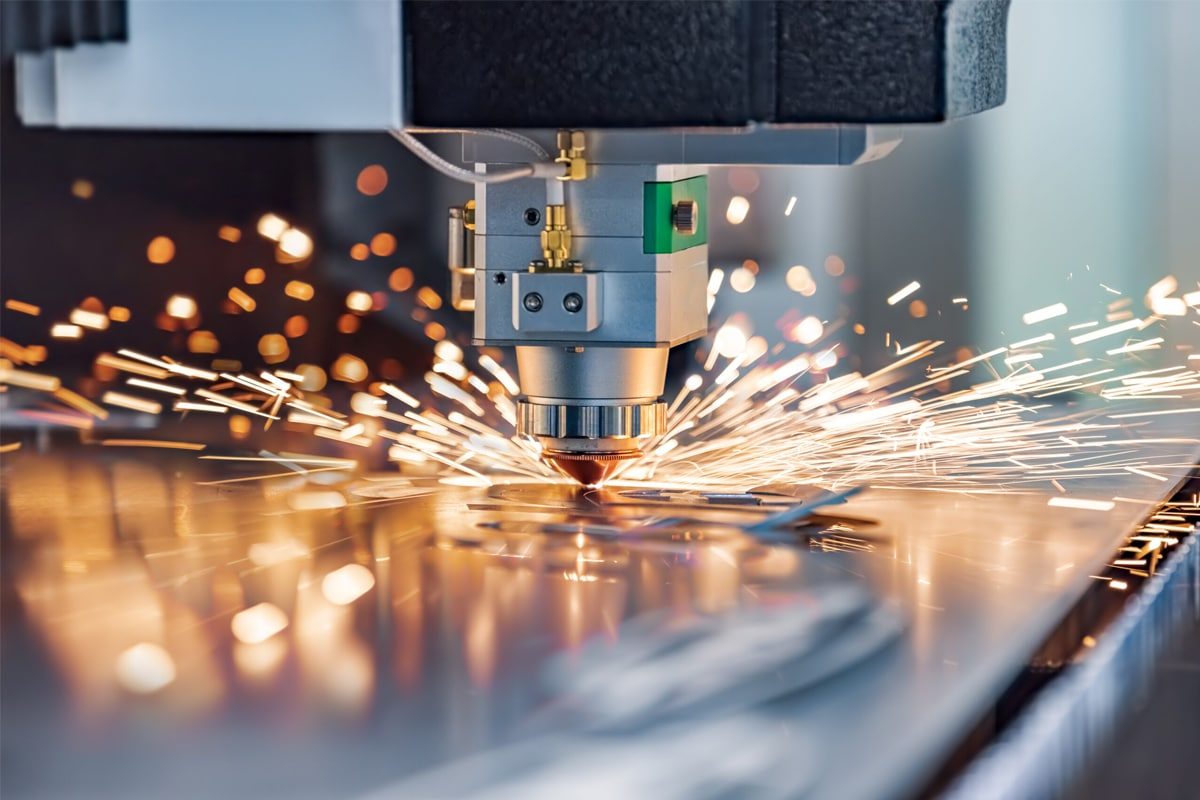
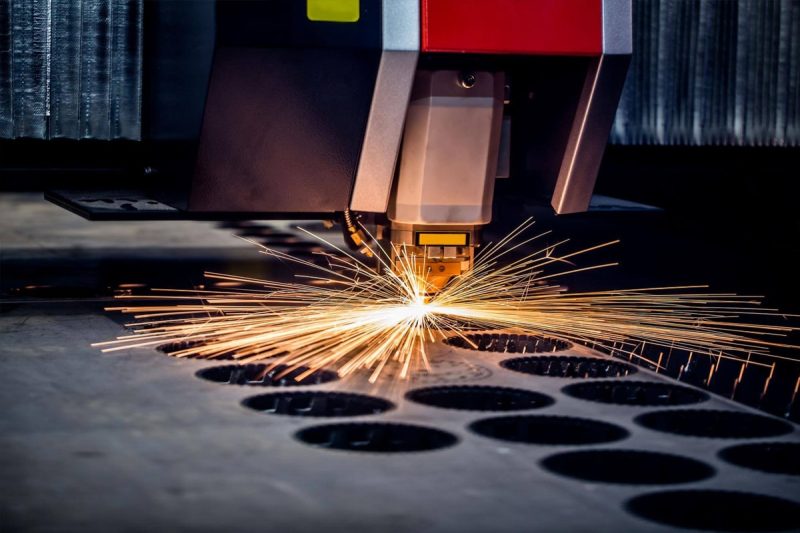


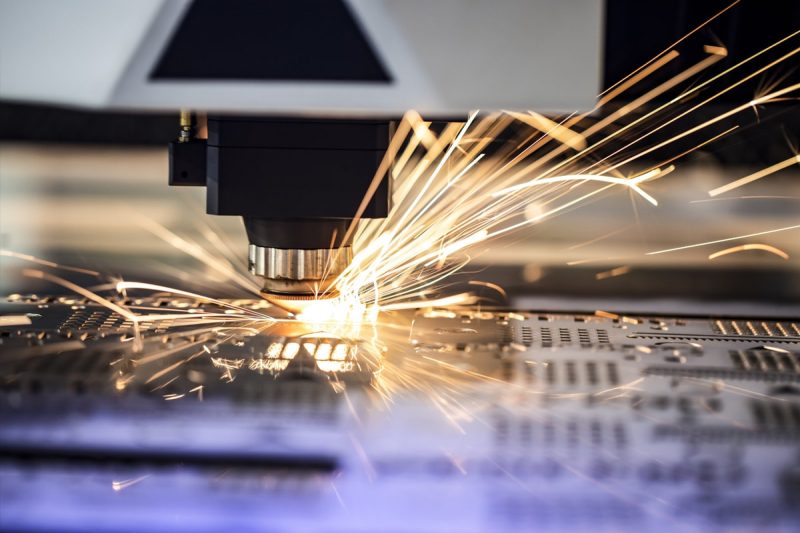
Overview of Laser Cutting Technology
How Laser Cutting Works
Types of Laser Cutting Machines
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: Fiber lasers use optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements to amplify the laser beam, making them especially effective for cutting metals. Fiber lasers are ideal for cutting reflective materials like aluminum, copper, and brass. They are energy-efficient and offer faster cutting speeds for thin and medium-thickness metals.
- CO2 Laser Cutting Machines: CO2 lasers use carbon dioxide gas as the laser medium, making them well-suited for cutting non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, fabric, and plastics. They are widely used for engraving and cutting in industries like signage, decoration, and textiles due to their high-quality edge finish.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting offers several benefits that have made it a preferred choice across many industries:
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting achieves fine details and tight tolerances, ideal for intricate designs and precise parts.
- Versatility: Laser cutting is compatible with a vast range of materials, including metals, non-metals, and composites, accommodating various industries.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting provides rapid processing with minimal setup time, making it faster than traditional cutting methods, especially in high-production environments.
- Minimal Waste: Laser cutting minimizes material waste with its focused beam and optimized cutting paths, leading to cost savings and less material loss.
- High-Quality Edge Finish: Laser cutting often eliminates the need for post-processing, as it produces smooth, burr-free edges, especially important in applications requiring refined aesthetics.

Materials Suitable for Laser Cutting
Metals
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials for laser cutting due to its strength, durability, and availability. It is typically processed using fiber lasers, which provide fast and accurate cuts with minimal thermal distortion. Laser cutting enables complex shapes to be produced quickly and with excellent edge quality.
- Applications: Common applications include automotive parts (such as frames and panels), construction materials, tools, machinery components, and structural parts.
- Advantages: Laser cutting allows for precise cuts, sharp edges, and high-speed processing. Carbon steel can be cut in a wide range of thicknesses, from thin sheets to heavy plates, with high repeatability and accuracy.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel offers high strength, corrosion resistance, and a visually appealing finish, making it a preferred material for many industries. Laser cutting delivers precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones, preserving the material’s properties. It produces clean, smooth edges that often do not require post-processing, making it suitable for decorative as well as functional applications.
- Applications: Food processing equipment, medical devices, architectural elements, kitchenware, decorative panels, and automotive parts.
- Advantages: Laser cutting provides high precision, excellent edge quality, and the ability to cut intricate designs. It minimizes thermal distortion, preserving stainless steel’s aesthetic and mechanical properties.
Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight, versatile metal used across various industries. Its reflective surface poses challenges for traditional cutting methods, but fiber lasers make laser cutting aluminum efficient and precise. Proper laser settings and anti-reflective coatings are often used to optimize cutting performance.
- Applications: Aerospace components (e.g., aircraft panels), electronics enclosures, automotive parts, decorative items, and signage.
- Advantages: High-speed cutting, minimal distortion, and excellent surface finishes, even on thin or intricate designs. Laser cutting can handle aluminum sheets of varying thicknesses.
Copper and Brass
Copper and brass are known for their high thermal and electrical conductivity, as well as their reflective surfaces. Fiber lasers are effective for cutting these metals, as they offer precise control over the laser’s wavelength and power output, minimizing reflections and ensuring consistent cuts.
- Applications: Electrical components (such as connectors and contacts), plumbing fixtures, decorative elements, and artistic designs.
- Challenges: The reflectivity of these metals requires careful control to prevent damage to the laser source.
- Advantages: Laser cutting allows for high precision and consistency, making it ideal for intricate shapes and fine details in copper and brass applications.
Titanium
Titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance make it a high-value material for specialized applications. Laser cutting is an excellent choice for processing titanium, providing precise, clean cuts that maintain the material’s integrity and properties.
- Applications: Aerospace parts (including structural components), medical implants and devices, high-performance sports equipment, and chemical processing equipment.
- Advantages: Laser cutting ensures high accuracy, minimal thermal damage, and clean edges, even when producing complex shapes.
Other Alloys
Laser cutting is widely used for processing various other metal alloys, including nickel alloys, superalloys, and custom blends used in industrial and high-performance applications.
- Applications: Turbine blades, industrial equipment components, specialty tools, and high-temperature applications.
- Advantages: Laser cutting offers precision, repeatability, and the ability to cut complex shapes with high tolerance levels.
Non-Metals
Wood
Laser cutting and engraving of wood is widely used for applications that require intricate patterns and precise cuts. CO2 lasers are particularly effective for processing various types of wood, including softwoods, hardwoods, plywood, and MDF (medium-density fiberboard).
- Applications: Custom furniture, decorative items, toys, model-making, and signage.
- Advantages: Laser cutting allows for intricate detailing, smooth edges, and minimal charring or discoloration when optimized settings are used. The non-contact process also prevents wood splitting or damage during cutting.
Acrylics and Plastics
Acrylic and other plastics are popular materials for laser cutting due to their transparency, flexibility, and smooth finish. CO2 lasers provide high precision and can cut or engrave these materials without causing melting or warping.
- Applications: Signage, point-of-sale displays, decorative panels, protective barriers, and custom prototypes.
- Advantages: Laser cutting produces polished, smooth edges, eliminates the need for secondary finishing processes, and allows for detailed engraving and cutting of intricate patterns.
Leather
Laser cutting is widely used to cut and engrave leather, providing precise shapes and patterns without causing fraying or distortion. CO2 lasers are especially effective for this purpose, allowing for high customization and artistic designs.
- Applications: Bags, wallets, belts, shoes, and custom accessories.
- Advantages: Laser cutting ensures precision, sharp cuts, and intricate detailing. It offers high repeatability and consistent quality, which is especially important for large-scale production.
Paper and Cardboard
Laser cutting is an excellent method for creating detailed designs and custom shapes in paper and cardboard products. It provides precise cuts without the need for mechanical cutting tools, making it ideal for creative and commercial projects.
- Applications: Greeting cards, packaging prototypes, stencils, art projects, and promotional materials.
- Advantages: Laser cutting allows for high-speed production with detailed accuracy, clean edges, and the ability to create complex patterns with ease.
Fabrics and Textiles
Laser cutting of fabrics and textiles has become popular in the fashion, upholstery, and industrial textile industries due to its precision and non-contact process. The laser ensures clean cuts that prevent fraying and distortion.
- Applications: Apparel, embroidery, upholstery, technical textiles, and industrial fabrics.
- Advantages: Laser cutting provides precise and consistent shapes, reduces material waste, and allows for the creation of detailed patterns and complex designs.
Rubber
Laser cutting is frequently used for rubber components, providing precise, consistent shapes with no deformation or tool wear. The non-contact cutting method also minimizes the risk of material damage.
- Applications: Gaskets, seals, promotional items, mats, and industrial components.
- Advantages: Laser cutting ensures high accuracy, consistent quality, and the ability to create intricate designs without affecting the integrity of the material.
Composite Materials
Composite materials, such as those used in aerospace and industrial applications, can be challenging to cut with traditional tools. Laser cutting offers a precise and efficient solution, allowing complex shapes to be cut with high accuracy.
- Applications: Aerospace parts, automotive components, industrial panels, and custom prototypes.
- Advantages: Laser cutting can handle complex geometries and achieve high precision, even with challenging composite structures.

Limitations and Considerations in Laser Cutting
Materials Not Suitable for Laser Cutting
Despite laser cutting’s versatility, certain materials are not suitable for this process due to safety hazards, toxic emissions, or limitations in laser compatibility.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Cutting PVC is not recommended with laser technology due to the release of toxic chlorine gas, which is harmful to both the machine and the operator. This gas can corrode the laser equipment and compromise workplace safety.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Also known as Teflon, PTFE emits toxic fumes when exposed to high heat. Laser cutting this material can lead to serious health risks and equipment damage, making it unsuitable for laser applications.
- Polycarbonate (for thicknesses above 1 mm): While thin polycarbonate can be engraved, cutting thicker polycarbonatecan cause melting and produce rough edges due to its low melting point and tendency to discolor. Additionally, laser cutting thicker polycarbonate releases hazardous fumes.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass consists of both glass and resin, which can cause significant health hazards when vaporized. The resin component releases toxic fumes, while the glass component damages the laser optics, making it unsuitable for laser cutting.
- Certain Metals with High Reflectivity (for specific laser types): Some highly reflective metals, such as certain grades of copper and aluminum, can pose challenges for laser cutting, especially with CO2 The reflective nature of these materials can redirect the laser beam back into the machine, potentially damaging its components. Fiber lasers with anti-reflective technology are generally more suitable for cutting reflective metals.
Safety Considerations
Laser cutting requires adherence to safety protocols to protect operators and equipment from hazards associated with high-powered lasers, fumes, and material byproducts.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: Laser cutting often generates fumes, vapors, and smoke, especially when cutting plastics, rubber, and other organic materials. These emissions can be toxic or irritating to operators, so proper ventilation and fume extraction systems are essential to maintain air quality and reduce health risks.
- Protective Eyewear: Laser cutting produces high-intensity light that can be harmful to the eyes. Operators should wear protective eyewear rated for the specific laser wavelength to prevent eye injuries.
- Fire Risk Management: Laser cutting generates high heat, which poses a fire risk, particularly when cutting flammable materials like wood, fabric, and paper. Fire safety measures, such as fire suppression systems and extinguishers, should be readily available. Continuous monitoring of the cutting area can help mitigate the risk of fire.
- Machine Safety Enclosures: Modern laser-cutting machines often come with safety enclosures to contain the laser beam, preventing accidental exposure and improving operator safety. Ensuring that enclosures are intact and functioning correctly is essential.
- Hazardous Byproducts: Certain materials, such as PVC and polycarbonate, emit toxic fumes when laser cut. Cutting these materials can be hazardous to health and should be avoided or conducted only with adequate fume extraction and filtration systems.
Material Thickness Limitations
The thickness of the material being cut directly impacts the performance, quality, and efficiency of laser cutting. The laser’s power output and type, as well as material characteristics, influence the maximum thickness that can be effectively cut.
- Laser Power and Material Compatibility: Each laser-cutting machine has a specific power rating that determines the thickness it can cut. Higher-powered lasers (such as 10 kW or more) can cut thicker materials, but this often comes at the cost of slower cutting speeds and increased energy consumption. For example, fiber lasers are better suited for thick metals, while CO2 lasers perform best with thin to medium-thickness non-metals.
- Metal Thickness Limits: For metals like carbon steel and stainless steel, fiber lasers can handle substantial thicknesses, up to 25-30 mm or more for industrial applications. However, exceeding the machine’s optimal thickness limit can lead to rougher edges, burrs, and reduced precision, impacting the quality of the cut.
- Non-Metal Thickness Limits: For materials like wood, acrylic, and plastic, CO2 lasers typically provide excellent results up to medium thicknesses. Cutting thicker non-metals can result in charring, melting, and slower cutting speeds. For instance, thicker acrylic may melt or discolor when cut with lower-powered CO2 lasers.
- Impact on Cut Quality: As the material thickness increases, maintaining high-quality edges becomes challenging. Thicker materials are more likely to have heat-affected zones, resulting in rougher, less precise cuts. It’s essential to select the correct laser power and settings to achieve optimal cut quality while minimizing material waste and machine wear.

Factors Affecting Laser Cutting Quality
Material Properties
The properties of the material being cut play a significant role in determining the quality of laser cutting. Different materials respond differently to laser energy, and their unique characteristics can influence the cutting process.
- Material Type: Metals and non-metals respond differently to laser cutting. For instance, fiber lasers are more effective for metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper due to their high energy absorption rates, while CO₂ lasers work well with non-metals like wood, acrylic, and fabrics. Understanding the compatibility between the laser type and material is critical for achieving high-quality cuts.
- Thickness: Material thickness significantly affects laser cutting quality. Thicker materials generally require higher laser power to achieve a clean cut. However, as thickness increases, it becomes challenging to maintain sharp edges and precise cuts due to increased heat-affected zones, slower cutting speeds, and possible roughness at the edges. Optimizing the laser power and speed for specific thicknesses is essential to minimize these issues.
- Reflectivity: Highly reflective materials, such as aluminum, copper, and brass, can reflect the laser beam, potentially damaging the laser optics and reducing cutting efficiency. Special measures, such as adjusting laser settings and using anti-reflective coatings, are often necessary to handle reflective materials effectively.
- Thermal Conductivity: Materials with high thermal conductivity, like copper and aluminum, dissipate heat quickly, which can lead to slower cutting speeds and uneven edges. Effective laser control and optimized cutting parameters are required to counteract heat dissipation and achieve clean cuts.
- Surface Condition: Surface finish and cleanliness can impact laser cutting quality. For example, rust, dirt, or oil on the surface of metals can lead to uneven cutting and poor edge quality. Proper preparation and cleaning of the material before cutting can significantly improve the quality of the results.
Laser Parameters
The parameters of the laser itself, including power, frequency, and beam quality, play a crucial role in determining the cutting quality.
- Laser Power: The laser’s power output must be adjusted according to the material type and thickness. High power levels may be needed for cutting thick metals, but too much power can cause charring, rough edges, and excessive heat-affected zones in thinner materials. Balancing power ensures precise cuts without compromising edge quality.
- Beam Quality: The quality of the laser beam, often referred to as beam mode or M2 factor, impacts how precisely the laser can focus on a specific point. A high-quality beam produces a finer, more concentrated laser spot, resulting in cleaner cuts and more intricate details. Poor beam quality may lead to wider kerf widths and rougher edges.
- Frequency and Pulse Settings: For pulsed lasers, adjusting the frequency and pulse duration can influence the cutting process. Higher frequencies may be used for fine, detailed cuts, while lower frequencies are better suited for thicker cuts that require deeper penetration. Optimizing these settings for the specific material is essential for achieving the desired cut quality and minimizing defects.
- Assist Gas Type and Pressure: Assist gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air, are used during laser cutting to remove molten material from the cut area, cool the workpiece, and prevent oxidation. The type of gas and its pressure affect the edge quality and cutting speed. For example, oxygen creates a reactive cut that increases speed but can leave an oxidized edge, while nitrogen provides clean, non-oxidized edges ideal for stainless steel.
Cutting Speed and Focus
The speed at which the laser moves across the material and the precision of its focus are critical factors that influence cutting quality.
- Cutting Speed: The cutting speed must be carefully matched to the material type and thickness. Cutting too quickly can result in incomplete cuts, rough edges, and poor quality. Conversely, cutting too slowly can lead to excessive heat buildup, causing material deformation, increased burrs, and wider heat-affected zones. Finding the optimal cutting speed ensures smooth, precise cuts and high productivity.
- Focus Position: The focal point of the laser beam must be accurately set relative to the material’s surface for optimal cutting quality. The focal position affects the concentration of energy at the cutting point, influencing the width of the kerf and the edge quality. Properly focused beams produce narrow cuts with minimal heat-affected zones, while incorrect focusing can lead to rough edges, reduced precision, and poor-quality cuts. Auto-focus capabilities in modern laser machines enhance cutting accuracy by dynamically adjusting the focus based on material thickness and surface conditions.
- Kerf Width: The width of the cut, known as the kerf, is influenced by the laser’s focus and the material properties. Achieving a narrow kerf improves precision and reduces material waste. Maintaining consistent focus and optimizing laser parameters are key to achieving uniform kerf widths across cuts.

Choosing the Right Laser Cutting Machine
Material Type and Compatibility
Different laser-cutting machines are optimized for specific material types, so knowing the materials you plan to cut is crucial. There are two primary types of laser cutting machines, each suited to specific material characteristics:
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: Fiber lasers are ideal for cutting metals due to their high energy density and efficiency. They are well-suited for cutting reflective metals, such as aluminum, copper, and brass, as well as other metals like carbon steel, stainless steel, and titanium. Fiber lasers also offer excellent precision and cutting speed, making them a top choice for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication.
- CO2 Laser Cutting Machines: CO2 lasers are highly effective for non-metallic materials, such as wood, acrylic, leather, fabric, rubber, and paper. These lasers are commonly used in industries such as signage, woodworking, textiles, and packaging. CO2 lasers can also cut thin metals, but they are best suited for applications requiring precise, clean cuts on non-metal materials.
Material Thickness and Laser Power Requirements
The thickness of the material to be cut has a direct impact on the power requirements of the laser-cutting machine. Thicker materials require higher power to achieve clean and efficient cuts, while thinner materials benefit from lower power settings for precision and control.
- High Power for Thick Metals: For cutting thick metals (e.g., 10mm or more), a fiber laser with high power output, such as 3 kW or higher, is recommended. This power level ensures that the laser can penetrate the material fully and produce a clean edge without excessive heat-affected zones.
- Medium Power for Thin to Medium Materials: Medium-power lasers (1-2 kW) are effective for cutting thin to medium-thickness metals and non-metals. This power range is versatile and commonly used for applications in metal fabrication, advertising, and consumer goods.
- Low Power for Thin and Sensitive Materials: Lower-powered lasers are ideal for thin materials like paper, fabric, and some plastics. They prevent burning or warping, especially in materials sensitive to heat. CO2 lasers with adjustable power settings are well-suited for these applications, offering flexibility for delicate and intricate designs.
Precision and Detail Requirements
Laser-cutting machines vary in their ability to produce intricate details and fine cuts. If the application requires high precision and intricate designs, beam quality, control system accuracy, and focus precision become critical factors.
- High Precision for Complex Designs: Fiber lasers provide high precision, making them ideal for applications that require complex shapes and intricate details. Industries like electronics, medical device manufacturing, and jewelry benefit from laser-cutting machines with fine focus and stable control systems.
- Moderate Precision for Basic Shapes and Large Cuts: For applications that don’t require extreme precision, such as general metal fabrication, construction, or signage, a standard CO2 or fiber laser with moderate precision capabilities is often sufficient. These machines are efficient for straightforward cuts and larger parts, where extreme detail is not as critical.
Speed and Production Volume
The required cutting speed and production volume will also influence machine selection. Some laser-cutting machines are optimized for high-speed production, while others focus on precision at slower speeds.
- High-Speed Production: Fiber lasers are known for their high-speed performance on metals, allowing for faster production times in industries such as automotive and aerospace. This speed advantage helps maintain efficiency and is essential in high-volume manufacturing settings.
- Moderate Speed for Detailed Work: CO2 lasers may operate at a slower speed compared to fiber lasers, particularly when cutting metals. However, for detailed work on non-metals, CO2 lasers offer an excellent balance between speed and precision.
Machine Features and Customization Options
Advanced features and customization options enhance a laser cutting machine’s adaptability and efficiency in specific applications. When selecting a laser cutting machine, consider the following features based on your needs:
- Auto-Focus and Adjustable Bed Height: Machines with auto-focus capabilities and adjustable bed heights allow for precise adjustments when cutting materials of varying thicknesses. Auto-focus optimizes the laser position for a clear, clean cut, while bed height adjustments accommodate materials of different sizes.
- Rotary Axis and Dual Worktables: For users who need to cut cylindrical or tubular materials, a rotary axis option is beneficial. Dual worktables also enhance productivity by allowing one workpiece to be loaded or unloaded while another is being cut.
- Fume Extraction and Safety Enclosures: High-quality fume extraction systems and safety enclosures are essential for maintaining a safe work environment, especially when cutting materials that release toxic fumes. Machines with built-in extraction systems reduce airborne contaminants and protect operators from laser exposure.
- Software and Control Systems: Laser cutting machines are typically controlled by CNC software, enabling precise control over the cutting path, speed, and power. Advanced software features include pattern recognition, auto-nesting, and real-time monitoring, which can improve efficiency and reduce material waste.
Budget and Cost Considerations
Laser-cutting machines come with varying price points, influenced by factors such as power output, machine type, and additional features. It’s important to weigh initial costs against long-term productivity and ROI.
- Entry-Level Machines: Entry-level machines with lower power and fewer features are suitable for small businesses and hobbyists working with thin materials. These machines often offer basic functionalities at an affordable price, making them an accessible option for those with modest requirements.
- Mid-Range Machines: Mid-range laser cutters with moderate power and essential features are suitable for small to medium enterprises and industries that need reliable, versatile machines without the highest-end specifications. These machines balance performance and cost, making them a good choice for businesses with moderate production needs.
- High-End Industrial Machines: High-power, feature-rich machines are designed for large-scale operations requiring high-speed, high-precision cutting across diverse materials. While these machines come with a higher upfront cost, they often offer faster processing, increased productivity, and long-term durability, justifying the investment in high-demand environments.
Summary

Get Laser Cutting Solutions
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
