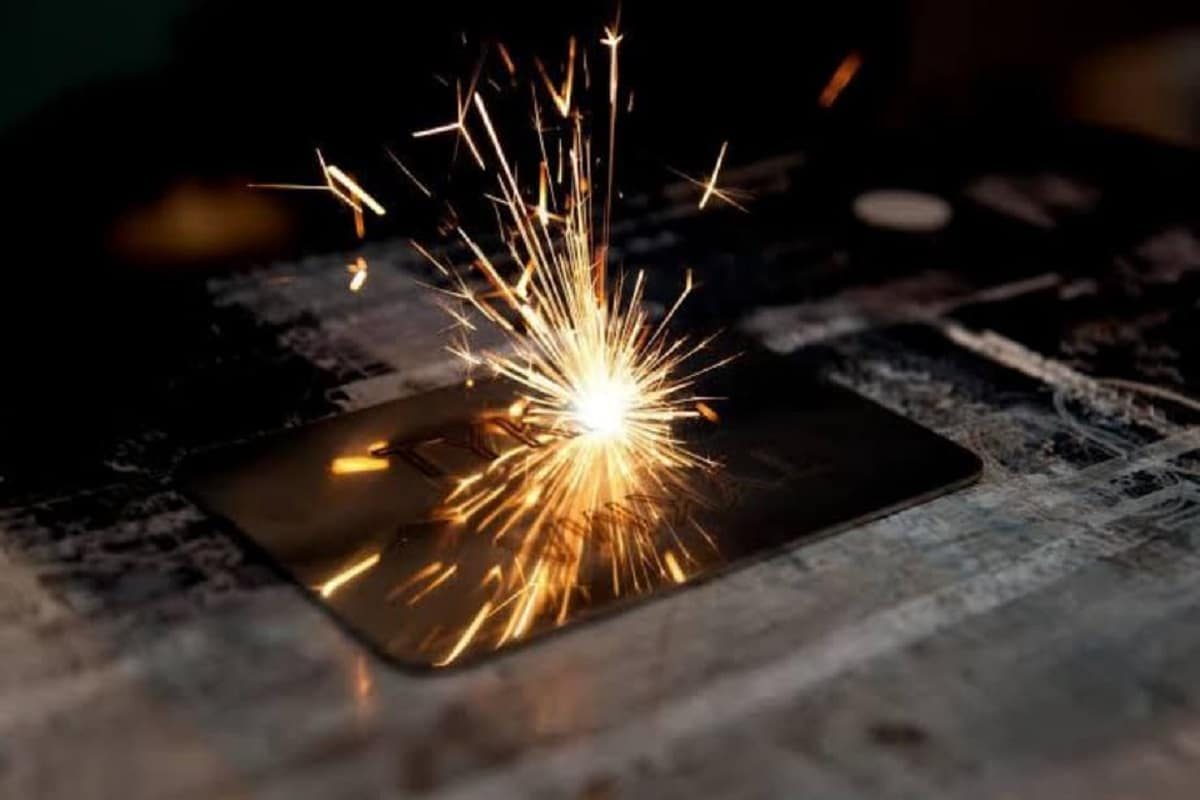
What is laser marking?
How Laser Marking Works
The working principle of laser marking is a laser marking machine using the technique of processing the surface of the material, and through the high-density energy of the laser beam, the chemical or physical nature of the material surface is produced. The process process is as follows:
- Choose the right laser equipment: According to the properties and requirements of the target material, choose the laser equipment with the appropriate power and wavelength. Different types of lasers (such as CO2 laser, fiber laser, or Nd: YAG laser, etc.) are suitable for different materials and applications.
- Laser irradiation: Start the laser equipment and focus the laser beam on a specific position on the surface of the material. The high energy of the laser beam causes reactions such as evaporation, oxidation, or color change on the surface of the material, leaving the desired pattern or text on the surface.
- Control and debugging: Operators usually monitor and debug laser equipment in real time, including adjusting laser parameters, such as power, scanning speed, and focal length, to control the marking effect and ensure that the resulting pattern is visible.
- Closing and Cleaning: After completing all marking tasks, turn off the laser equipment and remove the material from the working platform. If auxiliary equipment such as coolant is used, it also needs to be cleaned and maintained.
Advantages of laser marking
Compared with pad printing technology, laser marking technology has obvious advantages in terms of accuracy, durability, scope of application, and flexibility. The following are the main advantages of laser marking technology compared with pad printing technology:
- High precision and clarity: The focused nature of the laser beam allows for the creation of sharper patterns on the surface of the material, suitable for applications requiring high-precision marking.
- High durability: Marks produced by laser marking are usually extremely durable. Because the laser beam directly causes changes in the chemical or physical properties of the material surface, the marking is not easy to fade, peel off, or be affected by the external environment.
- Wide range of applications: Laser marking technology is suitable for many types of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, ceramics, etc. Its flexibility makes it applicable to a wider range of fields.
- Non-contact processing: Laser marking is a non-contact processing technology. The laser beam is directly irradiated on the surface of the material without any physical contact, so it will not damage the surface of the material.
- Fast and efficient: Since the laser beam travels at the speed of light, it can complete the marking in an instant, suitable for scenarios that require high-efficiency production.
- No waste generation: Laser marking is a waste-free technology as it does not require printing tape or ink, thus reducing the problem of waste disposal.
Disadvantages of laser marking
Compared with pad printing technology, laser marking technology also has some disadvantages. The following are some of the main disadvantages of laser marking technology compared to pad printing technology:
- Higher equipment costs: Laser marking equipment typically has high purchase and maintenance costs, which can add to the initial investment.
- Complex commissioning and operation: Laser marking technology requires precise adjustment of laser parameters to achieve the desired marking effect. This may require some technical knowledge and training of the operator.
- Safety issues: The laser beam has high energy and may cause injury to the operator if not handled correctly. Therefore, operators need to follow strict safety operating procedures.
- Limited applicability: While laser marking technology is suitable for many materials, it is not suitable for all materials. Certain materials that are high-temperature, highly reflective, or highly absorptive may not be suitable for laser marking.
- Limitations on complex shapes: Although laser marking technology is flexible, it may be limited when dealing with certain complex-shaped objects, especially if the surface is uneven or has a concave-convex structure.
Pad printing and laser marking: which way to choose
Pattern complexity and precision requirements
Durability and fade resistance requirements
Material type
Production efficiency
Equipment cost
Operation Difficulty
Environmental and safety considerations
Summarize
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
